Implantation of Embr..
... The allantois functions as the urinary receptacle for the embryo and, also, collects some solid wastes. The chorion, .the outer membrane, completely surrounds the embryo, arnion and allantoic cavity, is rich in blood vessels and lies in opposition to the uterine mucosa, through which, by diffusion a ...
... The allantois functions as the urinary receptacle for the embryo and, also, collects some solid wastes. The chorion, .the outer membrane, completely surrounds the embryo, arnion and allantoic cavity, is rich in blood vessels and lies in opposition to the uterine mucosa, through which, by diffusion a ...
SOMATIC NERVOUS SYSTEM Composed of somatic parts of CNS
... Greatly outnumber the presynaptic fibers within the paravertebral ganglia ...
... Greatly outnumber the presynaptic fibers within the paravertebral ganglia ...
An Application Interface Design for Backpropagation Artificial Neural
... The human brain consists of a large number, more than a billion of neural cells. Learning in biological systems occurs with synaptic connections between the neurons. This is true of ANN as well. ANN is an artificial illustration of the human brain that tries to imitate its learning process [2]. It h ...
... The human brain consists of a large number, more than a billion of neural cells. Learning in biological systems occurs with synaptic connections between the neurons. This is true of ANN as well. ANN is an artificial illustration of the human brain that tries to imitate its learning process [2]. It h ...
Pursuing commitments
... changes in mental states more mysterious than movement. In Moore and Fallah’s study6 (Fig. 1), monkeys were trained to detect a subtle change in one visual target among distracters. The task is easier if attention can be drawn to the appropriate part of the visual field. Normally this is accomplishe ...
... changes in mental states more mysterious than movement. In Moore and Fallah’s study6 (Fig. 1), monkeys were trained to detect a subtle change in one visual target among distracters. The task is easier if attention can be drawn to the appropriate part of the visual field. Normally this is accomplishe ...
Dynamics of Spontaneous Activity in Neocortical Slices
... stimulations. At the same time, EPSPs and IPSPs are routinely recorded intracellularly from neurons in slices even under conditions in which the slice is not stimulated. This suggests that some neurons in a “resting” brain slice must be active spontaneously and raises the issues of what is the natur ...
... stimulations. At the same time, EPSPs and IPSPs are routinely recorded intracellularly from neurons in slices even under conditions in which the slice is not stimulated. This suggests that some neurons in a “resting” brain slice must be active spontaneously and raises the issues of what is the natur ...
Excitatory Effect of GABAergic Axo
... have a bistable role in neural circuits. Indeed, firing of AACs stereotypically precedes or follows activation of pyramidal cells depending on the operational state of the network in vivo (23, 24). Simultaneous activation of a fraction of the several hundred postsynaptic pyramids innervated by a sin ...
... have a bistable role in neural circuits. Indeed, firing of AACs stereotypically precedes or follows activation of pyramidal cells depending on the operational state of the network in vivo (23, 24). Simultaneous activation of a fraction of the several hundred postsynaptic pyramids innervated by a sin ...
Slides - gserianne.com
... • portions of frontal lobe • portions of temporal lobe • hypothalamus • thalamus • basal nuclei • other deep nuclei • associated with sense of smell (less significant) Functions • controls emotions • produces feelings • interprets sensory impulses • facilitates memory storage and retrieval (learning ...
... • portions of frontal lobe • portions of temporal lobe • hypothalamus • thalamus • basal nuclei • other deep nuclei • associated with sense of smell (less significant) Functions • controls emotions • produces feelings • interprets sensory impulses • facilitates memory storage and retrieval (learning ...
REPRODUCTIVE AND DEVELOPMENTAL BIOLOGY (Level 2, 4 CU
... a. Brief Course Description This course will deal with the importance and significance of reproduction, embryology, gametogenesis, the role of hormones, fertilisation, implantation and type of placentas. b. Course objectives By the end of the course, the student should be able to: ...
... a. Brief Course Description This course will deal with the importance and significance of reproduction, embryology, gametogenesis, the role of hormones, fertilisation, implantation and type of placentas. b. Course objectives By the end of the course, the student should be able to: ...
the cerebellum - krigolson teaching
... different kinds of modeling because of its unusually regular cellular structure, which looks as if it had been wired purposefully by a Superior Designer. However, the present knowledge about the role of the cerebellum in various functions of the body is meager and fragmented. There have been quite a ...
... different kinds of modeling because of its unusually regular cellular structure, which looks as if it had been wired purposefully by a Superior Designer. However, the present knowledge about the role of the cerebellum in various functions of the body is meager and fragmented. There have been quite a ...
Neurons and Nervous Tissue
... Neurons and Nervous Tissue - How do neurons generate and conduct signals? Chemical synaptic transmission begins with the arrival of an action potential ...
... Neurons and Nervous Tissue - How do neurons generate and conduct signals? Chemical synaptic transmission begins with the arrival of an action potential ...
The Eye
... Define receptive field of a neuron The receptive field is an important concept that applies to all the senses. The definition of the receptive field of a ganglion cell is: “That area of retina over which light stimuli change the activity of a particular ganglion cell.” The receptive field shows whi ...
... Define receptive field of a neuron The receptive field is an important concept that applies to all the senses. The definition of the receptive field of a ganglion cell is: “That area of retina over which light stimuli change the activity of a particular ganglion cell.” The receptive field shows whi ...
EMBRYOLOGY GENERAL EMBRYOLOGY SECOND WEEK
... The amniotic cavity starts to form at this time whose roof is formed by Amnioblast( derives from inner surface of cytotrophoblast),while it's floor is the outer surface of the Ectoderm(Epiblast). DAYS 9 & 10:t of Development 1-Implantation is about to finish &fibrin coagulum appears at implantation ...
... The amniotic cavity starts to form at this time whose roof is formed by Amnioblast( derives from inner surface of cytotrophoblast),while it's floor is the outer surface of the Ectoderm(Epiblast). DAYS 9 & 10:t of Development 1-Implantation is about to finish &fibrin coagulum appears at implantation ...
A part of the cholinergic fibers in mouse superior cervical ganglia
... trunk showed a GABA-like immunoreactivity, and there were few GABA-like neurons in the spinal cord. Because their argument was based upon indirect evidence, further direct evidence is needed to elucidate the source of the GABAergic projection to the SCG. The vesicular acetylcholine transporter (VAch ...
... trunk showed a GABA-like immunoreactivity, and there were few GABA-like neurons in the spinal cord. Because their argument was based upon indirect evidence, further direct evidence is needed to elucidate the source of the GABAergic projection to the SCG. The vesicular acetylcholine transporter (VAch ...
The Nervous System
... by both the sympathetic and the parasympathetic divisions. The two systems work antagonistically to maintain homeostasis, with only one system stimulating the organ at any given time. Determining which system is in control is easy, based on the organ’s activity. If the organ is burning energy, relea ...
... by both the sympathetic and the parasympathetic divisions. The two systems work antagonistically to maintain homeostasis, with only one system stimulating the organ at any given time. Determining which system is in control is easy, based on the organ’s activity. If the organ is burning energy, relea ...
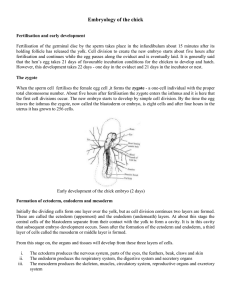
embryology of the chick
... that subsequent embryo development occurs. Soon after the formation of the ectoderm and endoderm, a third layer of cells called the mesoderm or middle layer is formed. From this stage on, the organs and tissues will develop from these three layers of cells. ...
... that subsequent embryo development occurs. Soon after the formation of the ectoderm and endoderm, a third layer of cells called the mesoderm or middle layer is formed. From this stage on, the organs and tissues will develop from these three layers of cells. ...
Lower motor neuron
... • The neurons in the red nucleus are activated monosynaptically by projections from the cortex • In humans most of the efferent fibers emerging from the red nucleus terminate in the inferior olive • Ends on interneurons that, in turn, project to the dorsal aspect of ventral (motor) horn cells • F ...
... • The neurons in the red nucleus are activated monosynaptically by projections from the cortex • In humans most of the efferent fibers emerging from the red nucleus terminate in the inferior olive • Ends on interneurons that, in turn, project to the dorsal aspect of ventral (motor) horn cells • F ...
LGN
... LGN interneurons make only local connections. There are more interneurons than relay neurons! LGN neurons get feedback connections from cortex. (The one-way connection from retina to rest of brain is unique in the visual system). LGN gets other inputs as well. For example: from brainstem and perigen ...
... LGN interneurons make only local connections. There are more interneurons than relay neurons! LGN neurons get feedback connections from cortex. (The one-way connection from retina to rest of brain is unique in the visual system). LGN gets other inputs as well. For example: from brainstem and perigen ...
The teratogenic effects of sugars on the chick embryo
... Another variant involves a partial anencephaly with the suppression of forebrain and midbrain. The heart projects forward beyond a truncated neural plate (Fig. 3A), which is greatly contorted into irregular grooves (Fig. 3D). These suggest a locally abnormal proliferation of the neural epithelium. I ...
... Another variant involves a partial anencephaly with the suppression of forebrain and midbrain. The heart projects forward beyond a truncated neural plate (Fig. 3A), which is greatly contorted into irregular grooves (Fig. 3D). These suggest a locally abnormal proliferation of the neural epithelium. I ...
Andrea Zecca Mechanisms responsible of sensory afferent projections into the hindbrain
... sensory information to the brain; and iii) central neurons organized in relay nuclei that process this information. To study the selective innervation of hindbrain regions by sensory afferents, we mapped the fine-grained topographical representation of sensory projections at the central level: senso ...
... sensory information to the brain; and iii) central neurons organized in relay nuclei that process this information. To study the selective innervation of hindbrain regions by sensory afferents, we mapped the fine-grained topographical representation of sensory projections at the central level: senso ...
a14a NeuroPhysI
... Two Kinds of Synapses Chemical Synapses • Specialized for the release and reception of neurotransmitters • Typically composed of two parts o Axon terminal of the presynaptic neuron, which contains synaptic vesicles o Receptor region on the postsynaptic neuron ...
... Two Kinds of Synapses Chemical Synapses • Specialized for the release and reception of neurotransmitters • Typically composed of two parts o Axon terminal of the presynaptic neuron, which contains synaptic vesicles o Receptor region on the postsynaptic neuron ...
PDF
... In rat embryos during neurulation the distribution of hyaluronate-rich extracellular spaces differs from that of the chick, in that the mesenchymal cells underlying the cranial neural plate or neural folds are widely separated, whereas those elsewhere are closely packed (Morriss & Solursh, 1978a). A ...
... In rat embryos during neurulation the distribution of hyaluronate-rich extracellular spaces differs from that of the chick, in that the mesenchymal cells underlying the cranial neural plate or neural folds are widely separated, whereas those elsewhere are closely packed (Morriss & Solursh, 1978a). A ...