2nd Midterm S09 - Penn Economics
... a. Plot the marginal cost curve, along with an average total cost curve that is consistent with the marginal cost curve, and the fact that there are high fixed costs. Answer: MC constant at 5. ATC always declining and getting closer to it. Points: 6 MC flat at 5: 2 ATC falling to it: 4 Let us start ...
... a. Plot the marginal cost curve, along with an average total cost curve that is consistent with the marginal cost curve, and the fact that there are high fixed costs. Answer: MC constant at 5. ATC always declining and getting closer to it. Points: 6 MC flat at 5: 2 ATC falling to it: 4 Let us start ...
Economics Midterm Review Sheet
... Factors of production: land, labor, capital. Physical capital includes buildings, tools, and machines. Human capital is the knowledge and skills a worker gains through education and experience. Entrepreneurs utilize factors of production to make profits. Trade-offs is what we give up when we choose ...
... Factors of production: land, labor, capital. Physical capital includes buildings, tools, and machines. Human capital is the knowledge and skills a worker gains through education and experience. Entrepreneurs utilize factors of production to make profits. Trade-offs is what we give up when we choose ...
Profit-Maximization by a monopolist
... Imagine there is some sort of monopoly over a product of software, like Microsoft. In columns 1 and 2 of Table 11.a.1 we can see the demand schedule for this particular monopoly. From this you can see that as the quantity increases the price decreases, representing the downward sloping demand curve ...
... Imagine there is some sort of monopoly over a product of software, like Microsoft. In columns 1 and 2 of Table 11.a.1 we can see the demand schedule for this particular monopoly. From this you can see that as the quantity increases the price decreases, representing the downward sloping demand curve ...
The allocation of resources in a market economy is described by
... computers because computers produce more output (E) keep the same number of workers and computers because the marginal revenue products of both workers and computers are positive 30. Imposing taxes that increase as a firm’s pollution increases is often recommended by economists as a means to reduce ...
... computers because computers produce more output (E) keep the same number of workers and computers because the marginal revenue products of both workers and computers are positive 30. Imposing taxes that increase as a firm’s pollution increases is often recommended by economists as a means to reduce ...
Lecture Week 06
... free, he splits his time between the two to maximize utility. At each successive step, he chooses the activity with the greatest MU. ...
... free, he splits his time between the two to maximize utility. At each successive step, he chooses the activity with the greatest MU. ...
PPA 723: Managerial Economics
... The SR market supply curve is the horizontal summation of the firm supply curves for the firms in the market. The more firms in the market, the more elastic the SR market supply curve. ...
... The SR market supply curve is the horizontal summation of the firm supply curves for the firms in the market. The more firms in the market, the more elastic the SR market supply curve. ...
What causes changes in SUPPLY?
... Hurricane Katrina hit the Louisiana coast pretty hard, wiping out homes and businesses such as Home Depot and Lowe’s. How would you expect the hurricane to affect the market price and quantity of lumber, ceteris ...
... Hurricane Katrina hit the Louisiana coast pretty hard, wiping out homes and businesses such as Home Depot and Lowe’s. How would you expect the hurricane to affect the market price and quantity of lumber, ceteris ...
Economics Chapter 5 Supply
... payment to support a business or market. Since the subsidy lowers producer’s costs, its effect is usually to increase supply. ...
... payment to support a business or market. Since the subsidy lowers producer’s costs, its effect is usually to increase supply. ...
Chapter 5 Supply
... Increasing returns B. Diminishing returns C. Equaling returns D. Negative returns The period of production that allows producers to change only the amount of the variable input called labor is: A. The long run B. The short run C. The production function D. A stage of production A production function ...
... Increasing returns B. Diminishing returns C. Equaling returns D. Negative returns The period of production that allows producers to change only the amount of the variable input called labor is: A. The long run B. The short run C. The production function D. A stage of production A production function ...
Introduction to Supply and Demand
... Surplus: a situation in which quantity supplied is greater than quantity demanded Shortage: a situation in which quantity demanded is greater than quantity supplied ...
... Surplus: a situation in which quantity supplied is greater than quantity demanded Shortage: a situation in which quantity demanded is greater than quantity supplied ...
PowerPoint File
... Problem 1 (9:30 AM Class) State Landsburg’s equimarginal principle. Economists talking about a firm’s production decision also frequently say that “fixed costs don’t matter.” Do these two principles contradict each other? Explain how each of these principles apply to the behavior of the firm and ...
... Problem 1 (9:30 AM Class) State Landsburg’s equimarginal principle. Economists talking about a firm’s production decision also frequently say that “fixed costs don’t matter.” Do these two principles contradict each other? Explain how each of these principles apply to the behavior of the firm and ...
CHAPTER 11 MONOPOLISTIC COMPETITION AND
... 2. False. In the long run, a monopolistic competitor will not produce at minimum ATC. In longrun equilibrium, there are too many firms producing too little output to achieve minimum ATC. 4. In oligopoly there are fewer firms than in perfect competition or monopolistic competition, but more than in m ...
... 2. False. In the long run, a monopolistic competitor will not produce at minimum ATC. In longrun equilibrium, there are too many firms producing too little output to achieve minimum ATC. 4. In oligopoly there are fewer firms than in perfect competition or monopolistic competition, but more than in m ...
Combining Supply and Demand Section 1: Guided Reading and Review
... 9. Negative results of ending rent control: - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 10. Effect on labor when minimum wage exceeds equilibrium: 11. Purpose of Northeas~ Dairy Compact: - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - ...
... 9. Negative results of ending rent control: - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 10. Effect on labor when minimum wage exceeds equilibrium: 11. Purpose of Northeas~ Dairy Compact: - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - ...
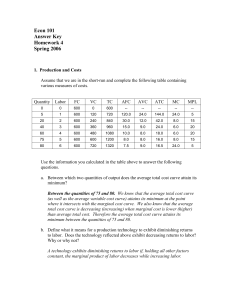
Answers to Homework #4
... price of public transportation, more people are driving to work and air pollution is increasing. They therefore decide that in order to discourage people from driving, they will issue a $4 excise tax on consumers on the consumption of gasoline. Assume the market demand curve is Pd = 900 – 2Qd. a. Wh ...
... price of public transportation, more people are driving to work and air pollution is increasing. They therefore decide that in order to discourage people from driving, they will issue a $4 excise tax on consumers on the consumption of gasoline. Assume the market demand curve is Pd = 900 – 2Qd. a. Wh ...
Perfect Competition
... • There are many sellers and many buyers, none of which is large in relation to total sales or purchases. • Each firm produces and sells a homogeneous product. • Buyers and sellers have all relevant information about prices, product quality, sources of supply, and so forth. • Firms have easy entry a ...
... • There are many sellers and many buyers, none of which is large in relation to total sales or purchases. • Each firm produces and sells a homogeneous product. • Buyers and sellers have all relevant information about prices, product quality, sources of supply, and so forth. • Firms have easy entry a ...
Externality

In economics, an externality is the cost or benefit that affects a party who did not choose to incur that cost or benefit.For example, manufacturing activities that cause air pollution impose health and clean-up costs on the whole society, whereas the neighbors of an individual who chooses to fire-proof his home may benefit from a reduced risk of a fire spreading to their own houses. If external costs exist, such as pollution, the producer may choose to produce more of the product than would be produced if the producer were required to pay all associated environmental costs. Because responsibility or consequence for self-directed action lies partly outside the self, an element of externalization is involved. If there are external benefits, such as in public safety, less of the good may be produced than would be the case if the producer were to receive payment for the external benefits to others. For the purpose of these statements, overall cost and benefit to society is defined as the sum of the imputed monetary value of benefits and costs to all parties involved. Thus, unregulated markets in goods or services with significant externalities generate prices that do not reflect the full social cost or benefit of their transactions; such markets are therefore inefficient.