Neuronal Development
... • Neurons that divide are located next to the ventricles • Where is the gray matter (soma) in the cerebral cortex? • Neurons will either migrate by: – Sending out processes – Follow radial glia ...
... • Neurons that divide are located next to the ventricles • Where is the gray matter (soma) in the cerebral cortex? • Neurons will either migrate by: – Sending out processes – Follow radial glia ...
Answer Key
... 12. With regard to the process of neural transmission, a refractory period refers to a time interval in which A) a neuron fires more rapidly than usual. B) an electrical charge travels from a sensory neuron to a motor neuron. C) positively charged ions are pumped back outside a neural membrane. D) a ...
... 12. With regard to the process of neural transmission, a refractory period refers to a time interval in which A) a neuron fires more rapidly than usual. B) an electrical charge travels from a sensory neuron to a motor neuron. C) positively charged ions are pumped back outside a neural membrane. D) a ...
Chapter Three Study Guide
... If they are the right shape, they fit into receptors, simulating the receiving neuron and the message is carried forward. After the transmitting molecules have done their work, they are broken down by chemicals and recycled back to the terminal buttons, where they are reassembled and reused Reuptake ...
... If they are the right shape, they fit into receptors, simulating the receiving neuron and the message is carried forward. After the transmitting molecules have done their work, they are broken down by chemicals and recycled back to the terminal buttons, where they are reassembled and reused Reuptake ...
Chapter 2 - Biological Basis of Behavior
... Certain behaviors, that would serve to the survival and reproduction of the organism would become geneticallydetermined over many generations ...
... Certain behaviors, that would serve to the survival and reproduction of the organism would become geneticallydetermined over many generations ...
Quiz - Web Adventures
... A Plaguing Problem Episode 4 – Mystery of Morpheus: Quiz 1) Which scientist won a Nobel Prize for discovering how nerve cells communicate? a) Friedrich Serturner b) Hippocrates c) Linnaeus d) Otto Loewi 2) The part of a neuron where the receptors are located is the: a) Axon b) Cell body c) Dendrite ...
... A Plaguing Problem Episode 4 – Mystery of Morpheus: Quiz 1) Which scientist won a Nobel Prize for discovering how nerve cells communicate? a) Friedrich Serturner b) Hippocrates c) Linnaeus d) Otto Loewi 2) The part of a neuron where the receptors are located is the: a) Axon b) Cell body c) Dendrite ...
Chapter 3 – early studies of the central nervous system
... Phrenologists like Gall & Spurzheim considered themselves anatomists and scientists. Gall’s books were considered deterministic, materialistic and atheistic and placed on the Index of Prohibited Books by the Catholic church. After Gall’s death, Spurzheim & George Combe turned phrenology into a cult, ...
... Phrenologists like Gall & Spurzheim considered themselves anatomists and scientists. Gall’s books were considered deterministic, materialistic and atheistic and placed on the Index of Prohibited Books by the Catholic church. After Gall’s death, Spurzheim & George Combe turned phrenology into a cult, ...
Chapter 6 Body and Behavior
... material, Research and find out who or how it was discovered • Level Three: Choose one additional disease/disorder and do Level 0ne/Two work on that disease/disorder • Completed assignment is a word document ...
... material, Research and find out who or how it was discovered • Level Three: Choose one additional disease/disorder and do Level 0ne/Two work on that disease/disorder • Completed assignment is a word document ...
BCH 450 Nervous Tissues
... carrying signals from various parts of the cerebral cortex to the cerebellum cerebellum Its most clearly-understood function is to coordinate body movements. So the cerebellum appears to be a center for learning ...
... carrying signals from various parts of the cerebral cortex to the cerebellum cerebellum Its most clearly-understood function is to coordinate body movements. So the cerebellum appears to be a center for learning ...
Learning Styles PowerPoint
... Student needs to take time after class and pick out important information for notes. Notes need to be in their own words. Studying needs to be done alone ...
... Student needs to take time after class and pick out important information for notes. Notes need to be in their own words. Studying needs to be done alone ...
The Brain!
... speech and happiness center; while the right side is known as being more fretful, more creative, and holistic processing center. ...
... speech and happiness center; while the right side is known as being more fretful, more creative, and holistic processing center. ...
PDF version
... Implants could one day help people who are paralysed or unable to communicate because of spinal injury or conditions such as amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (Lou Gehrig’s disease). Electrodes implanted in the brain could, in principle, pick up neural signals and convey them to a prosthetic arm or a ...
... Implants could one day help people who are paralysed or unable to communicate because of spinal injury or conditions such as amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (Lou Gehrig’s disease). Electrodes implanted in the brain could, in principle, pick up neural signals and convey them to a prosthetic arm or a ...
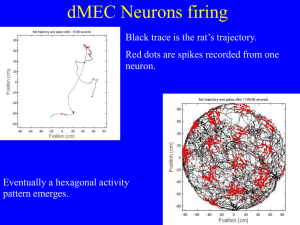
How grid cells neurons encode rat position
... activity to drift depending on direction the rat faces ...
... activity to drift depending on direction the rat faces ...
The_road_to_brain-scale_simulation
... This is the story of the endeavor of the Brain and Neural Systems Team (BNT) to make the computational power of K available to the field of computational neuroscience. An extended version of this report can be found at [1]. The human brain comprises about 1011 neurons, each connected to 10000 others ...
... This is the story of the endeavor of the Brain and Neural Systems Team (BNT) to make the computational power of K available to the field of computational neuroscience. An extended version of this report can be found at [1]. The human brain comprises about 1011 neurons, each connected to 10000 others ...
Ms. Setzer-The Brain!
... mathematics, and comprehension skills. In the 1960s, it was termed as the dominant brain. -The right hemisphere houses most spatial abilities-the ability to precieve or organize things in a given space. Also helps make connections between words. ...
... mathematics, and comprehension skills. In the 1960s, it was termed as the dominant brain. -The right hemisphere houses most spatial abilities-the ability to precieve or organize things in a given space. Also helps make connections between words. ...
Lecture 7 (Jan 31): BRAIN DEVELOPMENT and EVOLUTION
... New cells migrate outwardly towards the cortical surface. (Along radial glia) ...
... New cells migrate outwardly towards the cortical surface. (Along radial glia) ...
The Human Brain
... and has the texture of toothpaste. It is made up of 50 to 100 billion nerve cells called neurons as well as 500-1000 billion other cells. Neurons have a cell body with lots of branches coming off them called dendrites. They also have long tails called axons which are insulated by a sheath (myelin sh ...
... and has the texture of toothpaste. It is made up of 50 to 100 billion nerve cells called neurons as well as 500-1000 billion other cells. Neurons have a cell body with lots of branches coming off them called dendrites. They also have long tails called axons which are insulated by a sheath (myelin sh ...
UNIT 2 REVIEW GUIDE *Be able to identify/label parts of the neuron
... increases the likelihood that the receiving neuron will fire an impulse, it is considered a(n)…. ...
... increases the likelihood that the receiving neuron will fire an impulse, it is considered a(n)…. ...
The Nervous System
... The Nervous System: • is a rapid communication system using electrical signals. • enables movement, perception, thought, emotion and learning. • consists of a network of specialized cells called neurons. ...
... The Nervous System: • is a rapid communication system using electrical signals. • enables movement, perception, thought, emotion and learning. • consists of a network of specialized cells called neurons. ...
Click Here To
... Consists of the brain and spinal cord Brain: protected by the skull Spinal cord: protected by the spine Both surrounded by cerebrospinal fluid Cushions the brain and spinal cord from injury ...
... Consists of the brain and spinal cord Brain: protected by the skull Spinal cord: protected by the spine Both surrounded by cerebrospinal fluid Cushions the brain and spinal cord from injury ...
Sam Wangdescribes some of the physics of our most complex organ
... the cortex, the grey matter forms a rind that surrounds the white matter. When you look more closely, any given bit of grey matter in the cerebral cortex is layered like a cake, with connections passing from layer to layer. The layers are arranged such that a hypothetical shuffling of the order of t ...
... the cortex, the grey matter forms a rind that surrounds the white matter. When you look more closely, any given bit of grey matter in the cerebral cortex is layered like a cake, with connections passing from layer to layer. The layers are arranged such that a hypothetical shuffling of the order of t ...
Neurons and the BOLD response
... With the advent of high-powered computers, it also became possible to analyze very complex EEG/MEG into its components --- sine waves. (Using Fourier Analysis). ...
... With the advent of high-powered computers, it also became possible to analyze very complex EEG/MEG into its components --- sine waves. (Using Fourier Analysis). ...
Nervous Systems - manorlakesscience
... sensory detectors to the brain and impulses that pass from the brain to other parts of the body travel along the spinal cord. ...
... sensory detectors to the brain and impulses that pass from the brain to other parts of the body travel along the spinal cord. ...