MCB 163: Mammalian Neuroanatomy
... rapid feedback about actual muscle state for ongoing movement; the magnocellular part contributes to the rubrospinal system, which conveys cerebellar influence to distal flexors. 4. LATERAL GENICULATE BODY Recipient of retinal input from X- and Y-ganglion cells that terminate, respectively in the pa ...
... rapid feedback about actual muscle state for ongoing movement; the magnocellular part contributes to the rubrospinal system, which conveys cerebellar influence to distal flexors. 4. LATERAL GENICULATE BODY Recipient of retinal input from X- and Y-ganglion cells that terminate, respectively in the pa ...
Modeling and Imagery
... Intersensory integration and sensory dominance • Overall sense of what is going on dependent on information flowing from many receptors simultaneously • Occasionally they contradict each other • Vision is dominant…can lead to some amusing experiments (and experiences) ...
... Intersensory integration and sensory dominance • Overall sense of what is going on dependent on information flowing from many receptors simultaneously • Occasionally they contradict each other • Vision is dominant…can lead to some amusing experiments (and experiences) ...
Interfacing Real-Time Spiking I/O with the SpiNNaker neuromimetic
... approaches to robot control offering alternative benefits rather than attempting to compete feature-for-feature. The closed-loop system presented is formed by interfacing the spiking neural network with sensors and actuators: the whole system runs in real-time and interacts with the outside world ex ...
... approaches to robot control offering alternative benefits rather than attempting to compete feature-for-feature. The closed-loop system presented is formed by interfacing the spiking neural network with sensors and actuators: the whole system runs in real-time and interacts with the outside world ex ...
Neurons and Neurotransmission with Nerve slides
... more likely that the receiving neuron will generate an action potential (impulse) •The second neuron is more likely to fire. ...
... more likely that the receiving neuron will generate an action potential (impulse) •The second neuron is more likely to fire. ...
Chapter Objectives - Website of Neelay Gandhi
... Tight Junction between capillary endothelial cells BCSFB Tight Junctions between epithelial cells in Choroid Plexus All solutes must cross both cell membranes of the capillary endothelial cells. BBB capillary walls allow passive transport of lipid soluble molecules and facilitated diffusion and prim ...
... Tight Junction between capillary endothelial cells BCSFB Tight Junctions between epithelial cells in Choroid Plexus All solutes must cross both cell membranes of the capillary endothelial cells. BBB capillary walls allow passive transport of lipid soluble molecules and facilitated diffusion and prim ...
Full-Text PDF
... In recent times, neuroscience has received much attention as important research field for understanding the connections between neuron cells and reaction mechanisms. These kinds of research have been focused on recording electrical signals from living brains or cells, called neural spikes, for study ...
... In recent times, neuroscience has received much attention as important research field for understanding the connections between neuron cells and reaction mechanisms. These kinds of research have been focused on recording electrical signals from living brains or cells, called neural spikes, for study ...
BOX 25.3 GIANT SYNAPTIC TERMINALS: ENDBULBS AND
... ventral cochlear nucleus (Fig. 25.18A), and (2) calyceal endings, which are found in the medial nucleus of the trapezoid body. Calyces are so large that it is possible to use patch electrodes to record and clamp the presynaptic terminal while simultaneously doing the same with their postsynaptic tar ...
... ventral cochlear nucleus (Fig. 25.18A), and (2) calyceal endings, which are found in the medial nucleus of the trapezoid body. Calyces are so large that it is possible to use patch electrodes to record and clamp the presynaptic terminal while simultaneously doing the same with their postsynaptic tar ...
answers - Easy Peasy All-in
... What is a synapse and how do nerve impulses pass across a synapse? A synapse is the gap between neurons. Nerve impulses change to a chemical signal when they near the synapse and it triggers an electrical signal when it enters the next neuron. What is a reflex action and how is this a good test of t ...
... What is a synapse and how do nerve impulses pass across a synapse? A synapse is the gap between neurons. Nerve impulses change to a chemical signal when they near the synapse and it triggers an electrical signal when it enters the next neuron. What is a reflex action and how is this a good test of t ...
File - CYPA Psychology
... 36. Most axons end in a knoblike swelling structure called the: A) terminal button. B) axon knob. C) swelling button. D) vesicle ...
... 36. Most axons end in a knoblike swelling structure called the: A) terminal button. B) axon knob. C) swelling button. D) vesicle ...
Blue= rods Green = Cones
... – Layers 1 & 2 – Process information related to form, movement, depth, small changes in brightness – Connected mostly with rods ...
... – Layers 1 & 2 – Process information related to form, movement, depth, small changes in brightness – Connected mostly with rods ...
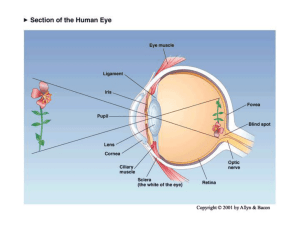
Control and Coordination
... increase in diameter of pupil, which allows more light in. When we come out of the dark room into broad day light the diameter of the pupil decreases allowing less light to enter into the eyes. Both these functions occur under the influence of the autonomic nervous system. ...
... increase in diameter of pupil, which allows more light in. When we come out of the dark room into broad day light the diameter of the pupil decreases allowing less light to enter into the eyes. Both these functions occur under the influence of the autonomic nervous system. ...
Part 1: True/False
... 4. __ All neurotransmitters are synthesized in the soma and carried to the axon terminal through axoplasmic transport. 5. __ The two main families of neurotransmitter receptors are ligand-gated and neural-gated. 6. __ Postsynaptic responses mediated by G-protein coupled receptors are faster than tho ...
... 4. __ All neurotransmitters are synthesized in the soma and carried to the axon terminal through axoplasmic transport. 5. __ The two main families of neurotransmitter receptors are ligand-gated and neural-gated. 6. __ Postsynaptic responses mediated by G-protein coupled receptors are faster than tho ...
Nervous System
... This is a progressive, degenerative disease that occurs in the brain and results loss of memory, thinking, and behavior. This disease usually occurs in mid to old age people. This disease is the cause of neurons breaking connection with each other and eventually passing. ...
... This is a progressive, degenerative disease that occurs in the brain and results loss of memory, thinking, and behavior. This disease usually occurs in mid to old age people. This disease is the cause of neurons breaking connection with each other and eventually passing. ...
BRAIN GLUCOSE-SENSING: AGE- AND ENERGY
... facilitated the success of your research? This approach has been fundamental. As a group comprising both commercial companies ...
... facilitated the success of your research? This approach has been fundamental. As a group comprising both commercial companies ...
Autonomic Nervous System
... - smooth muscle - cardiac muscle - some glands - composed entirely of visceral efferent neurons (motor neurons to internal organs) - has no sensory function MOTOR ONLY - neurons are organized into: - nerves - ganglia - plexuses Divisions of the ANS 1. Sympathetic 2. Parasympathetic - these two syste ...
... - smooth muscle - cardiac muscle - some glands - composed entirely of visceral efferent neurons (motor neurons to internal organs) - has no sensory function MOTOR ONLY - neurons are organized into: - nerves - ganglia - plexuses Divisions of the ANS 1. Sympathetic 2. Parasympathetic - these two syste ...
Nerve activates contraction
... • SPINAL CORD, as flexor reflex • BRAIN ( for proper evaluation) as response of pupils to light ...
... • SPINAL CORD, as flexor reflex • BRAIN ( for proper evaluation) as response of pupils to light ...
KKDP4: The role of neurotransmitters in the transmission of neural
... NOTE: The effects of a neurotransmitter are not entirely caused by the chemical. Its effects are also due to the receptor to which the neurotransmitter binds. The same neurotransmitter can be excitatory or inhibitory, depending on the properties of the receptor and on the receptor’s location in the ...
... NOTE: The effects of a neurotransmitter are not entirely caused by the chemical. Its effects are also due to the receptor to which the neurotransmitter binds. The same neurotransmitter can be excitatory or inhibitory, depending on the properties of the receptor and on the receptor’s location in the ...
Keshara Senanayake Page # 1 -an individual nerve cells is called
... -nervous system uses convergence, many neurons funnel their signals to fewer neurons >many sensory neurons many converge onto a small number of brain cells -these brain cells add up postsynaptic potentials that result from the synaptic activity of the sensory neurons (depending on their relative str ...
... -nervous system uses convergence, many neurons funnel their signals to fewer neurons >many sensory neurons many converge onto a small number of brain cells -these brain cells add up postsynaptic potentials that result from the synaptic activity of the sensory neurons (depending on their relative str ...
The Nervous System
... Axons- a threadlike extension that carries impulses away from a cell body. Most have a myelin sheath that insulates the nerve fiber that speeds the transmission of impulses. ...
... Axons- a threadlike extension that carries impulses away from a cell body. Most have a myelin sheath that insulates the nerve fiber that speeds the transmission of impulses. ...
Slide 1
... synaptic efficacy. The efficacy of a synapse can be potentiated through at least sixmechanisms. First, there could be an increase in the fraction (release probability) of available presynaptic vesicles that undergo exocytosis. For example, in mechanism 1, two out of four available vesicles are relea ...
... synaptic efficacy. The efficacy of a synapse can be potentiated through at least sixmechanisms. First, there could be an increase in the fraction (release probability) of available presynaptic vesicles that undergo exocytosis. For example, in mechanism 1, two out of four available vesicles are relea ...
Dendritic organization of sensory input to cortical neurons in vivo
... The results reveal basic insights into the dendritic organization of sensory inputs to neurons of the visual cortex in vivo. • Identified discrete dendritic hotspots as synaptic entry sites for specific sensory features • Afferent sensory inputs with the same orientation preference are widely disper ...
... The results reveal basic insights into the dendritic organization of sensory inputs to neurons of the visual cortex in vivo. • Identified discrete dendritic hotspots as synaptic entry sites for specific sensory features • Afferent sensory inputs with the same orientation preference are widely disper ...
Sensory and Motor Systems
... The nervous system basically goes sensory -> inter -> motor neurons You convert energy from the environment to energy in your nervous system This is called transduction Agnosia ...
... The nervous system basically goes sensory -> inter -> motor neurons You convert energy from the environment to energy in your nervous system This is called transduction Agnosia ...
packet - mybiologyclass
... Interneurons: nerve cell located entirely in the central nervous system that integrates sensory information and sends motor commands Motor Neuron: nerve cell that carries signals from the central nervous system to muscle or gland cells. Neuron: nerve cell; basic unit of nervous tissue Peripheral Ner ...
... Interneurons: nerve cell located entirely in the central nervous system that integrates sensory information and sends motor commands Motor Neuron: nerve cell that carries signals from the central nervous system to muscle or gland cells. Neuron: nerve cell; basic unit of nervous tissue Peripheral Ner ...