S - cloudfront.net
... Clement VII. Their pursuit of policies that advanced the Medici drew their attention from vital matters such as the Protestant Reformation*. Pope Leo XI also a Medici, was less influential. The Medici were major patrons of Renaissance intellectuals and artists. Cosimo I did much to make Florence a c ...
... Clement VII. Their pursuit of policies that advanced the Medici drew their attention from vital matters such as the Protestant Reformation*. Pope Leo XI also a Medici, was less influential. The Medici were major patrons of Renaissance intellectuals and artists. Cosimo I did much to make Florence a c ...
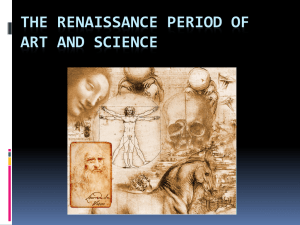
The Renaissance Period of Art and Science
... ✫ Leonardo conceptualized and sketched the first flying machines, which included the working sketches of a parachute, a helicopter, a hang glider, and an airplane. ✫ Da Vinci conceptualized a 33-barrelled organ, a sort of a gun that could fire multiple bullets in quick succession. It surely seems l ...
... ✫ Leonardo conceptualized and sketched the first flying machines, which included the working sketches of a parachute, a helicopter, a hang glider, and an airplane. ✫ Da Vinci conceptualized a 33-barrelled organ, a sort of a gun that could fire multiple bullets in quick succession. It surely seems l ...
The Sonnet - cloudfront.net
... Use of conceits: a metaphor that the poet usually extends and elaborates throughout the course of his poem. Poets chronicled stories of unrequited love in sonnet sequences, which were many sonnets tied together with the thread of narrative Check out: Sonnet Central ...
... Use of conceits: a metaphor that the poet usually extends and elaborates throughout the course of his poem. Poets chronicled stories of unrequited love in sonnet sequences, which were many sonnets tied together with the thread of narrative Check out: Sonnet Central ...
File
... The French word renaissance, meaning rebirth, is used to describe a period of Western European history between the 15th and 17th centuries. Before the Renaissance, Europeans lived in a period we now call the Middle Ages. During the Middle Ages, Europeans were concerned with the church and religion, ...
... The French word renaissance, meaning rebirth, is used to describe a period of Western European history between the 15th and 17th centuries. Before the Renaissance, Europeans lived in a period we now call the Middle Ages. During the Middle Ages, Europeans were concerned with the church and religion, ...
European Renaissance and Reformation
... The Renaissance Revolutionizes Art Supported by patrons like Isabella d’Este, dozens of artists worked in northern Italy. As the Renaissance advanced, artistic styles changed. Medieval artists had used religious subjects to convey a spiritual ideal. Renaissance artists often portrayed religious sub ...
... The Renaissance Revolutionizes Art Supported by patrons like Isabella d’Este, dozens of artists worked in northern Italy. As the Renaissance advanced, artistic styles changed. Medieval artists had used religious subjects to convey a spiritual ideal. Renaissance artists often portrayed religious sub ...
Leonardo da Vinci Michelangelo
... a robot, a calculator, and a flying machine that looks much like a modern helicopter. Leonardo was born in Vinci, a town in Tuscany that is near Florence. The name Leonardo da Vinci actually means “Leonardo from Vinci.” As a young man, Leonardo was apprenticed to a painter named Andrea del Verrocchi ...
... a robot, a calculator, and a flying machine that looks much like a modern helicopter. Leonardo was born in Vinci, a town in Tuscany that is near Florence. The name Leonardo da Vinci actually means “Leonardo from Vinci.” As a young man, Leonardo was apprenticed to a painter named Andrea del Verrocchi ...
The Renaissance in England
... • Humanism was the main driving force of the period ("English Humanists", "Rise of Humanism") • Humanist - someone who teaches, promotes, or studies classical literature, history, spirituality and the spiritual value of the beauty in art and nature, the power of human reason, philosophy, and moralit ...
... • Humanism was the main driving force of the period ("English Humanists", "Rise of Humanism") • Humanist - someone who teaches, promotes, or studies classical literature, history, spirituality and the spiritual value of the beauty in art and nature, the power of human reason, philosophy, and moralit ...
About Michelangelo - Core Knowledge Foundation
... Perhaps the most famous “Renaissance Man” was Leonardo da Vinci. Leonardo was a painter, sculptor, architect, engineer, naturalist, and inventor. He filled notebook after notebook with sketches and notes for inventions, including a robot, a calculator, and a flying machine that looks much like a mod ...
... Perhaps the most famous “Renaissance Man” was Leonardo da Vinci. Leonardo was a painter, sculptor, architect, engineer, naturalist, and inventor. He filled notebook after notebook with sketches and notes for inventions, including a robot, a calculator, and a flying machine that looks much like a mod ...
CHY4U_Renaissance_Art_2016
... National Gallery of Art and Oxford University Press, Italian Renaissance Learning Resources: Recovering the Golden Age, 2016, http://italianrenaissanceresources.com/units/unit-7/essays/rise-fall-and-resurrection-of-ancient- ...
... National Gallery of Art and Oxford University Press, Italian Renaissance Learning Resources: Recovering the Golden Age, 2016, http://italianrenaissanceresources.com/units/unit-7/essays/rise-fall-and-resurrection-of-ancient- ...
Renaissance Artists
... Portrait of Pope Julius II by Raphael, 1511-1512 More concerned with politics than with theology. ...
... Portrait of Pope Julius II by Raphael, 1511-1512 More concerned with politics than with theology. ...
Document
... During the tumultuous but fascinating 16th century of Reformation and CounterReformation, Michiel Coxcie resolutely supported the Catholic side. He painted religious scenes commissioned by and to serve as propaganda for the Catholic church. One can identify numerous traces of this turbulent period i ...
... During the tumultuous but fascinating 16th century of Reformation and CounterReformation, Michiel Coxcie resolutely supported the Catholic side. He painted religious scenes commissioned by and to serve as propaganda for the Catholic church. One can identify numerous traces of this turbulent period i ...
Chapter 14: The High Renaissance in Italy
... of __________. a. Raphael's Galatea b. Michelanglo's Sybils c. Leonardo's Virgin and Child with Saint Anne* d. Masaccio’s Trinity 10. Which of the following is the best match? a. Leonardo's Last Supper -- Milan* b. Bramante's Tempietto -- Florence c. The Sistine Chapel -- Siena d. The Mona Lisa -- R ...
... of __________. a. Raphael's Galatea b. Michelanglo's Sybils c. Leonardo's Virgin and Child with Saint Anne* d. Masaccio’s Trinity 10. Which of the following is the best match? a. Leonardo's Last Supper -- Milan* b. Bramante's Tempietto -- Florence c. The Sistine Chapel -- Siena d. The Mona Lisa -- R ...
The Italian Renaissance
... Much of Michelangelo’s work focused on themes and ideas that formed during the Renaissance. Individualism: An interest and value of individual people. ...
... Much of Michelangelo’s work focused on themes and ideas that formed during the Renaissance. Individualism: An interest and value of individual people. ...
The Medici and Boccaccio: Renaissance Men
... Man/Woman” emerged as a description of those who became masters of many different trades. Many famous Florentines were scholars, poets, painters, architects, politicians, and mathematicians all at once. Two areas that changed drastically during this period were art and banking, both of which involve ...
... Man/Woman” emerged as a description of those who became masters of many different trades. Many famous Florentines were scholars, poets, painters, architects, politicians, and mathematicians all at once. Two areas that changed drastically during this period were art and banking, both of which involve ...
Humanist History as Moral Philosophy and the Secular Immortality of
... with various changes we see these beginnings, warmed by the summer heat, shaping themselves into the abundance of the coming fruit; then, when they are ripe for the birth they give each its fruit in due season, and, by as much as they were warmed by the summer's heat, they are tempered by the autum ...
... with various changes we see these beginnings, warmed by the summer heat, shaping themselves into the abundance of the coming fruit; then, when they are ripe for the birth they give each its fruit in due season, and, by as much as they were warmed by the summer's heat, they are tempered by the autum ...
Florence: With and Without the Medici Dr Sunnie Evers February 28
... Giovanni was born: unbaptized: Antonino Pierozzi, archbishop of Florence, who died in 1459, claimed that unbaptized babies would be resurrected with the full body of a 33 year-old and would experience neither pain nor glory. Savonarola: “Original sin is not, as some believe, a stain or an infect ...
... Giovanni was born: unbaptized: Antonino Pierozzi, archbishop of Florence, who died in 1459, claimed that unbaptized babies would be resurrected with the full body of a 33 year-old and would experience neither pain nor glory. Savonarola: “Original sin is not, as some believe, a stain or an infect ...
1.1 the renaissance in italy
... During the Renaissance there was a new spirit of adventure and curiosity. • Trade assumed greater importance than before. • Navigators sailed across the oceans. • Scientists viewed the universe in new ways. • Writers and artists experimented with new techniques. ...
... During the Renaissance there was a new spirit of adventure and curiosity. • Trade assumed greater importance than before. • Navigators sailed across the oceans. • Scientists viewed the universe in new ways. • Writers and artists experimented with new techniques. ...
Italian Renaissance Art
... that there is a front, middle and back to the painting. It is not flat like Middle Ages art, it had depth. What you are, I once was; what I am, you will become. ...
... that there is a front, middle and back to the painting. It is not flat like Middle Ages art, it had depth. What you are, I once was; what I am, you will become. ...
Document
... 4. Which religion increased in power during the Dark Ages? [1] 5. Which group of people kept ancient knowledge in the Dark Ages? [1] 6. What types of construction characterized the High Middle Ages? [1] 7. By the 1200s, approximately what percentage of people in Western Europe led religious lives as ...
... 4. Which religion increased in power during the Dark Ages? [1] 5. Which group of people kept ancient knowledge in the Dark Ages? [1] 6. What types of construction characterized the High Middle Ages? [1] 7. By the 1200s, approximately what percentage of people in Western Europe led religious lives as ...
Influence and Implications of Renaissance Humanism
... to the conception of true nobility as the product of a “noble heart.” 7 While there is some suggestion that this attitude may have been profitably requisitioned by mendicant orders, who promoted a release from one's sins in return for charitable donations, the significance of a “noble heart” became ...
... to the conception of true nobility as the product of a “noble heart.” 7 While there is some suggestion that this attitude may have been profitably requisitioned by mendicant orders, who promoted a release from one's sins in return for charitable donations, the significance of a “noble heart” became ...
Chapter Seventeen Renaissance Artists
... They are the painter himself and a young man, perhaps arriving to act as witnesses to the marriage. The essential point, however, is the fact that the convex mirror is able to absorb and reflect in a single image both the floor and the ceiling of the room, as well as the sky and the garden outside, ...
... They are the painter himself and a young man, perhaps arriving to act as witnesses to the marriage. The essential point, however, is the fact that the convex mirror is able to absorb and reflect in a single image both the floor and the ceiling of the room, as well as the sky and the garden outside, ...
RESEARCH_PAPER - Mr. Grande`s World History OMG History
... expect that you will work very hard on this essay and create something that you and I will be very proud of. This is an opportunity for you to investigate and develop in-depth understanding of something that interests you—the Buddhist arts, Aztec warfare, Tang Dynasty fashion, ancient Greek food, et ...
... expect that you will work very hard on this essay and create something that you and I will be very proud of. This is an opportunity for you to investigate and develop in-depth understanding of something that interests you—the Buddhist arts, Aztec warfare, Tang Dynasty fashion, ancient Greek food, et ...
Rethinking the Renaissance - Assets
... The art of fifteenth-century Europe tends to be studied in parochial terms, with greatest attention paid to individual masters, regional developments, and local patronage. Europe, however, was then, as now, highly cosmopolitan, its diverse countries and polities linked into larger communities throug ...
... The art of fifteenth-century Europe tends to be studied in parochial terms, with greatest attention paid to individual masters, regional developments, and local patronage. Europe, however, was then, as now, highly cosmopolitan, its diverse countries and polities linked into larger communities throug ...
The AP European History Free Response Question
... Botticelli’s “Birth of Venus” portrays the moment that the goddess Venus is born. Zephyrs blow her to the shore as she rides on a shell. Venus covers herself in a manner that is reminiscent of ancient sculptures of her. His use of nudes and figures from ancient mythology show the strong influence hu ...
... Botticelli’s “Birth of Venus” portrays the moment that the goddess Venus is born. Zephyrs blow her to the shore as she rides on a shell. Venus covers herself in a manner that is reminiscent of ancient sculptures of her. His use of nudes and figures from ancient mythology show the strong influence hu ...