Module 8
... The left-hand side just represents the time rate of change following the motion (we are using the material derivative notation capital D by capital D lowercase t) of the total linear momentum of the fluid in the material volume capital V of lowercase t. So lowercase v is the velocity vector, rho is ...
... The left-hand side just represents the time rate of change following the motion (we are using the material derivative notation capital D by capital D lowercase t) of the total linear momentum of the fluid in the material volume capital V of lowercase t. So lowercase v is the velocity vector, rho is ...
Learning Objectives
... 3.A.4.3: The student is able to analyze situations involving interactions among several objects by using free-‐ body diagrams that include the application of Newton’s third law to identify forces. [SP 1.4] 3. ...
... 3.A.4.3: The student is able to analyze situations involving interactions among several objects by using free-‐ body diagrams that include the application of Newton’s third law to identify forces. [SP 1.4] 3. ...
Dynamical relations in the system of two objects with internal
... material point with internal degrees of freedom, obtained in [11]- [13]. The aim of this paper is to obtain a system of equations of motion, describing non-relativistic motion of two interacting spinning objects. Having non-relativistic classical theory it is easy later on to pass on to relativistic ...
... material point with internal degrees of freedom, obtained in [11]- [13]. The aim of this paper is to obtain a system of equations of motion, describing non-relativistic motion of two interacting spinning objects. Having non-relativistic classical theory it is easy later on to pass on to relativistic ...
8th class Physics Bridge Program
... Distance : It is defined as the actual path followed by a body between the points between which its moves. Unit : C.G.S unit : cm S.I unit : m Note: The distance travelled by body is always positive. Displacement : It is the shortest distance between between initial and final point in a definite dir ...
... Distance : It is defined as the actual path followed by a body between the points between which its moves. Unit : C.G.S unit : cm S.I unit : m Note: The distance travelled by body is always positive. Displacement : It is the shortest distance between between initial and final point in a definite dir ...
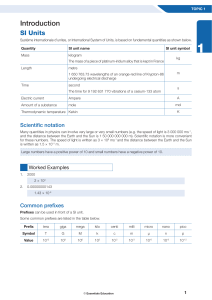
Introduction - Essentials Education
... Constant speed means that an object travels exactly the same distance every unit of time. Light travels with a constant speed of 3 × 108 metres every second. Sound waves travel with a constant speed of 330 metres every second in air (this can change depending on the density of the air). If a car is ...
... Constant speed means that an object travels exactly the same distance every unit of time. Light travels with a constant speed of 3 × 108 metres every second. Sound waves travel with a constant speed of 330 metres every second in air (this can change depending on the density of the air). If a car is ...