University of Jordan Faculty of Medicine L15 –Dr. Loai Physiology
... 1) Make sure you understand everything, exams questions will be based on understanding NOT memorizing alone 2) Anything between *** was not mentioned during the lecture (only for your knowledge) 3) make sure you go through the slides for the nervous system by Dr.loai -------------------------------- ...
... 1) Make sure you understand everything, exams questions will be based on understanding NOT memorizing alone 2) Anything between *** was not mentioned during the lecture (only for your knowledge) 3) make sure you go through the slides for the nervous system by Dr.loai -------------------------------- ...
Monday, June 20, 2005
... receptors appear not to be the dominant mechanisms for expression of plasticity. Expression of LTP or LTD under physiological conditions is not associated with formation or loss of dendritic spines, nor with detectable changes in spine morphology, up to at least 4h after induction of plasticity; thu ...
... receptors appear not to be the dominant mechanisms for expression of plasticity. Expression of LTP or LTD under physiological conditions is not associated with formation or loss of dendritic spines, nor with detectable changes in spine morphology, up to at least 4h after induction of plasticity; thu ...
GENETIC CONTROL OF EMBRYONIC DEVELOPMENT – Lecture 1
... evolved by changing the arrangement of cells with respect to each other. Differences between cells first arise as a result of two broad mechanisms: 1) cytoplasmic determinants, which are molecules asymmetrically localized in the cytoplasm of the egg (or of somatic cells, see below), which become une ...
... evolved by changing the arrangement of cells with respect to each other. Differences between cells first arise as a result of two broad mechanisms: 1) cytoplasmic determinants, which are molecules asymmetrically localized in the cytoplasm of the egg (or of somatic cells, see below), which become une ...
B6 – Brain and mind - The Bicester School
... that can increase an animal’s chance of survival. In some circumstances the brain can modify a reflex response via a neuron to the motor neuron of the reflex arc, for example keeping hold of a ...
... that can increase an animal’s chance of survival. In some circumstances the brain can modify a reflex response via a neuron to the motor neuron of the reflex arc, for example keeping hold of a ...
The nervous system can be divided into several connected systems
... space between the two cells (the synapse), under the influence of small concentrations of calcium ions. ...
... space between the two cells (the synapse), under the influence of small concentrations of calcium ions. ...
Overview of the Reticular Formation (RF)
... within these groups play a role in modulating our level of arousal, sleep, learning, memory, cognition, locomotion and pain, by altering cell properties (e.g. excitation). The cerebral cortex also affects our level of alertness via projections to these neurons, as can real or imaginary mental imager ...
... within these groups play a role in modulating our level of arousal, sleep, learning, memory, cognition, locomotion and pain, by altering cell properties (e.g. excitation). The cerebral cortex also affects our level of alertness via projections to these neurons, as can real or imaginary mental imager ...
WHY HAVE MULTIPLE CORTICAL AREAS?
... and a circle concentric with the fovea maps to a vertical line. The mi&fe section shows a non-topographic map of motion. The observer fixates a tree seen through the window of a moving vehicle; this point is stationary on the retina and is mapped at the origin of the motion map. The frame of the win ...
... and a circle concentric with the fovea maps to a vertical line. The mi&fe section shows a non-topographic map of motion. The observer fixates a tree seen through the window of a moving vehicle; this point is stationary on the retina and is mapped at the origin of the motion map. The frame of the win ...
The Nervous System
... Myelin Sheath Myelin Sheath - an arrangement of cells around the axon. It helps protect the axon and speed up impulses. ...
... Myelin Sheath Myelin Sheath - an arrangement of cells around the axon. It helps protect the axon and speed up impulses. ...
General anatomy [edit]
... The most medial part of the medulla is the posterior median fissure. Moving laterally on each side is the fasciculus gracilis, and lateral to that is the fasciculus cuneatus. Superior to each of these, and directly inferior to the obex, are the gracile and cuneate tubercles, respectively. Underlying ...
... The most medial part of the medulla is the posterior median fissure. Moving laterally on each side is the fasciculus gracilis, and lateral to that is the fasciculus cuneatus. Superior to each of these, and directly inferior to the obex, are the gracile and cuneate tubercles, respectively. Underlying ...
The History and Scope of Psychology Module 1
... Studying Hemispheric Differences in the Intact Brain ...
... Studying Hemispheric Differences in the Intact Brain ...
Quiz
... 13. In one cycle of neural communication, which is the correct order of events? a. Neurotransmitter release -‐> action potential -‐> threshold of excitation reached -‐> inhibitory or excitatory post-‐synaptic ...
... 13. In one cycle of neural communication, which is the correct order of events? a. Neurotransmitter release -‐> action potential -‐> threshold of excitation reached -‐> inhibitory or excitatory post-‐synaptic ...
File nervous system, ppt
... Helps control muscle contractions to produce coordinated movements so that we can maintain balance, move smoothly, and sustain normal postures Recent evidence shows the cerebellum may also have wider coordinating effects, assisting the cerebrum and other regions of the brain ...
... Helps control muscle contractions to produce coordinated movements so that we can maintain balance, move smoothly, and sustain normal postures Recent evidence shows the cerebellum may also have wider coordinating effects, assisting the cerebrum and other regions of the brain ...
2_Development of the Vertebrate Body Plan
... centre that produces BMPs, which provide dorsal paaerning informaQon. Neural crest cells derive from the dorsal neural tube and migrate out to form the PNS, as well as melanocytes and carQlage in the ...
... centre that produces BMPs, which provide dorsal paaerning informaQon. Neural crest cells derive from the dorsal neural tube and migrate out to form the PNS, as well as melanocytes and carQlage in the ...
Slide ()
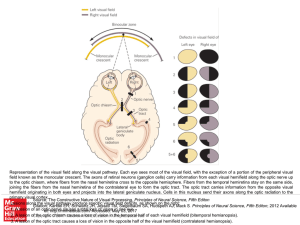
... Representation of the visual field along the visual pathway. Each eye sees most of the visual field, with the exception of a portion of the peripheral visual field known as the monocular crescent. The axons of retinal neurons (ganglion cells) carry information from each visual hemifield along the op ...
... Representation of the visual field along the visual pathway. Each eye sees most of the visual field, with the exception of a portion of the peripheral visual field known as the monocular crescent. The axons of retinal neurons (ganglion cells) carry information from each visual hemifield along the op ...
SPINA BIFIDA
... gestation. This disorders arise from abnormalities occuring during three major concurrent migrations of cell groups during embryogenesis which include those of the neural tube, the notochord, and the mesenchymal tissue. ...
... gestation. This disorders arise from abnormalities occuring during three major concurrent migrations of cell groups during embryogenesis which include those of the neural tube, the notochord, and the mesenchymal tissue. ...
Slide ()
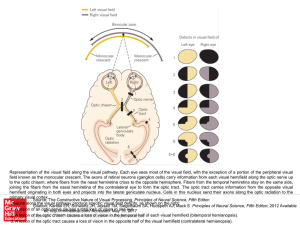
... Representation of the visual field along the visual pathway. Each eye sees most of the visual field, with the exception of a portion of the peripheral visual field known as the monocular crescent. The axons of retinal neurons (ganglion cells) carry information from each visual hemifield along the op ...
... Representation of the visual field along the visual pathway. Each eye sees most of the visual field, with the exception of a portion of the peripheral visual field known as the monocular crescent. The axons of retinal neurons (ganglion cells) carry information from each visual hemifield along the op ...
Autonomic Nervous System
... Reflexes are rapid, automatic responses to stimuli. They serve to protect the body and maintain homeostasis • ____________ reflexes - involve contraction of skeletal muscles • _______________ reflexes - regulate smooth muscle, cardiac ...
... Reflexes are rapid, automatic responses to stimuli. They serve to protect the body and maintain homeostasis • ____________ reflexes - involve contraction of skeletal muscles • _______________ reflexes - regulate smooth muscle, cardiac ...
Neurological Systemppt
... nerve impulse along the axon • Myelin is a fatty substance that protects the axon • Schwann cells white fatty substance that wraps itself around some axons. • Nodes of Ranvier indentions between Schwann cells • Neuroglia-Supporting cells that hold the neuron together. “Glia“is Greek for glue. ...
... nerve impulse along the axon • Myelin is a fatty substance that protects the axon • Schwann cells white fatty substance that wraps itself around some axons. • Nodes of Ranvier indentions between Schwann cells • Neuroglia-Supporting cells that hold the neuron together. “Glia“is Greek for glue. ...
Biology 105
... the fertilization of the egg by more than one sperm. Results in extra chromosomes and is usually lethal. ...
... the fertilization of the egg by more than one sperm. Results in extra chromosomes and is usually lethal. ...
3rd week of development
... the notochordal plate. This plate lies between the endoderm & ectoderm. This plate will form solid cord called the notochord. - The notochord is a solid mid line axis, so it forms fetal skeleton. Formation of the 3 germ layers occurred in a cephalocaudal direction, this means that the 3 germ layer a ...
... the notochordal plate. This plate lies between the endoderm & ectoderm. This plate will form solid cord called the notochord. - The notochord is a solid mid line axis, so it forms fetal skeleton. Formation of the 3 germ layers occurred in a cephalocaudal direction, this means that the 3 germ layer a ...
– Necrosis Brain, Neuron 1
... marked contrast between adjacent normal and necrotic cells is helpful in differentiation of autolysis from genuine lesions of nervous tissue. ...
... marked contrast between adjacent normal and necrotic cells is helpful in differentiation of autolysis from genuine lesions of nervous tissue. ...
Effects of cutting a mixed nerve
... • Regeneration DOES NOT take place in optic nerve and in the CNS due to the following reasons: 1. The endoneural tubes are absent in the CNS as there are no schwann cells are present; so the regenerating axons cannot be guided. 2. The oligodendrocytes cannot aid in regeneration as the schwann cells. ...
... • Regeneration DOES NOT take place in optic nerve and in the CNS due to the following reasons: 1. The endoneural tubes are absent in the CNS as there are no schwann cells are present; so the regenerating axons cannot be guided. 2. The oligodendrocytes cannot aid in regeneration as the schwann cells. ...
60 Vertebrate Development
... from symmetrical blastulas, gastrulation begins as the surface of the blastula invaginates into the blastocoel. About half of the blastula’s cells move into the interior of the blastula, forming a structure that looks something like an indented tennis ball. Eventually, the inward-moving wall of cell ...
... from symmetrical blastulas, gastrulation begins as the surface of the blastula invaginates into the blastocoel. About half of the blastula’s cells move into the interior of the blastula, forming a structure that looks something like an indented tennis ball. Eventually, the inward-moving wall of cell ...
Name - IB Bio Y2
... E.6.6 – Brain death is “that time when a physician(s) has determined that the brain and brain stem have irreversibly lost all neurological function”. The pupil reflex, along with other tests, is useful because it is a cranial reflex rather than a spinal reflex. Some spinal reflexes, such as the knee ...
... E.6.6 – Brain death is “that time when a physician(s) has determined that the brain and brain stem have irreversibly lost all neurological function”. The pupil reflex, along with other tests, is useful because it is a cranial reflex rather than a spinal reflex. Some spinal reflexes, such as the knee ...







![General anatomy [edit]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/000712414_1-9f164978a5775158fafd921c8e3d4cef-300x300.png)