APOPTOSIS
... From the beginning of the 20th Century until the 1990s, it was stated that neurons DID NOT proliferate. The fact that they COULD NOT proliferate did not exclude the possibility of proliferation under “specific conditions.” In fact, the CNS has a considerable regenerative potential depending on ...
... From the beginning of the 20th Century until the 1990s, it was stated that neurons DID NOT proliferate. The fact that they COULD NOT proliferate did not exclude the possibility of proliferation under “specific conditions.” In fact, the CNS has a considerable regenerative potential depending on ...
Nerve Muscle Physiology
... – Maintain chemical environment of ECF around CNS neurons – Provides Ca+ and potassium and regulate neurotransmitter level in synapses – Regulate recycling and neurotransmitter during synaptic ...
... – Maintain chemical environment of ECF around CNS neurons – Provides Ca+ and potassium and regulate neurotransmitter level in synapses – Regulate recycling and neurotransmitter during synaptic ...
Tango and mirror neurons
... • Such activation is notably only present for actions belonging to the personal repertoire of the observer • Just as for monkey, this system seems to be sensitive to the goal of movement, thus being probably involved in recognizing intentions •In spite of some debate about the reality of mirror neur ...
... • Such activation is notably only present for actions belonging to the personal repertoire of the observer • Just as for monkey, this system seems to be sensitive to the goal of movement, thus being probably involved in recognizing intentions •In spite of some debate about the reality of mirror neur ...
Phylum Chordata
... Earlier theories were based on a relationship with the protostome branch; this is considered unlikely. The important common features are: radial cleavage, anus derived from the blastopore, mouth derived from a secondary opening, and a coelom formed by fusion of enterocoelous pouches. ...
... Earlier theories were based on a relationship with the protostome branch; this is considered unlikely. The important common features are: radial cleavage, anus derived from the blastopore, mouth derived from a secondary opening, and a coelom formed by fusion of enterocoelous pouches. ...
Dorsal Cochlear Nucleus - Neurobiology of Hearing
... Fusiform and giant cell responses to sound are shaped by multiple excitatory and inhibitory inputs. Combined, these two types of responses allows detection of sounds with spectral peaks and notches. ...
... Fusiform and giant cell responses to sound are shaped by multiple excitatory and inhibitory inputs. Combined, these two types of responses allows detection of sounds with spectral peaks and notches. ...
Nerve Muscle Physiology
... – Maintain chemical environment of ECF around CNS neurons – Provides Ca+ and potassium and regulate neurotransmitter level in synapses – Regulate recycling and neurotransmitter during synaptic ...
... – Maintain chemical environment of ECF around CNS neurons – Provides Ca+ and potassium and regulate neurotransmitter level in synapses – Regulate recycling and neurotransmitter during synaptic ...
Development - MSU Denver
... becomes fully functional by 12 weeks • Provides nourishment and oxygen for fetus, removes fetal waste and makes estrogen and progesterone ...
... becomes fully functional by 12 weeks • Provides nourishment and oxygen for fetus, removes fetal waste and makes estrogen and progesterone ...
Certain Histological and Anatomical Features of the Central Nervous
... devoid of synaptic endings (Bullock and Horridge, 1965). The neuropile, which can be distinguished by its finer and more tangled texture, thus becomes the most important region, because this is the only known place of neuronal contacts. Hence it has acquired functional significance as the primary pl ...
... devoid of synaptic endings (Bullock and Horridge, 1965). The neuropile, which can be distinguished by its finer and more tangled texture, thus becomes the most important region, because this is the only known place of neuronal contacts. Hence it has acquired functional significance as the primary pl ...
Resting potential
... • Early Greeks were not impressed with the brain. They suggested that the brain’s main function was to cool the blood. They were much more impressed by the heart. They proposed that the heart was the source of feelings and thoughts. Hippocrates, however, observed the effect of head injuries on peopl ...
... • Early Greeks were not impressed with the brain. They suggested that the brain’s main function was to cool the blood. They were much more impressed by the heart. They proposed that the heart was the source of feelings and thoughts. Hippocrates, however, observed the effect of head injuries on peopl ...
cns structure - Department of Physiology
... center of receptive field, due to increased receptor density. However, this is not a precise mechanism because an increase in the number of action potentials could also mean a more intense stimulus was applied. Two stimulus points ...
... center of receptive field, due to increased receptor density. However, this is not a precise mechanism because an increase in the number of action potentials could also mean a more intense stimulus was applied. Two stimulus points ...
Mouse-chick neural chimeras
... cells. The capacities of mouse neural crest cells to differentiate into medullary cells in adrenal gland were tested, but paradoxically their differentiation into enteric neurons of the host guts could not be tested directly. This may relate to the difficulty of delivering transplanted cells into a ...
... cells. The capacities of mouse neural crest cells to differentiate into medullary cells in adrenal gland were tested, but paradoxically their differentiation into enteric neurons of the host guts could not be tested directly. This may relate to the difficulty of delivering transplanted cells into a ...
Fifty years of CPGs: two neuroethological papers that shaped BEHAVIORAL NEUROSCIENCE
... M. Hughes, visiting from Cambridge, found that the deafferented crayfish abdominal nerve cord sometimes continued to produce coordinated bursts of spikes in motor axons that innervated different swimmerets (Hughes and Wiersma, 1960), a motor pattern that drives coordinated swimmeret beating during n ...
... M. Hughes, visiting from Cambridge, found that the deafferented crayfish abdominal nerve cord sometimes continued to produce coordinated bursts of spikes in motor axons that innervated different swimmerets (Hughes and Wiersma, 1960), a motor pattern that drives coordinated swimmeret beating during n ...
Deep Learning - UCF Computer Science
... Multiple Layers of Feature Representation • The neurons at each layer provides distinct levels of abstract ...
... Multiple Layers of Feature Representation • The neurons at each layer provides distinct levels of abstract ...
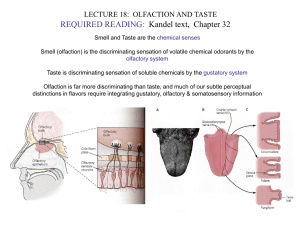
LECTURE18.Olfaction&Taste
... Olfactory sensory neurons are fairly short-lived (1-2 months), and regenerate from basal stem cells Each sensory neuron responds to a single odorant or a specific repertoire of chemically related odorants An odor is ENCODED by the specific combination of neurons which respond to it Sensory neurons r ...
... Olfactory sensory neurons are fairly short-lived (1-2 months), and regenerate from basal stem cells Each sensory neuron responds to a single odorant or a specific repertoire of chemically related odorants An odor is ENCODED by the specific combination of neurons which respond to it Sensory neurons r ...
PowerPoint Presentation - HUMAN EMBRYOLOGY
... Continued divisions make the hollow blastula These few cells are pluripotent (have the potential to become ANY of the 220 types of cells in the human body). These are embryonic stem cells ...
... Continued divisions make the hollow blastula These few cells are pluripotent (have the potential to become ANY of the 220 types of cells in the human body). These are embryonic stem cells ...
The auditory pathway: Levels of integration of information and
... ganglion of Corti (SGC), the auditory nerve (AN), the cochlear nuclei (CN), the superior olivary complex (SOC), the lateral lemniscus (LL), the inferior colliculus (IC), the medial geniculate body and the AC, including the auditory efferent pathway, are given. We describe how electrical impulses tra ...
... ganglion of Corti (SGC), the auditory nerve (AN), the cochlear nuclei (CN), the superior olivary complex (SOC), the lateral lemniscus (LL), the inferior colliculus (IC), the medial geniculate body and the AC, including the auditory efferent pathway, are given. We describe how electrical impulses tra ...
Central Nervous System
... The architecture of the cortex is determined by genetic and developmental processes but it can be modified due to “use-dependent competition” for cortical space Formation of new neural pathways and connections between existing neurons Some cortical regions can be remodeled throughout life while othe ...
... The architecture of the cortex is determined by genetic and developmental processes but it can be modified due to “use-dependent competition” for cortical space Formation of new neural pathways and connections between existing neurons Some cortical regions can be remodeled throughout life while othe ...
Intrinsic firing patterns of diverse neocortical neurons
... intrinsically bursting (IB). For each type, classification is based on three general variables - the characteristics of individual action potentialafterpotential complexes, the response to a justthreshold intracellular current pulse, and the repetitive response to prolonged, intracellularly applied ...
... intrinsically bursting (IB). For each type, classification is based on three general variables - the characteristics of individual action potentialafterpotential complexes, the response to a justthreshold intracellular current pulse, and the repetitive response to prolonged, intracellularly applied ...
CNS neurotransmitters
... propeptides). However, several forms may be “active,” and several slightly different structures may confer subtle changes in selectivity. Many neuroactive peptides appear to coexist and be released along with one or more of the “traditional” neurotransmitters, such as ACh, dopamine, or serotonin. ...
... propeptides). However, several forms may be “active,” and several slightly different structures may confer subtle changes in selectivity. Many neuroactive peptides appear to coexist and be released along with one or more of the “traditional” neurotransmitters, such as ACh, dopamine, or serotonin. ...
The vestibular stimulus is provided by Earth`s
... d. Cochlear duct - contains Organ of Corti 1. Tectorial membrane (top) 2. Basilar membrane (bottom) 3. Hair cells ...
... d. Cochlear duct - contains Organ of Corti 1. Tectorial membrane (top) 2. Basilar membrane (bottom) 3. Hair cells ...
File
... Mirror neurons and the environment. • Scientists have long wondered why we get that feeling, and more than two decades ago, a team of Italian researchers thought they stumbled on an answer. • While observing monkeys’ brains, Gallese et. Al (1996) noticed that certain cells activated both when a mon ...
... Mirror neurons and the environment. • Scientists have long wondered why we get that feeling, and more than two decades ago, a team of Italian researchers thought they stumbled on an answer. • While observing monkeys’ brains, Gallese et. Al (1996) noticed that certain cells activated both when a mon ...
Linear associator
... of models of human memory. In this tutorial, you will explore the properties of one of the more basic memory models, the linear associator. In the linear associator, two layers of neurons (layers “f “and “g”) each receive external sensory input. In addition, the neurons of one layer “feed forward” o ...
... of models of human memory. In this tutorial, you will explore the properties of one of the more basic memory models, the linear associator. In the linear associator, two layers of neurons (layers “f “and “g”) each receive external sensory input. In addition, the neurons of one layer “feed forward” o ...
Bio_246_files/Motor Control
... • Descending tracts deliver efferent impulses from the brain to the spinal cord, and are divided into two groups – Direct pathways (pyramidal): tracts which originate in the cerebral cortex. • Initiate movement from premotor and prefrontal areas that are receiving sensory information ( Multimodal) f ...
... • Descending tracts deliver efferent impulses from the brain to the spinal cord, and are divided into two groups – Direct pathways (pyramidal): tracts which originate in the cerebral cortex. • Initiate movement from premotor and prefrontal areas that are receiving sensory information ( Multimodal) f ...