perfect competition - the economics of competitive markets
... resources (technology, other factor inputs) and improvements in production technologies achieved by one firm can spill-over to all the other suppliers in the market 5. There are assumed to be no barriers to entry & exit of firms in long run – which means that the market is open to competition from n ...
... resources (technology, other factor inputs) and improvements in production technologies achieved by one firm can spill-over to all the other suppliers in the market 5. There are assumed to be no barriers to entry & exit of firms in long run – which means that the market is open to competition from n ...
MANAGERIAL ECONOMICS 11th Edition
... - the positive sign indicates that as the temperature increases so will the demand for this good. Hence, it’s more likely to be a product such as Pepsi. In which coefficients would you have at least 95% confidence that you have a good estimate of the marginal relationship between the independent var ...
... - the positive sign indicates that as the temperature increases so will the demand for this good. Hence, it’s more likely to be a product such as Pepsi. In which coefficients would you have at least 95% confidence that you have a good estimate of the marginal relationship between the independent var ...
What is the relationship between economic and accounting profit
... 4. The demand for personal computers has been estimated to be Q = 500,000 – 700P + 200I - 500S. Assume that per capita income I is $13,000 and the average price of software S is $400.When the price of personal computers is P = $3,000, the price elasticity of demand is: a. –2.625 b. –7.0 c. –1.0 d. – ...
... 4. The demand for personal computers has been estimated to be Q = 500,000 – 700P + 200I - 500S. Assume that per capita income I is $13,000 and the average price of software S is $400.When the price of personal computers is P = $3,000, the price elasticity of demand is: a. –2.625 b. –7.0 c. –1.0 d. – ...
market power - McGraw Hill Higher Education
... Still used for electricity, natural gas, local telephone service More common in some other countries ...
... Still used for electricity, natural gas, local telephone service More common in some other countries ...
California State University, Sacramento
... A) present when producing more than 10,000 tons. B) present when producing more than 20,000 tons. C) present when producing more than 30,000 tons. D) never present. E) 14) The returns to scale of the production function Q = 50 L.4K.2 are A) 50. B) .6. C) .8. D) 50.6. 15) The Nifty Gum Co. has purcha ...
... A) present when producing more than 10,000 tons. B) present when producing more than 20,000 tons. C) present when producing more than 30,000 tons. D) never present. E) 14) The returns to scale of the production function Q = 50 L.4K.2 are A) 50. B) .6. C) .8. D) 50.6. 15) The Nifty Gum Co. has purcha ...
SA6 - Trinity College Dublin
... Giffen goods arise when the income effect is so severely negative that it offsets the substitution effect. This can happen because in consumer choice, income was an exogenous variable – therefore, changes in price affect both the relative substitutability of goods (via the tangency condition) as wel ...
... Giffen goods arise when the income effect is so severely negative that it offsets the substitution effect. This can happen because in consumer choice, income was an exogenous variable – therefore, changes in price affect both the relative substitutability of goods (via the tangency condition) as wel ...
PPT
... Externality on Economic Efficiency (2 of 2) When there is a positive externality in producing or consuming a good or service, too little of the good or service will be produced at ...
... Externality on Economic Efficiency (2 of 2) When there is a positive externality in producing or consuming a good or service, too little of the good or service will be produced at ...
notes
... considered harmful to the public good. 1. Cigarettes 2. Alcohol 3. Tariff on Imported Goods (Foreign Food) makes them more expensive to buy ...
... considered harmful to the public good. 1. Cigarettes 2. Alcohol 3. Tariff on Imported Goods (Foreign Food) makes them more expensive to buy ...
ECO 335 Economics of Regulation and Antitrust Dr. David Loomis Department of Economics
... response to the demands of interest groups struggling among themselves to maximize the incomes of their members. Regulators are “captured” by the industries that they serve No linkage or mechanism by which a perception of the public interest is translated into legislative action. Regulators don’t al ...
... response to the demands of interest groups struggling among themselves to maximize the incomes of their members. Regulators are “captured” by the industries that they serve No linkage or mechanism by which a perception of the public interest is translated into legislative action. Regulators don’t al ...
w05ex2 - Rose
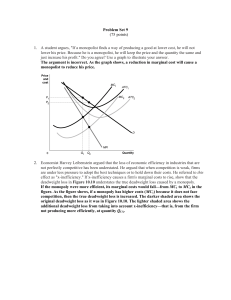
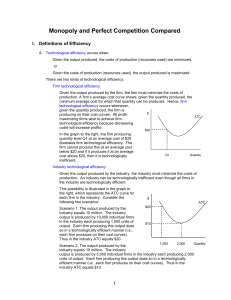
... Suppose an increasing-cost, perfectly competitive industry is initially in long-run equilibrium. Using two graphs, one showing the market demand and supply curves and the other showing the short-run average cost curves of a typical firm, illustrate and describe the short-run and long-run effects of ...
... Suppose an increasing-cost, perfectly competitive industry is initially in long-run equilibrium. Using two graphs, one showing the market demand and supply curves and the other showing the short-run average cost curves of a typical firm, illustrate and describe the short-run and long-run effects of ...
... input is increased, while all other outputs are kept unchanged. Or All the input used in productions of are increased simultaneously and in the same proportion. What are its possible effects on total production? Explain with the help of a numerical example and diagram. 16. Define ‘producer’s equilib ...
Document
... B) the non-monetary opportunity cost of using the firm's own resources. C) the deferred cost of production. D) total cost minus fixed costs. Answer: B 12) The marginal product of labor is defined as A) the additional sales revenue that results when one more worker is hired. B) the additional output ...
... B) the non-monetary opportunity cost of using the firm's own resources. C) the deferred cost of production. D) total cost minus fixed costs. Answer: B 12) The marginal product of labor is defined as A) the additional sales revenue that results when one more worker is hired. B) the additional output ...
Factor Markets Teaching Notes
... just income) and that includes both wages and non-monetary benefits and disbenefits. If in the long-term, wages in Regina wages are less than wages in Sudbury (and the costs of living and the marginal productivity of labour are the same), one can infer that Regina is a more attractive place to live. ...
... just income) and that includes both wages and non-monetary benefits and disbenefits. If in the long-term, wages in Regina wages are less than wages in Sudbury (and the costs of living and the marginal productivity of labour are the same), one can infer that Regina is a more attractive place to live. ...
Lecture 12
... - CS and PS. -and the idea that the force of maximization lead to the equilibrium of P* and Q*. ...
... - CS and PS. -and the idea that the force of maximization lead to the equilibrium of P* and Q*. ...
Analyzing Customer Profitability, And Activity-Based Pricing
... less than full cost. 2. In some cases it may be beneficial to charge a price less than full cost. 3. Special order. a. Order will not affect demand for a firm’s other products (or current ...
... less than full cost. 2. In some cases it may be beneficial to charge a price less than full cost. 3. Special order. a. Order will not affect demand for a firm’s other products (or current ...
No Slide Title
... b. This divisibility requirement is almost never met in actuality c. The model does predict that consumers will get as close as possible to the utility maximizing condition ...
... b. This divisibility requirement is almost never met in actuality c. The model does predict that consumers will get as close as possible to the utility maximizing condition ...
Externality

In economics, an externality is the cost or benefit that affects a party who did not choose to incur that cost or benefit.For example, manufacturing activities that cause air pollution impose health and clean-up costs on the whole society, whereas the neighbors of an individual who chooses to fire-proof his home may benefit from a reduced risk of a fire spreading to their own houses. If external costs exist, such as pollution, the producer may choose to produce more of the product than would be produced if the producer were required to pay all associated environmental costs. Because responsibility or consequence for self-directed action lies partly outside the self, an element of externalization is involved. If there are external benefits, such as in public safety, less of the good may be produced than would be the case if the producer were to receive payment for the external benefits to others. For the purpose of these statements, overall cost and benefit to society is defined as the sum of the imputed monetary value of benefits and costs to all parties involved. Thus, unregulated markets in goods or services with significant externalities generate prices that do not reflect the full social cost or benefit of their transactions; such markets are therefore inefficient.