Chapter 12 Lecture Outline
... – Protect neurons and help them function – Bind neurons together and form framework for nervous tissue – In fetus, guide migrating neurons to their destination – If mature neuron is not in synaptic contact with another neuron, it is covered by glial cells • Prevents neurons from touching each other ...
... – Protect neurons and help them function – Bind neurons together and form framework for nervous tissue – In fetus, guide migrating neurons to their destination – If mature neuron is not in synaptic contact with another neuron, it is covered by glial cells • Prevents neurons from touching each other ...
Cognition and Perception as Interactive Activation
... – they believe that nearly all great discoveries by logicians and mathematicians arise through imagery – after they make a discovery, they then attempt to verify it formally • they attempt to develop a proof for their insight • whereas the insight may have happened quickly, the proof may take years ...
... – they believe that nearly all great discoveries by logicians and mathematicians arise through imagery – after they make a discovery, they then attempt to verify it formally • they attempt to develop a proof for their insight • whereas the insight may have happened quickly, the proof may take years ...
P312Ch02_Nervous System, Neurons Lecture
... The Central Nervous System (CNS) – The brain and the spinal cord The Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) – Cells outside the brain and spinal cord ...
... The Central Nervous System (CNS) – The brain and the spinal cord The Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) – Cells outside the brain and spinal cord ...
Motor Systems II Loops and Tracts
... indirect pathway. Thus, the balance between the direct and indirect pathways becomes tipped in favor of the direct pathway. Without their normal inhibitory inputs, thalamic neurons can fire randomly and inappropriately, causing the motor cortex to execute motor programs without proper control. ...
... indirect pathway. Thus, the balance between the direct and indirect pathways becomes tipped in favor of the direct pathway. Without their normal inhibitory inputs, thalamic neurons can fire randomly and inappropriately, causing the motor cortex to execute motor programs without proper control. ...
The Child’s Growth
... Photoreceptors – one of the visual-pigment-filled light-sensitive cells at the back of the retina transduce light energy into neural impulses 2 Types of Photoreceptors: i. Cones – respond to greater light intensities, give rise to chromatic (color) sensations. ii. Rods – respond to lower light i ...
... Photoreceptors – one of the visual-pigment-filled light-sensitive cells at the back of the retina transduce light energy into neural impulses 2 Types of Photoreceptors: i. Cones – respond to greater light intensities, give rise to chromatic (color) sensations. ii. Rods – respond to lower light i ...
The Visual System
... that exploits the brain’s energy metabolism A monkey which had had one eye masked was injected with 3H-labeled 2-deoxy D glucose. This glucose analogue is taken up by cells as if it were glucose, but can’t be metabolized. After a few minutes the animal was sacrificed and the visual cortex sliced for ...
... that exploits the brain’s energy metabolism A monkey which had had one eye masked was injected with 3H-labeled 2-deoxy D glucose. This glucose analogue is taken up by cells as if it were glucose, but can’t be metabolized. After a few minutes the animal was sacrificed and the visual cortex sliced for ...
Schmidtea mediterranea Taxonomy -
... (triploblast tissue organization). Planaria possess a centralized nervous system which consists of a primitive "brain" and sensory organs located at the organism's anterior (cephalization), as well as of two ventral nerve cords running along the body from "head" to "tail". Decapitated planarians can ...
... (triploblast tissue organization). Planaria possess a centralized nervous system which consists of a primitive "brain" and sensory organs located at the organism's anterior (cephalization), as well as of two ventral nerve cords running along the body from "head" to "tail". Decapitated planarians can ...
Phylum Cnidaria
... • Sperm are released and fertilize the ovum of another hydra. This produces a zygote which divides and eventually breaks off and continues to develop into a new hydra. ...
... • Sperm are released and fertilize the ovum of another hydra. This produces a zygote which divides and eventually breaks off and continues to develop into a new hydra. ...
Therapeutic Possibilities of Stem Cell Research
... to appropriate neuronal sites in the spinal cord ...
... to appropriate neuronal sites in the spinal cord ...
THALAMUS
... systems to prepare thalamocortical systems for sensory transmission, processing (McCormick). 4.The three brain rhythms (spindle, delta and slow oscillation) are obliterated by brainstem cholinergic and n. basalis cholinergic and GABAergic actions exerted on thalamocortical,, thalamic reticular and n ...
... systems to prepare thalamocortical systems for sensory transmission, processing (McCormick). 4.The three brain rhythms (spindle, delta and slow oscillation) are obliterated by brainstem cholinergic and n. basalis cholinergic and GABAergic actions exerted on thalamocortical,, thalamic reticular and n ...
Chapter 9 Lesson Two-Nervous System
... brain The command center, or coordinator, or the nervous system ...
... brain The command center, or coordinator, or the nervous system ...
Chapter 9 Part II Review
... Which malfunction is described by the inflammation of the membranes surrounding the brain and spinal cord? a)cerebral palsy b) Polio ...
... Which malfunction is described by the inflammation of the membranes surrounding the brain and spinal cord? a)cerebral palsy b) Polio ...
NEURAL REGULATION OF RESPIRATION LEARNING
... • Contraction of the diaphragm & • intercostal muscles ...
... • Contraction of the diaphragm & • intercostal muscles ...
04 Physiology of large hemispheres, cerebellum
... function because the number of sensory neurons declines, the function of remaining neurons decreases, and CNS processing decreases. In the skin, free nerve endings and hair follicle receptors remain largely unchanged with age. Meissner’s corpuscles and pacinian corpuscles, however, decrease in numbe ...
... function because the number of sensory neurons declines, the function of remaining neurons decreases, and CNS processing decreases. In the skin, free nerve endings and hair follicle receptors remain largely unchanged with age. Meissner’s corpuscles and pacinian corpuscles, however, decrease in numbe ...
Malformations - Hospital Universitari de Bellvitge
... •migration of last neuroblasts from the external to the internal granular layer: first post-natal year Cerebral cortex •migration of neuroblast to cerebral cortical plate starts by week 7 and finishes at about month 6 ...
... •migration of last neuroblasts from the external to the internal granular layer: first post-natal year Cerebral cortex •migration of neuroblast to cerebral cortical plate starts by week 7 and finishes at about month 6 ...
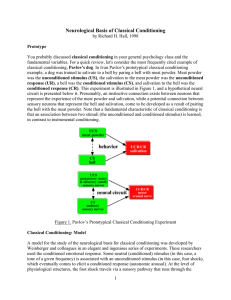
Neurological Basis of Classical Conditioning
... In order to test the viability of the neurological model presented above, Weinberger and colleagues began by establishing the tonotopic frequency of a set of neurons within the auditory system, in particular the auditory cortex. Many cells in the auditory system are "tuned" to a given frequency, tha ...
... In order to test the viability of the neurological model presented above, Weinberger and colleagues began by establishing the tonotopic frequency of a set of neurons within the auditory system, in particular the auditory cortex. Many cells in the auditory system are "tuned" to a given frequency, tha ...
Implications in absence epileptic seizures
... Paroxysms by the Nigrothalamic Pathway. Journal of Neuroscience, 27(4), 929-941. Pellegrini, A., Musgrave, J., & Gloor, P. (1979) Role of afferent input of subcortical origin in the genesis of bilaterally synchronous epileptic discharges of feline generalized epilepsy. Exp. Neurol. 64, 155- 173. Pol ...
... Paroxysms by the Nigrothalamic Pathway. Journal of Neuroscience, 27(4), 929-941. Pellegrini, A., Musgrave, J., & Gloor, P. (1979) Role of afferent input of subcortical origin in the genesis of bilaterally synchronous epileptic discharges of feline generalized epilepsy. Exp. Neurol. 64, 155- 173. Pol ...
1 - Lone Star College
... Sense of Smell, cont 2. How the brain receives odor information a. Nerve fibers lead to the olfactory bulb b. Combinations of activated receptor proteins account for different odors c. An odor’s signature is determined by which neurons are stimulated in the olfactory bulb d. Neurons send signals th ...
... Sense of Smell, cont 2. How the brain receives odor information a. Nerve fibers lead to the olfactory bulb b. Combinations of activated receptor proteins account for different odors c. An odor’s signature is determined by which neurons are stimulated in the olfactory bulb d. Neurons send signals th ...
Document
... • Most nerves are mixtures of afferent and efferent fibers and somatic and autonomic (visceral) fibers • Pure sensory (afferent) or motor (efferent) nerves are rare • Types of fibers in mixed nerves: ...
... • Most nerves are mixtures of afferent and efferent fibers and somatic and autonomic (visceral) fibers • Pure sensory (afferent) or motor (efferent) nerves are rare • Types of fibers in mixed nerves: ...
Synapses and Synaptic Transmission
... INTRODUCTION TO SYNAPSE: The CNS contains more than 100 billion neurons. Incoming signals enter the neuron through synapses located mostly on the neuronal dendrites, but also on the cell body. For different types of neurons, there may be only a few hundred or as many as 200,000 such synaptic connec ...
... INTRODUCTION TO SYNAPSE: The CNS contains more than 100 billion neurons. Incoming signals enter the neuron through synapses located mostly on the neuronal dendrites, but also on the cell body. For different types of neurons, there may be only a few hundred or as many as 200,000 such synaptic connec ...