File
... To identify the various uses of ecosystems Be able to distinguish between the economic, environmental and cultural values ...
... To identify the various uses of ecosystems Be able to distinguish between the economic, environmental and cultural values ...
Priceless or worthless?
... hurdler with a fine stud pedigree may fetch large sums in the racing market, but it would be virtually worthless to a farmer with a cart to transport. A shire horse would be very valuable for that role, but of no use to a dressage contestant. Value, rather like beauty, lies in the eye of the beholde ...
... hurdler with a fine stud pedigree may fetch large sums in the racing market, but it would be virtually worthless to a farmer with a cart to transport. A shire horse would be very valuable for that role, but of no use to a dressage contestant. Value, rather like beauty, lies in the eye of the beholde ...
Chapter 48 - Community Ecology
... commensalism and given an example of a pair of species that illustrates each. 2. Search for information on the internet on the relationship between Monarch and Viceroy butterflies. Is this a case of Batesian or Müllerian mimicry? Explain your reasoning. 3. Explain the Competitive Exclusion Principle ...
... commensalism and given an example of a pair of species that illustrates each. 2. Search for information on the internet on the relationship between Monarch and Viceroy butterflies. Is this a case of Batesian or Müllerian mimicry? Explain your reasoning. 3. Explain the Competitive Exclusion Principle ...
Ecology Review - Issaquah Connect
... Easter Island faced similar dilemmas when it’s inhabitants introduced new species that became invasive, overused their resources and began to fight one another. ...
... Easter Island faced similar dilemmas when it’s inhabitants introduced new species that became invasive, overused their resources and began to fight one another. ...
Communities, Ecosystems, and Biodiversity
... Similar to photosynthesis, but some predation Nutrient input from smokers, detritus Organisms tightly coupled with environment Open or closed system? Patches far apart, smokers ltd time Organisms have to get there somehow! ...
... Similar to photosynthesis, but some predation Nutrient input from smokers, detritus Organisms tightly coupled with environment Open or closed system? Patches far apart, smokers ltd time Organisms have to get there somehow! ...
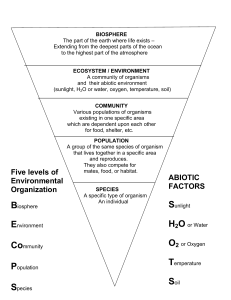
Five levels of Environmental Organization ABIOTIC FACTORS
... BIOSPHERE The part of the earth where life exists – Extending from the deepest parts of the ocean to the highest part of the atmosphere ...
... BIOSPHERE The part of the earth where life exists – Extending from the deepest parts of the ocean to the highest part of the atmosphere ...
The number of different species in an area.
... • It is estimated that biodiversity provides between $3-$33 trillion dollars to the global economy. • The annual economic and environmental benefits of biodiversity in the United States total approximately $300 billion. • In 1995 alone, visitors to national wildlife refuges contributed $401 million ...
... • It is estimated that biodiversity provides between $3-$33 trillion dollars to the global economy. • The annual economic and environmental benefits of biodiversity in the United States total approximately $300 billion. • In 1995 alone, visitors to national wildlife refuges contributed $401 million ...
The competitive exclusion principle Gause`s Experiment Reduced
... they are sympatric than when they are allopatric. ...
... they are sympatric than when they are allopatric. ...
Limiting Factors & Carrying Capacity
... and Tolerance Ranges create a… • Carrying Capacity: The maximum number of individuals of a species able to survive in an area. • Carrying capacity for all consumers increases as the amount of producers increase… *** Producers are VERY important to healthy ecosystems!!*** ...
... and Tolerance Ranges create a… • Carrying Capacity: The maximum number of individuals of a species able to survive in an area. • Carrying capacity for all consumers increases as the amount of producers increase… *** Producers are VERY important to healthy ecosystems!!*** ...
From Fred: After collecting information on available habitat priorities
... of gull and waterfowl species that stage and over-winter there, the nesting colonies of herons and egrets, and the exceptional diversity of songbirds that use habitat along the river corridor during migration. General goals of the IBA Program: o Identify a network of sites that are essential for sus ...
... of gull and waterfowl species that stage and over-winter there, the nesting colonies of herons and egrets, and the exceptional diversity of songbirds that use habitat along the river corridor during migration. General goals of the IBA Program: o Identify a network of sites that are essential for sus ...
Biodiversity and Sustainability
... services like clean air and fresh water. Every time we lose a species from an ecosystem we change the way the whole system works. ...
... services like clean air and fresh water. Every time we lose a species from an ecosystem we change the way the whole system works. ...
Think like an Ecologist… a scientist who studies the relationships
... Biodiversity: The combined differences of living things, generally classified in four broad categories of diversity: Genetic, Species, Culture, & Ecosystem. Biome: A specific type of terrestrial region inhabited by well-defined types of life that generally cannot live outside that specific region. E ...
... Biodiversity: The combined differences of living things, generally classified in four broad categories of diversity: Genetic, Species, Culture, & Ecosystem. Biome: A specific type of terrestrial region inhabited by well-defined types of life that generally cannot live outside that specific region. E ...
Chapter 6: Humans in the Biosphere
... Ecosystem diversity: includes the variety of habitats, communities, and ecological process in the world ...
... Ecosystem diversity: includes the variety of habitats, communities, and ecological process in the world ...
Warren Austin and Cory Soltys Aquatic Biodiversity
... THE IMPORTANCE OF BIODIVERSITY • UTILITARIAN VALUES-MEDICINAL USE OF PLANTS, AGRICULTURAL GENE STOCKS, AND FISHING • INDIRECT UTILITARIAN VALUES-ECOSYSTEM SERVICES SUCH AS AIR QUALITY AND CLIMATE AMELIORATION • BIOGEOCHEMICAL CYCLES • PHOTOSYNTHESIS AND CELLULAR RESPIRATION (OXYGEN) • CLEANING WAT ...
... THE IMPORTANCE OF BIODIVERSITY • UTILITARIAN VALUES-MEDICINAL USE OF PLANTS, AGRICULTURAL GENE STOCKS, AND FISHING • INDIRECT UTILITARIAN VALUES-ECOSYSTEM SERVICES SUCH AS AIR QUALITY AND CLIMATE AMELIORATION • BIOGEOCHEMICAL CYCLES • PHOTOSYNTHESIS AND CELLULAR RESPIRATION (OXYGEN) • CLEANING WAT ...
Biodiversity Quiz - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... ____ 3. About 10 million species have been identified by scientists. ____ 4. The Earth has many more species than it needs. ____ 5. More species are of no direct benefit to humans. ____ 6. Some habitats have more species than others. ____ 7. Biodiversity includes genetic diversity, species diversity ...
... ____ 3. About 10 million species have been identified by scientists. ____ 4. The Earth has many more species than it needs. ____ 5. More species are of no direct benefit to humans. ____ 6. Some habitats have more species than others. ____ 7. Biodiversity includes genetic diversity, species diversity ...
Biology Notes: Ecology
... 2. What are two reasons that populations will increase?__________________________ , ________________________ 3. What are two reasons that populations will decrease?_________________________ , ________________________ 4. What are factors that control population growth called? ______________________ ...
... 2. What are two reasons that populations will increase?__________________________ , ________________________ 3. What are two reasons that populations will decrease?_________________________ , ________________________ 4. What are factors that control population growth called? ______________________ ...
Project Presentation - Instituto Ecológica
... Studies reveal that climate effects are becoming more extreme in the region. • The region has great potential for maintenance and sequestration of carbon. • Research's can explain how changes in land use are affecting the global climate and how global climate changes are affecting the forest. • Ac ...
... Studies reveal that climate effects are becoming more extreme in the region. • The region has great potential for maintenance and sequestration of carbon. • Research's can explain how changes in land use are affecting the global climate and how global climate changes are affecting the forest. • Ac ...
Chapter 9 Study Guide
... Biotic resources used by humans: food, materials to build shelter, and materials that compose fuels. *Human activities may affect the balance in an ecosystem and thereby change the ecosystem. Examples include: introducing non-native species and overuse of resources. *Some technologies used in energy ...
... Biotic resources used by humans: food, materials to build shelter, and materials that compose fuels. *Human activities may affect the balance in an ecosystem and thereby change the ecosystem. Examples include: introducing non-native species and overuse of resources. *Some technologies used in energy ...
Ecosystem and Genetic Diversity
... In review, Charles Darwin’s Theory of Evolution by means of Natural Selection is based on the view that organisms that are more suited (physically or behaviorally) for their environment have a better chance of surviving and reproducing than those that are not (remember “survival of the fittest?”) In ...
... In review, Charles Darwin’s Theory of Evolution by means of Natural Selection is based on the view that organisms that are more suited (physically or behaviorally) for their environment have a better chance of surviving and reproducing than those that are not (remember “survival of the fittest?”) In ...
Ecosystem Stability
... • People chopping down forests to make farmland, build roads, shopping malls, etc… • deforestation ...
... • People chopping down forests to make farmland, build roads, shopping malls, etc… • deforestation ...
Structure and Function of Marine Ecosystems
... An ecosystem is a geographically specified system of organisms (including humans), the environment, and the processes that control its dynamics. ...
... An ecosystem is a geographically specified system of organisms (including humans), the environment, and the processes that control its dynamics. ...
DOC - The Great Trossachs Forest
... The Great Trossachs Forest The Great Trossachs Forest (TGTF) lies at the heart of the Loch Lomond and The Trossachs National Park, and is a landscape scale woodland conservation project covering an area roughly the size of Glasgow. TGTF has a range of habitats (including native ancient woodland, moo ...
... The Great Trossachs Forest The Great Trossachs Forest (TGTF) lies at the heart of the Loch Lomond and The Trossachs National Park, and is a landscape scale woodland conservation project covering an area roughly the size of Glasgow. TGTF has a range of habitats (including native ancient woodland, moo ...
Biodiversity action plan

This article is about a conservation biology topic. For other uses of BAP, see BAP (disambiguation).A biodiversity action plan (BAP) is an internationally recognized program addressing threatened species and habitats and is designed to protect and restore biological systems. The original impetus for these plans derives from the 1992 Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD). As of 2009, 191 countries have ratified the CBD, but only a fraction of these have developed substantive BAP documents.The principal elements of a BAP typically include: (a) preparing inventories of biological information for selected species or habitats; (b) assessing the conservation status of species within specified ecosystems; (c) creation of targets for conservation and restoration; and (d) establishing budgets, timelines and institutional partnerships for implementing the BAP.