Geoid Isostasy
... • Endogenic: “from the inside” – formed beneath the surface of the Earth • Volcanism: hotspot activity, sea-floor spreading, volcanic arcs • Seismicity/Plate Tectonics • Regional uplift and subsidence ...
... • Endogenic: “from the inside” – formed beneath the surface of the Earth • Volcanism: hotspot activity, sea-floor spreading, volcanic arcs • Seismicity/Plate Tectonics • Regional uplift and subsidence ...
All of the processes listed below cause changes in Earth`s surface
... The movement of the two continents as shown may best be explained by A. volcanic eruptions. B. magnetic changes. C. coastal flooding. D. plate tectonics. 16. Where would you most likely find a delta? A. On a mountain top B. In a deep valley C. Near a river’s mouth D. At a volcano’s base 17. Which of ...
... The movement of the two continents as shown may best be explained by A. volcanic eruptions. B. magnetic changes. C. coastal flooding. D. plate tectonics. 16. Where would you most likely find a delta? A. On a mountain top B. In a deep valley C. Near a river’s mouth D. At a volcano’s base 17. Which of ...
General Geology
... 2. DESCRIPTION OF THE COURSE: Includes the study of the origin and evolution of the Earth, the rocks and minerals which compose it, the processes which are constantly changing it, the concepts of relative and absolute time, the risks associated with geologic hazards, and the role of geology in shapi ...
... 2. DESCRIPTION OF THE COURSE: Includes the study of the origin and evolution of the Earth, the rocks and minerals which compose it, the processes which are constantly changing it, the concepts of relative and absolute time, the risks associated with geologic hazards, and the role of geology in shapi ...
304
... Geomorphology is the scientific study of the processes, history and landforms found at the surface of the earth. Geomorphology approaches these questions by identifying all of the earth’s landforms, including mountains, lakes, lava flows, fault scarps, beaches, terraces, moraines, etc., and then stu ...
... Geomorphology is the scientific study of the processes, history and landforms found at the surface of the earth. Geomorphology approaches these questions by identifying all of the earth’s landforms, including mountains, lakes, lava flows, fault scarps, beaches, terraces, moraines, etc., and then stu ...
Felix Waldhauser, Lamont-Doherty Earth Observatory Title
... including earthquake physics, the structure and dynamics of the Earth’s interior, and seismic hazards. Yet, the accuracy with which we know these locations is typically poor, and often unknown. Using advanced analysis techniques that harness both the vast amount of digital seismic data and increasin ...
... including earthquake physics, the structure and dynamics of the Earth’s interior, and seismic hazards. Yet, the accuracy with which we know these locations is typically poor, and often unknown. Using advanced analysis techniques that harness both the vast amount of digital seismic data and increasin ...
Landforms - Rankin County School District / Homepage
... • Erosion: Movement of surface material from one location to another – Water-Rainfall, rivers, and waves: ExampleGrand Canyon – Wind- Abrasion-blast particles of sand against rock, from one place to another (sand dunes) • Dust from Sahara in Africa goes across the Atlantic Ocean to the Caribbean Isl ...
... • Erosion: Movement of surface material from one location to another – Water-Rainfall, rivers, and waves: ExampleGrand Canyon – Wind- Abrasion-blast particles of sand against rock, from one place to another (sand dunes) • Dust from Sahara in Africa goes across the Atlantic Ocean to the Caribbean Isl ...
Geography 12
... and floats on the denser rocks of the asthenosphere Asthenosphere: the plastic (part solid, part liquid) layer of the upper mantle directly below the lithosphere that can flow slowly when put under constant pressure. Tectonics: the processes that deform the earth’s lithosphere and the rock structure ...
... and floats on the denser rocks of the asthenosphere Asthenosphere: the plastic (part solid, part liquid) layer of the upper mantle directly below the lithosphere that can flow slowly when put under constant pressure. Tectonics: the processes that deform the earth’s lithosphere and the rock structure ...
8. Explain erosion. How does this impact the land?
... 12. Provide examples of constructive forces. Be able to identify the constructive force at work when given an example or picture. Flooding, coastlines, rivers/streams, wind, convergent plate boundaries, divergent plate boundaries, and volcanic activity 13. What is a destructive force? A destructive ...
... 12. Provide examples of constructive forces. Be able to identify the constructive force at work when given an example or picture. Flooding, coastlines, rivers/streams, wind, convergent plate boundaries, divergent plate boundaries, and volcanic activity 13. What is a destructive force? A destructive ...
The Rock Cycle Rock – a naturally occurring solid mixture of one or
... The Rock Cycle Rock – a naturally occurring solid mixture of one or more minerals or organic material Rock cycle – the continual process by which new rock forms from old rock material Erosion – the process by which wind, water, ice, or gravity moves soil and sediment from one location to another Dep ...
... The Rock Cycle Rock – a naturally occurring solid mixture of one or more minerals or organic material Rock cycle – the continual process by which new rock forms from old rock material Erosion – the process by which wind, water, ice, or gravity moves soil and sediment from one location to another Dep ...
Earth`s Landforms
... • Deposition – Process of dropping sediment into a new location – Deposits add to the floodplain (the land next to a river) ...
... • Deposition – Process of dropping sediment into a new location – Deposits add to the floodplain (the land next to a river) ...
Geol 201 - American University of Beirut
... • Identify common minerals and rocks and explain how they are formed. • Compare and contrast igneous, metamorphic and sedimentary rocks and relate the different rock types using the rock cycle. • Relate major rock deformation features to the geologic processes that cause them. • Describe the geologi ...
... • Identify common minerals and rocks and explain how they are formed. • Compare and contrast igneous, metamorphic and sedimentary rocks and relate the different rock types using the rock cycle. • Relate major rock deformation features to the geologic processes that cause them. • Describe the geologi ...
Тестовые задания к тексту «Landforms» для студентов
... volcanoes, waterfalls, cliffs and sand dunes. The science that studies landforms is called geomorphology. Geomorphologists are in-terested in the shape of landforms, the processes that make them, the shape they are, and how their shape has changed over time. Very few landscapes are flat. Most land s ...
... volcanoes, waterfalls, cliffs and sand dunes. The science that studies landforms is called geomorphology. Geomorphologists are in-terested in the shape of landforms, the processes that make them, the shape they are, and how their shape has changed over time. Very few landscapes are flat. Most land s ...
Date: Block
... S6E5.d: Describe processes that change rocks and the surface of the Earth. S6E5.e: Recognize that lithospheric plates constantly move and cause major geological events on the Earth’s surface. S6E5.f: Explain the effects of physical processes (plate tectonics) on geological features including oceans. ...
... S6E5.d: Describe processes that change rocks and the surface of the Earth. S6E5.e: Recognize that lithospheric plates constantly move and cause major geological events on the Earth’s surface. S6E5.f: Explain the effects of physical processes (plate tectonics) on geological features including oceans. ...
Earth Science Name Web Inquiry—Plate Tectonics/Earth`s Interior
... e. Recognize that lithospheric plates constantly move and cause major geological events on the earth’s surface. f. Explain the effects of physical processes (plate tectonics, erosion, deposition, volcanic eruption, gravity) on geological features including oceans (composition, currents, and tides). ...
... e. Recognize that lithospheric plates constantly move and cause major geological events on the earth’s surface. f. Explain the effects of physical processes (plate tectonics, erosion, deposition, volcanic eruption, gravity) on geological features including oceans (composition, currents, and tides). ...
Plate Tectonics Crossword
... 19. a crack in the earth's surface where there has been movement of one or both sides 20. valley a long narrow valley ...
... 19. a crack in the earth's surface where there has been movement of one or both sides 20. valley a long narrow valley ...
Outline General Geology 2011
... 4. Igneous activity and plate tectonics - Landscape Fashioned by Water 1. Earth’s External Processes 2. Mass Wasting 3. The Water Cycle 4. Depositional Landforms 5. Drainage Patterns 6. Groundwater, Springs and Wells ...
... 4. Igneous activity and plate tectonics - Landscape Fashioned by Water 1. Earth’s External Processes 2. Mass Wasting 3. The Water Cycle 4. Depositional Landforms 5. Drainage Patterns 6. Groundwater, Springs and Wells ...
Constructive and Destructive Forces Study Guide
... A. GPS – helps seismologists measure movement of __faults_________ B. Seismographs – records movement of the Earth’s crust C. Beach restoration – replacing sand on the beach D. Jetty – prevents the current from carrying away ___sand________ E. Levee – keeps rising water within channels F. Coral reef ...
... A. GPS – helps seismologists measure movement of __faults_________ B. Seismographs – records movement of the Earth’s crust C. Beach restoration – replacing sand on the beach D. Jetty – prevents the current from carrying away ___sand________ E. Levee – keeps rising water within channels F. Coral reef ...
Spheres glossary quiz - HSIE Teachers
... Disturbances in the earth’s crust that result from the earth’s internal energy and which create physical features, such as mountains, on the earth’s surface ...
... Disturbances in the earth’s crust that result from the earth’s internal energy and which create physical features, such as mountains, on the earth’s surface ...
D. Tectonics
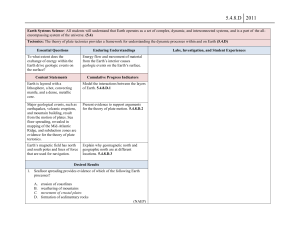
... Earth Systems Science: All students will understand that Earth operates as a set of complex, dynamic, and interconnected systems, and is a part of the allencompassing system of the universe. (5.4) Tectonics: The theory of plate tectonics provides a framework for understanding the dynamic processes w ...
... Earth Systems Science: All students will understand that Earth operates as a set of complex, dynamic, and interconnected systems, and is a part of the allencompassing system of the universe. (5.4) Tectonics: The theory of plate tectonics provides a framework for understanding the dynamic processes w ...
Physical Geography 1
... • The North American plate is moving toward the west and meeting resistance from the Pacific, Juan de Fuca and Cocos plates. • Western North America’s surface features are younger and steeper (angular) than the Eastern North America. • Eastern North America’s features are older and more worn down (r ...
... • The North American plate is moving toward the west and meeting resistance from the Pacific, Juan de Fuca and Cocos plates. • Western North America’s surface features are younger and steeper (angular) than the Eastern North America. • Eastern North America’s features are older and more worn down (r ...
Geomorphology
Geomorphology (from Greek: γῆ, ge, ""earth""; μορφή, morfé, ""form""; and λόγος, logos, ""study"") is the scientific study of the origin and evolution of topographic and bathymetric features created by physical or chemical processes operating at or near the earth's surface. Geomorphologists seek to understand why landscapes look the way they do, to understand landform history and dynamics and to predict changes through a combination of field observations, physical experiments and numerical modeling. Geomorphology is practiced within physical geography, geology, geodesy, engineering geology, archaeology and geotechnical engineering. This broad base of interests contributes to many research styles and interests within the field.