SWES 474 - Research Paper #1
... • “The protection, preservation, management, or restoration of wildlife and of natural resources such as forests, soil, and water.” • “The maintenance of a physical quantity, such as energy or mass, during a physical or chemical change.” ...
... • “The protection, preservation, management, or restoration of wildlife and of natural resources such as forests, soil, and water.” • “The maintenance of a physical quantity, such as energy or mass, during a physical or chemical change.” ...
Living things in their environment.
... Biotic – living parts of the environment. Ex. Producers and consumers. Abiotic – nonliving parts of the environment. Ex. water, sunlight, oxygen, temperature, and soil. Photosynthesis: The process of a plant making its own food. ...
... Biotic – living parts of the environment. Ex. Producers and consumers. Abiotic – nonliving parts of the environment. Ex. water, sunlight, oxygen, temperature, and soil. Photosynthesis: The process of a plant making its own food. ...
ES CH 5 Test Review
... 17. Parasitism is a relationship in which one organism, the parasite, depends on another, the host, for nourishment or some other benefit. 18. We define symbiosis as a long-lasting and physically close relationship in which at least one organism benefits. 19. The interaction in which an animal feed ...
... 17. Parasitism is a relationship in which one organism, the parasite, depends on another, the host, for nourishment or some other benefit. 18. We define symbiosis as a long-lasting and physically close relationship in which at least one organism benefits. 19. The interaction in which an animal feed ...
Ch 2 Principles of Ecology
... _____________ (-) orbit the nucleus. D. Organisms in Ecosystems 1. ____________________ – the ____________________ where an organism lives out its life. Ex: an earthworm feeds on organic material from the soil it moves through 2. ____________________ – the ____________________ and position a species ...
... _____________ (-) orbit the nucleus. D. Organisms in Ecosystems 1. ____________________ – the ____________________ where an organism lives out its life. Ex: an earthworm feeds on organic material from the soil it moves through 2. ____________________ – the ____________________ and position a species ...
CHARACTERISTICS OF LIVING THINGS
... Living things respond or react to their environment in some way. A stimulus is any condition in an environment that requires an organism to respond. A stimulus can be internal or external. ...
... Living things respond or react to their environment in some way. A stimulus is any condition in an environment that requires an organism to respond. A stimulus can be internal or external. ...
Abstract
... have been found, leaving the history of the first 600 million years missing. The oldest evidence for life can be traced back to between 3800 and 3500 million years and is based on chemical signatures, putative microfossils, and layered rocks known as stromatolites. Based on phylogenetic analyses it ...
... have been found, leaving the history of the first 600 million years missing. The oldest evidence for life can be traced back to between 3800 and 3500 million years and is based on chemical signatures, putative microfossils, and layered rocks known as stromatolites. Based on phylogenetic analyses it ...
AP Biology - Boone County Schools
... Biological evolution is supported by scientific evidence from many disciplines, including mathematics. Speciation may occur when two populations become reproductively isolated from each other. There are several hypotheses about the natural origin of life on Earth, each with supporting scientific evi ...
... Biological evolution is supported by scientific evidence from many disciplines, including mathematics. Speciation may occur when two populations become reproductively isolated from each other. There are several hypotheses about the natural origin of life on Earth, each with supporting scientific evi ...
28 Ecosystems - answers
... 5 (a) The abiotic factors which might affect an animal living at the bottom of the sea might be; water pressure, light, salinity. (any two) (b) The abiotic factors which might affect a plant growing on mountains might be; temperature, wind speed, drainage of water, light intensity. (any two) 6 The b ...
... 5 (a) The abiotic factors which might affect an animal living at the bottom of the sea might be; water pressure, light, salinity. (any two) (b) The abiotic factors which might affect a plant growing on mountains might be; temperature, wind speed, drainage of water, light intensity. (any two) 6 The b ...
Interactions Chapter 4
... A. Snakes and lizards live where it is warmer B. Monarch butterflies require milkweed plants as food source for caterpillars C. Fish and amount of DO in water-trout need more than bass, which need more than catfish D. Plants and availability of sunlight or nutrients in soil ...
... A. Snakes and lizards live where it is warmer B. Monarch butterflies require milkweed plants as food source for caterpillars C. Fish and amount of DO in water-trout need more than bass, which need more than catfish D. Plants and availability of sunlight or nutrients in soil ...
4th Grade Life Science Vocabulary
... Shelter: Cover from elements, for natal activity, for breeding, for bedding, etc.; varies depending on species. Mutually dependent: An arrangement in which two different organisms live in close association to the advantage of both. Ecology: The branch of biology dealing with the interrelationships b ...
... Shelter: Cover from elements, for natal activity, for breeding, for bedding, etc.; varies depending on species. Mutually dependent: An arrangement in which two different organisms live in close association to the advantage of both. Ecology: The branch of biology dealing with the interrelationships b ...
Ecology in One Page - Lakewood City School District
... Because there is a limited amount of food, habitat, water etc. in an ecosystem, there will be competition for it by the organisms present. The number of individuals in a population that can be supported by an ecosystem is called it carrying capacity. Species that exist together over long times are c ...
... Because there is a limited amount of food, habitat, water etc. in an ecosystem, there will be competition for it by the organisms present. The number of individuals in a population that can be supported by an ecosystem is called it carrying capacity. Species that exist together over long times are c ...
Biology Test
... A. the way the organism uses the range of physical and biological conditions in which it lives B. all the physical and biological factors in the organism’s environment C. the range of temperatures that the organisms need to survive D. a full description of the place and organism lives ...
... A. the way the organism uses the range of physical and biological conditions in which it lives B. all the physical and biological factors in the organism’s environment C. the range of temperatures that the organisms need to survive D. a full description of the place and organism lives ...
Master List and Directions
... Adaptation – Structures and behaviors that help organisms survive in their surroundings Inherited Traits – Traits that pass from parents to offspring Instinctive Behavior – A behavior that an animal inherits from its parents Structural Adaptation – A body part that does a certain job for an organism ...
... Adaptation – Structures and behaviors that help organisms survive in their surroundings Inherited Traits – Traits that pass from parents to offspring Instinctive Behavior – A behavior that an animal inherits from its parents Structural Adaptation – A body part that does a certain job for an organism ...
Paris Mountain State Park Forest Ecology Vocabulary List Abiotic
... Forest floor – bottom layer, made of soil, decomposing leaves and other organisms. Herb layer – layer near the ground, made of soft-stemmed small plants. Shrub layer – middle layer made of low woody plants with branching trunks. Understory layer – fourth layer up made of smaller, shade tolerant tree ...
... Forest floor – bottom layer, made of soil, decomposing leaves and other organisms. Herb layer – layer near the ground, made of soft-stemmed small plants. Shrub layer – middle layer made of low woody plants with branching trunks. Understory layer – fourth layer up made of smaller, shade tolerant tree ...
Ecology
... from the tree that is hosting it. If there are too many mistletoe on one tree, the tree could die. ...
... from the tree that is hosting it. If there are too many mistletoe on one tree, the tree could die. ...
Ecosystem
... Habitat- An environment that provides the things the organism needs to live, grow, and reproduce. An organism obtains food, water, shelter, and other things it needs to live, grow, and reproduce from its environment. Organisms live in different habitats because they have different requirements for s ...
... Habitat- An environment that provides the things the organism needs to live, grow, and reproduce. An organism obtains food, water, shelter, and other things it needs to live, grow, and reproduce from its environment. Organisms live in different habitats because they have different requirements for s ...
Ecology SOL Questions
... Bacteria that live in the soil and on plant roots called legumes convert nitrogen gas into ammonia. ...
... Bacteria that live in the soil and on plant roots called legumes convert nitrogen gas into ammonia. ...
What is an inference
... Bacteria that live in the soil and on plant roots called legumes convert nitrogen gas into ammonia. ...
... Bacteria that live in the soil and on plant roots called legumes convert nitrogen gas into ammonia. ...
Biome:
... environments they live in. As an ecologist, you don't just study a fish. You study the fish, water, sunlight, food supply, things that eat the fish, and every possible factor that might affect the fish in its lifetime. ...
... environments they live in. As an ecologist, you don't just study a fish. You study the fish, water, sunlight, food supply, things that eat the fish, and every possible factor that might affect the fish in its lifetime. ...
Predation, Mutualism, Commensalism, or Parasitism
... Commensalism is a relationship between two living organisms where one benefits and the other is neither harmed nor helped. ...
... Commensalism is a relationship between two living organisms where one benefits and the other is neither harmed nor helped. ...
DEFINING KEY TERMS 1points each (14 points)
... _____ Potential energy is the energy contained in moving objects. ...
... _____ Potential energy is the energy contained in moving objects. ...
Your “Environmental Stuff” www.wordle.net Ecology
... Includes all of the biotic factors: species’ populations (like the lions, giraffes, antelope, trees, etc.) And all of the abiotic factors: pride rock, the water hole, the land, etc. ...
... Includes all of the biotic factors: species’ populations (like the lions, giraffes, antelope, trees, etc.) And all of the abiotic factors: pride rock, the water hole, the land, etc. ...
Evolution and Biodiversity
... 1) fossils: skeletons of organisms trapped in bedrocks and sediments and date back to as much as millions of years 2) Homologuous body structures: similar bone arrangement in the skeletons of animals is considered to be an evidence of evolution from a common ancestor. 3) Embryology: the early embryo ...
... 1) fossils: skeletons of organisms trapped in bedrocks and sediments and date back to as much as millions of years 2) Homologuous body structures: similar bone arrangement in the skeletons of animals is considered to be an evidence of evolution from a common ancestor. 3) Embryology: the early embryo ...
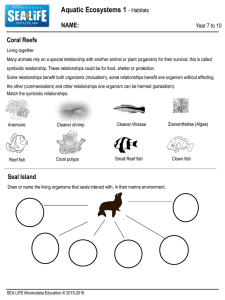
Aquatic Ecosystems 1 - Habitats
... Many animals rely on a special relationship with another animal or plant (organism) for their survival, this is called symbiotic relationship. These relationships could be for food, shelter or protection. Some relationships benefit both organisms (mutualism), some relationships benefit one organism ...
... Many animals rely on a special relationship with another animal or plant (organism) for their survival, this is called symbiotic relationship. These relationships could be for food, shelter or protection. Some relationships benefit both organisms (mutualism), some relationships benefit one organism ...