Outline - web.biosci.utexas.edu
... another (the host). The parasite benefits; the host is usually harmed ...
... another (the host). The parasite benefits; the host is usually harmed ...
131 Lecture 1.ppt [Read
... another country: here Australia. Prickly pear was eventually controlled by introducing a moth Cactoblastis cactorum whose caterpillars ate it ...
... another country: here Australia. Prickly pear was eventually controlled by introducing a moth Cactoblastis cactorum whose caterpillars ate it ...
Areas of high Natural Character that are also Ecological Sites
... With regard to the area defined as ‘Coastal Environment’ in the notified PDP, an additional 62 Ecological Sites are located either fully or partially within this area but outside of the SEV’s defined ‘Coastal Environment’. © 2015 Environmental Management Services ...
... With regard to the area defined as ‘Coastal Environment’ in the notified PDP, an additional 62 Ecological Sites are located either fully or partially within this area but outside of the SEV’s defined ‘Coastal Environment’. © 2015 Environmental Management Services ...
chapter 4
... nonnative species, indicator species, keystone species. Explain why these labels are important. ...
... nonnative species, indicator species, keystone species. Explain why these labels are important. ...
Niche & Community Interactions PPT
... Is the ability to survive and reproduce under a range of environmental conditions. All organisms have an upper and lower limit of tolerance for every environmental factor. Habitat Is the general place where an organism lives. ...
... Is the ability to survive and reproduce under a range of environmental conditions. All organisms have an upper and lower limit of tolerance for every environmental factor. Habitat Is the general place where an organism lives. ...
Ecosystems
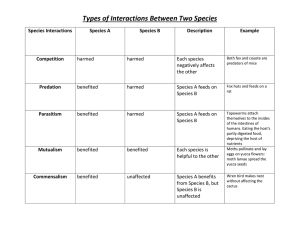
... • Competition: two or more organisms attempt to use the same resource E.g. – two plants on forest floor compete for sunlight • Parasitism: the relationship between the parasite and its host E.g. – Ticks on a Hedgehog • Mutualism: relationship between two species in which both benefit E.g. – Ants and ...
... • Competition: two or more organisms attempt to use the same resource E.g. – two plants on forest floor compete for sunlight • Parasitism: the relationship between the parasite and its host E.g. – Ticks on a Hedgehog • Mutualism: relationship between two species in which both benefit E.g. – Ants and ...
Garnier, E
... Key results The wide variety of land use systems that characterise marginal landscapes across Europe was reflected by the different disturbance indices, but they also often correspond to soil and/or nutrient availability gradients. The trait toolkit allowed us to describe adequately the functional r ...
... Key results The wide variety of land use systems that characterise marginal landscapes across Europe was reflected by the different disturbance indices, but they also often correspond to soil and/or nutrient availability gradients. The trait toolkit allowed us to describe adequately the functional r ...
Muscular System - walker2011
... ecosystems that have been disturbed or disrupted by humans, animals, or by natural process such as storms, floods, earthquakes, or volcanic eruptions. ...
... ecosystems that have been disturbed or disrupted by humans, animals, or by natural process such as storms, floods, earthquakes, or volcanic eruptions. ...
Envi Sci @ CHS
... Areas where you would find this type of succession Average time to occur Condition of soil at beginning of succession 3. Disturbances in an ecosystem’s environment can cause an ecological succession to revert. Give several examples of disturbances caused by nature and several caused by humans. ...
... Areas where you would find this type of succession Average time to occur Condition of soil at beginning of succession 3. Disturbances in an ecosystem’s environment can cause an ecological succession to revert. Give several examples of disturbances caused by nature and several caused by humans. ...
SWES 474 - Research Paper #1
... Transition of Perspective… • Space-time continuum. • Loss of species = transformation of energy. • Speciation = transformation of energy. • What is conservation? – All organisms participate in micro- and macroscale systems of input and output. – Concept of conservation is inherently dependent upon ...
... Transition of Perspective… • Space-time continuum. • Loss of species = transformation of energy. • Speciation = transformation of energy. • What is conservation? – All organisms participate in micro- and macroscale systems of input and output. – Concept of conservation is inherently dependent upon ...
22-3 interactions among living things notes
... specific living conditions. • An organism’s particular role, or how it makes its living is called its niche. ...
... specific living conditions. • An organism’s particular role, or how it makes its living is called its niche. ...
Understanding Populations Section 2 Predation
... – both attempt to use the same limited resource – both are negatively affected • members of the same species must compete: same niche • different species compete when niches overlap: use some of the same resources ...
... – both attempt to use the same limited resource – both are negatively affected • members of the same species must compete: same niche • different species compete when niches overlap: use some of the same resources ...
Fact Sheet Contact: Daniel Boone Phone: 928-523
... takes these connections to a whole new scientific level by exploring the frontiers of ecology with one of the smallest biological units, the gene. • The documentary is based on 30 years of interdisciplinary research, involving nearly 100 collaborators from across the United States and around the wor ...
... takes these connections to a whole new scientific level by exploring the frontiers of ecology with one of the smallest biological units, the gene. • The documentary is based on 30 years of interdisciplinary research, involving nearly 100 collaborators from across the United States and around the wor ...
Presentation - National Forest Foundation
... John Stanturf, Southern Research Station Athens, GA [email protected] ...
... John Stanturf, Southern Research Station Athens, GA [email protected] ...
Week 2-3 Notes File
... One species (parasite) obtains energy by living off of another species. EX: Tapeworms live in the intestines of a dog, absorbing nutrients from the food it eats ...
... One species (parasite) obtains energy by living off of another species. EX: Tapeworms live in the intestines of a dog, absorbing nutrients from the food it eats ...
Population Genetics
... Evolution of species (speciation) Divergent evolution: species become different over a long period of time. Adaptative radiation (species spread out to new territories). Convergent evolution: Different species undergoing similar adaptations and evolving more alike ...
... Evolution of species (speciation) Divergent evolution: species become different over a long period of time. Adaptative radiation (species spread out to new territories). Convergent evolution: Different species undergoing similar adaptations and evolving more alike ...
Chapter 54 – Community Ecology Ecological Niche
... Bats use echolocation…Moth uses evasive maneuvers when it hears bat Bat changes frequency…Moth make clicks to jam bat’s radar Bat stops making noise, listens for moth’s clicks ...
... Bats use echolocation…Moth uses evasive maneuvers when it hears bat Bat changes frequency…Moth make clicks to jam bat’s radar Bat stops making noise, listens for moth’s clicks ...
Ecological fitting

Ecological fitting is ""the process whereby organisms colonize and persist in novel environments, use novel resources or form novel associations with other species as a result of the suites of traits that they carry at the time they encounter the novel condition.” It can be understood as a situation in which a species' interactions with its biotic and abiotic environment seem to indicate a history of coevolution, when in actuality the relevant traits evolved in response to a different set of biotic and abiotic conditions. The simplest form of ecological fitting is resource tracking, in which an organism continues to exploit the same resources, but in a new host or environment. In this framework, the organism occupies a multidimensional operative environment defined by the conditions in which it can persist, similar to the idea of the Hutchinsonian niche. In this case, a species can colonize new environments (e.g. an area with the same temperature and water regime) and/or form new species interactions (e.g. a parasite infecting a new host) which can lead to the misinterpretation of the relationship as coevolution, although the organism has not evolved and is continuing to exploit the same resources it always has. The more strict definition of ecological fitting requires that a species encounter an environment or host outside of its original operative environment and obtain realized fitness based on traits developed in previous environments that are now co-opted for a new purpose. This strict form of ecological fitting can also be expressed either as colonization of new habitat or the formation of new species interactions.