T C N B
... al., 1997]. A search in Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man (OMIM) reveals that mental retardation is a clinical manifestation in 1,228 genetic syndromes. Brain abnormalities in subjects with MR are very common. Postmortem studies have found brain abnormalities in 34 –98% of deceased, severely retar ...
... al., 1997]. A search in Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man (OMIM) reveals that mental retardation is a clinical manifestation in 1,228 genetic syndromes. Brain abnormalities in subjects with MR are very common. Postmortem studies have found brain abnormalities in 34 –98% of deceased, severely retar ...
Regulation of rCBF by Diffusible Signals: An Analysis of Constraints
... activity-dependent hemodynamic response places a the dynamics of concentration changes; the microveslower limit on the apparent rates of diffusion and sels themselves were not explicitly modeled. elimination. Using simulations of microdiffusion we Because of the complicated spatiotemporal changes ex ...
... activity-dependent hemodynamic response places a the dynamics of concentration changes; the microveslower limit on the apparent rates of diffusion and sels themselves were not explicitly modeled. elimination. Using simulations of microdiffusion we Because of the complicated spatiotemporal changes ex ...
Ch 49 Pract Test Nervous System
... Tolerance means that decreasing amounts of a drug are needed to be effective. d. A lethal dose is a dose that results in death. ...
... Tolerance means that decreasing amounts of a drug are needed to be effective. d. A lethal dose is a dose that results in death. ...
Mental activities
... change the environment so the signal can penetrate a cluttered environment ...
... change the environment so the signal can penetrate a cluttered environment ...
Abstract Browser - The Journal of Neuroscience
... movements. It is also thought to contribute to motor learning and adaptation in response to changing conditions, such as external forces or muscle fatigue. More specifically, the cerebellumhasbeenhypothesizedtoprovideforward internal models, that is, predictions about what body movements will result ...
... movements. It is also thought to contribute to motor learning and adaptation in response to changing conditions, such as external forces or muscle fatigue. More specifically, the cerebellumhasbeenhypothesizedtoprovideforward internal models, that is, predictions about what body movements will result ...
The Nervous System
... • Neurotransmitter can't remain in cleft (would continue to stimulate uncontrollably) – ACh removed by acetylcholinesterase (AChE) – Acetate & choline reabsorbed by axon end, resynthesized to ACh – Other neurotransmitters taken back by axon or diffuse away ...
... • Neurotransmitter can't remain in cleft (would continue to stimulate uncontrollably) – ACh removed by acetylcholinesterase (AChE) – Acetate & choline reabsorbed by axon end, resynthesized to ACh – Other neurotransmitters taken back by axon or diffuse away ...
Nervous System: Speech
... transfer and associations between either vision or touch and hearing (2). As the angular gyrus is important in the processing of associating a heard name to a seen or felt object, it is probably also important for associations in the reverse direction. A "name" passes through Wernicke's area, then v ...
... transfer and associations between either vision or touch and hearing (2). As the angular gyrus is important in the processing of associating a heard name to a seen or felt object, it is probably also important for associations in the reverse direction. A "name" passes through Wernicke's area, then v ...
Name: PID: SPRING 2013 COGS 1 Midterm 2 – Form B 1. Which of
... a. Prior probability b. Posterior probability c. Marginal probability d. Likelihood e. Evidence 42. Referring to an object's location as being ""due north"" is an example of a(n): a. Relative frame of reference b. Centric frame of reference c. Absolute frame of reference d. Intrinsic frame of refere ...
... a. Prior probability b. Posterior probability c. Marginal probability d. Likelihood e. Evidence 42. Referring to an object's location as being ""due north"" is an example of a(n): a. Relative frame of reference b. Centric frame of reference c. Absolute frame of reference d. Intrinsic frame of refere ...
Viscoelastic Properties of the Rat Brain in the Horizontal Plane
... mechanical model that explicitly accounts for the different mechanical properties of different anatomical structures is required. Finite element modeling can predict the loading of various anatomical structures during a traumatic event[4]. However, there are several c ...
... mechanical model that explicitly accounts for the different mechanical properties of different anatomical structures is required. Finite element modeling can predict the loading of various anatomical structures during a traumatic event[4]. However, there are several c ...
What We Know About the Brain and Learning
... When scientists first discovered this seemingly wasteful procedure it was alarming. Yet we now know this happens during all normal brain development. In the last two months before birth, the brain prunes away about half of its cells. From that point on no appreciable number of neurons is lost in the ...
... When scientists first discovered this seemingly wasteful procedure it was alarming. Yet we now know this happens during all normal brain development. In the last two months before birth, the brain prunes away about half of its cells. From that point on no appreciable number of neurons is lost in the ...
Document
... cortex. Some cortical neurons send their axons to the thalamus, while others receive input from ...
... cortex. Some cortical neurons send their axons to the thalamus, while others receive input from ...
States of consciousness
... When leaving the brain the person experiences withdrawal symptoms which are usually opposite the initial drug effect ...
... When leaving the brain the person experiences withdrawal symptoms which are usually opposite the initial drug effect ...
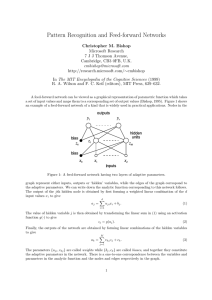
Pattern Recognition and Feed-forward Networks
... to note that the derivatives could be calculated in a computationally efficient manner using a technique called ‘back-propagation’, so called because it has a graphical interpretation in terms of a propagation of error signals from the output nodes backwards through the network. Originally these gra ...
... to note that the derivatives could be calculated in a computationally efficient manner using a technique called ‘back-propagation’, so called because it has a graphical interpretation in terms of a propagation of error signals from the output nodes backwards through the network. Originally these gra ...
Central Nervous System - Home Page of Ken Jones
... Substance of Schwann cell composed of lipoprotein Transmits impulse from sensory to motor neuron within CNS Unmyelinated axon between Schwann cells on neurons of the peripheral nervous system Transmits impulse into brain or spinal cord from receptors A nerve fiber; conducts impulse away from a neuro ...
... Substance of Schwann cell composed of lipoprotein Transmits impulse from sensory to motor neuron within CNS Unmyelinated axon between Schwann cells on neurons of the peripheral nervous system Transmits impulse into brain or spinal cord from receptors A nerve fiber; conducts impulse away from a neuro ...
Unit 2 Multiple Choice test Name
... 15. Stimulated digestion is to inhibited digestion as the ________ nervous system is to the ________ nervous system. A) somatic; autonomic B) autonomic; somatic C) central; peripheral D) sympathetic; parasympathetic E) parasympathetic; sympathetic 16. Motor neurons are to the ________ nervous system ...
... 15. Stimulated digestion is to inhibited digestion as the ________ nervous system is to the ________ nervous system. A) somatic; autonomic B) autonomic; somatic C) central; peripheral D) sympathetic; parasympathetic E) parasympathetic; sympathetic 16. Motor neurons are to the ________ nervous system ...
Build a Brain KEY - Belle Vernon Area School District
... communication in the human body. This organ not only allows your systems to communicate with one another, but allows you to communicate with and respond to your surroundings. The central nervous system (CNS) consists of the brain and the spinal cord, while the peripheral nervous system (PNS) consist ...
... communication in the human body. This organ not only allows your systems to communicate with one another, but allows you to communicate with and respond to your surroundings. The central nervous system (CNS) consists of the brain and the spinal cord, while the peripheral nervous system (PNS) consist ...
Unit 2: Biological Psychology
... What are neural networks and where are they found? What is the peripheral nervous system, and what does it do? What is the central nervous system, and what structures is it comprised of? What are the two components of the peripheral nervous system? What does the somatic nervous system do? What is th ...
... What are neural networks and where are they found? What is the peripheral nervous system, and what does it do? What is the central nervous system, and what structures is it comprised of? What are the two components of the peripheral nervous system? What does the somatic nervous system do? What is th ...
Invitation to the Life Span by Kathleen Stassen Berger
... • CVD is considered secondary aging because not everyone develops it. • No single factor (including age, hypertension, inactivity, and smoking) makes CVD inevitable. • The links among aging, risk, and CVD are undeniable. – A 90-year-old is 1,000 times more likely to die of cardiovascular disease tha ...
... • CVD is considered secondary aging because not everyone develops it. • No single factor (including age, hypertension, inactivity, and smoking) makes CVD inevitable. • The links among aging, risk, and CVD are undeniable. – A 90-year-old is 1,000 times more likely to die of cardiovascular disease tha ...
Chapter 12 The Nervous System
... • The CNS and the PNS are both composed of a series of interconnected neurons. ...
... • The CNS and the PNS are both composed of a series of interconnected neurons. ...
How Opioid Drugs Bind to Receptors
... The transmembrane structures of the four In other words, the unusual conformation could provide necessary — although not ORs are very similar to each other, as expected of TM1 in κ-OR may simply be one of many sufficient — information for elucidating the given that the amino-acid sequences of these ...
... The transmembrane structures of the four In other words, the unusual conformation could provide necessary — although not ORs are very similar to each other, as expected of TM1 in κ-OR may simply be one of many sufficient — information for elucidating the given that the amino-acid sequences of these ...
The Ten-Percent Myth
... percent of our brains. Another variant is that only ten percent of the brain had been mapped, and this in turn became misunderstood as ten percent used. A third variant was described earlier by Craig Karges. This view is that the brain is somehow divided neatly into two parts: the conscious mind whi ...
... percent of our brains. Another variant is that only ten percent of the brain had been mapped, and this in turn became misunderstood as ten percent used. A third variant was described earlier by Craig Karges. This view is that the brain is somehow divided neatly into two parts: the conscious mind whi ...
Slides from Discussion section VI 11/15/2004 (Elissa
... selectivity in the primate temporal cortex ...
... selectivity in the primate temporal cortex ...
Neural ensemble coding and statistical periodicity: Speculations on
... tivities. Intuitively one might anticipate that these two notions are not that distinct, but rather lie at opposite extremes of a continuum. Here we briefly summarize those observations which are particularly relevant for our discussion of the statistical properties of dynamical systems with retarde ...
... tivities. Intuitively one might anticipate that these two notions are not that distinct, but rather lie at opposite extremes of a continuum. Here we briefly summarize those observations which are particularly relevant for our discussion of the statistical properties of dynamical systems with retarde ...
Discoveries from the Black Box - Boulder Institute for Psychotherapy
... inside us whose functioning is determined primarily by our inborn biology," says Siegel, who coined the term interpersonal neurobiology to describe how advances in research have created a conceptual bridge among biology, attachment research, development psychology, brain science, and systems theory ...
... inside us whose functioning is determined primarily by our inborn biology," says Siegel, who coined the term interpersonal neurobiology to describe how advances in research have created a conceptual bridge among biology, attachment research, development psychology, brain science, and systems theory ...