Skeletal, Muscular and Nervous Systems
... A point where to more bones come together. ►Cartilage: A tough supportive tissue that is softer and more flexible than bone. ►Ossification: cartilage hardens and turns into bone. Remember, babies have approximately 100 more bones than adults. Cells continue to repair ...
... A point where to more bones come together. ►Cartilage: A tough supportive tissue that is softer and more flexible than bone. ►Ossification: cartilage hardens and turns into bone. Remember, babies have approximately 100 more bones than adults. Cells continue to repair ...
File
... membrane releasing the neurotransmitters into the synaptic cleft • Neurons can contain and release more than one kind of neurotransmitter • The neurotransmitter molecules then diffuse across the synaptic cleft where they can bind with receptor sites on the postsynaptic ending to influence the electr ...
... membrane releasing the neurotransmitters into the synaptic cleft • Neurons can contain and release more than one kind of neurotransmitter • The neurotransmitter molecules then diffuse across the synaptic cleft where they can bind with receptor sites on the postsynaptic ending to influence the electr ...
cranial nerves & pns
... controls the activity by varying the ratio of the signals. Depending on which motor neurons are selected by the CNS, the net effect of the arriving signals will either stimulate or inhibit the organ. ...
... controls the activity by varying the ratio of the signals. Depending on which motor neurons are selected by the CNS, the net effect of the arriving signals will either stimulate or inhibit the organ. ...
Cerebellum - UCSD Cognitive Science
... LTP (non-NMDA mediated since no NMDA receptors in cerebellum) ...
... LTP (non-NMDA mediated since no NMDA receptors in cerebellum) ...
a real-time spike domain sensory information processing system
... both worlds” solution, as it combines the speed of dedicated hardware with the programmability of software. The goal of our current research is to implement a biologically-plausible hierarchical model of visual information processing [16] entirely contained within the IFAT. The data described here i ...
... both worlds” solution, as it combines the speed of dedicated hardware with the programmability of software. The goal of our current research is to implement a biologically-plausible hierarchical model of visual information processing [16] entirely contained within the IFAT. The data described here i ...
How your Brain Works - Muncy School District
... As you practice something, your related dendrites develop a thick fatty coating. Thicker dendrites pass signals over the synapses more quickly. The coating also reduces interference, enabling you to come up with answers more quickly. Your volume of synapses is constantly changing, too, and some are ...
... As you practice something, your related dendrites develop a thick fatty coating. Thicker dendrites pass signals over the synapses more quickly. The coating also reduces interference, enabling you to come up with answers more quickly. Your volume of synapses is constantly changing, too, and some are ...
Research Article Suspension of Mitotic Activity in Dentate Gyrus of
... used to generate a high degree of cell cycle synchrony in some mammalian cultures. Other hypothermic regimes can also be used to enrich cultures for G2 cells and to significantly slow otherwise rapid cellular processes, including mitosis [4]. In this respect hibernating mammals provide a rich resour ...
... used to generate a high degree of cell cycle synchrony in some mammalian cultures. Other hypothermic regimes can also be used to enrich cultures for G2 cells and to significantly slow otherwise rapid cellular processes, including mitosis [4]. In this respect hibernating mammals provide a rich resour ...
FIGURE LEGNEDS FIGURE 24.1 A dorsal root ganglion cell is a
... terminate the spinal cord itself. Second-order axons cross the midline and ascend through the spinal cord and brainstemto terminate in VPL and other nuclei of the thalamus. Collaterals of these axons terminate in the reticular formation of the pons and medulla. FIGURE 24.9 The first somatosensory co ...
... terminate the spinal cord itself. Second-order axons cross the midline and ascend through the spinal cord and brainstemto terminate in VPL and other nuclei of the thalamus. Collaterals of these axons terminate in the reticular formation of the pons and medulla. FIGURE 24.9 The first somatosensory co ...
Heidi
... • Portion of nervous system outside the brain and spinal cord • Two types of cells in the Peripheral Nervous System: • Cells of sensory nervous system: send information to the central nervous system from internal organs or from external stimuli • Cells of motor nervous system: carry information from ...
... • Portion of nervous system outside the brain and spinal cord • Two types of cells in the Peripheral Nervous System: • Cells of sensory nervous system: send information to the central nervous system from internal organs or from external stimuli • Cells of motor nervous system: carry information from ...
Spinal cord 1
... prominent parts, the substantia gelatinosa and the body of the posterior horn Both are present at all spinal levels. Between the substantia gelatinosa and the surface of the cord is a relatively pale-staining area of white matter called Lissauer's tract.* ...
... prominent parts, the substantia gelatinosa and the body of the posterior horn Both are present at all spinal levels. Between the substantia gelatinosa and the surface of the cord is a relatively pale-staining area of white matter called Lissauer's tract.* ...
2320Lecture20
... – changes accompanied by full-field transients are hard to detect • e.g. change blindness • orienting mechanism is blinded by the transient ...
... – changes accompanied by full-field transients are hard to detect • e.g. change blindness • orienting mechanism is blinded by the transient ...
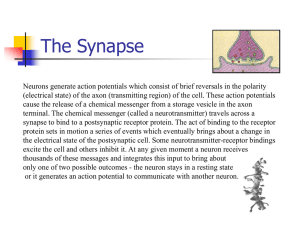
The Synapse
... (electrical state) of the axon (transmitting region) of the cell. These action potentials cause the release of a chemical messenger from a storage vesicle in the axon terminal. The chemical messenger (called a neurotransmitter) travels across a synapse to bind to a postsynaptic receptor protein. The ...
... (electrical state) of the axon (transmitting region) of the cell. These action potentials cause the release of a chemical messenger from a storage vesicle in the axon terminal. The chemical messenger (called a neurotransmitter) travels across a synapse to bind to a postsynaptic receptor protein. The ...
Developmental Biology
... • Cells on the outside are called trophoblast and become extraembryonic membranes and embryonic portion of the placenta • Cells on the inside are called Inner Cell Mass (ICM) and produce the embryo proper This is the first differentiation event in mammalian cells ...
... • Cells on the outside are called trophoblast and become extraembryonic membranes and embryonic portion of the placenta • Cells on the inside are called Inner Cell Mass (ICM) and produce the embryo proper This is the first differentiation event in mammalian cells ...
AP Biology Animal Form and Function
... example, that the cells of the notocord influence the development of the neural plate (which eventually becomes the nervous system). When the notocord was transplanted into a different part of an embryo, the neural plate grew in the new location. ...
... example, that the cells of the notocord influence the development of the neural plate (which eventually becomes the nervous system). When the notocord was transplanted into a different part of an embryo, the neural plate grew in the new location. ...
The Nervous System How your body responds to a stimulus
... touches the back of your neck with a wet, frosty ice cube. Before you even have a chance to think “who did that?” your body springs into action. • The ice cube triggers an automatic response called a withdrawal reflex that happens without a conscious decision on your part. ...
... touches the back of your neck with a wet, frosty ice cube. Before you even have a chance to think “who did that?” your body springs into action. • The ice cube triggers an automatic response called a withdrawal reflex that happens without a conscious decision on your part. ...
Skeletal System
... – The thalamus projects fibers (sorted out by sensation type) to the primary somatosensory cortex and to sensory association areas – First to those restricted to the same modality and then to those considering more than one – This allows for parallel processing of the various inputs, and results in ...
... – The thalamus projects fibers (sorted out by sensation type) to the primary somatosensory cortex and to sensory association areas – First to those restricted to the same modality and then to those considering more than one – This allows for parallel processing of the various inputs, and results in ...
The Autonomic Nervous System
... – The thalamus projects fibers (sorted out by sensation type) to the primary somatosensory cortex and to sensory association areas – First to those restricted to the same modality and then to those considering more than one – This allows for parallel processing of the various inputs, and results in ...
... – The thalamus projects fibers (sorted out by sensation type) to the primary somatosensory cortex and to sensory association areas – First to those restricted to the same modality and then to those considering more than one – This allows for parallel processing of the various inputs, and results in ...
Gastrulation: Formation of the Primary Germ Layers
... It is very likely that the anterior-posterior axis is established initially by implantation via mechanisms that remain to be elucidated. The establishment of the A-P Axis would in turn define the orientation of the primitive streak. In the mouse, the node (Hensen's node) that appears at gastrulation ...
... It is very likely that the anterior-posterior axis is established initially by implantation via mechanisms that remain to be elucidated. The establishment of the A-P Axis would in turn define the orientation of the primitive streak. In the mouse, the node (Hensen's node) that appears at gastrulation ...
Monday, June 20, 2005
... receptors appear not to be the dominant mechanisms for expression of plasticity. Expression of LTP or LTD under physiological conditions is not associated with formation or loss of dendritic spines, nor with detectable changes in spine morphology, up to at least 4h after induction of plasticity; thu ...
... receptors appear not to be the dominant mechanisms for expression of plasticity. Expression of LTP or LTD under physiological conditions is not associated with formation or loss of dendritic spines, nor with detectable changes in spine morphology, up to at least 4h after induction of plasticity; thu ...
University of Jordan Faculty of Medicine L15 –Dr. Loai Physiology
... 1) Make sure you understand everything, exams questions will be based on understanding NOT memorizing alone 2) Anything between *** was not mentioned during the lecture (only for your knowledge) 3) make sure you go through the slides for the nervous system by Dr.loai -------------------------------- ...
... 1) Make sure you understand everything, exams questions will be based on understanding NOT memorizing alone 2) Anything between *** was not mentioned during the lecture (only for your knowledge) 3) make sure you go through the slides for the nervous system by Dr.loai -------------------------------- ...