File
... together with their physical environment Biome Ex. Tropical rainforest group of ecosystems with the same climate and similar dominant communities Biosphere: Ex. Earth and atmosphere above it Consists of the portion of Earth that supports life. (includes land, water, atmosphere) ...
... together with their physical environment Biome Ex. Tropical rainforest group of ecosystems with the same climate and similar dominant communities Biosphere: Ex. Earth and atmosphere above it Consists of the portion of Earth that supports life. (includes land, water, atmosphere) ...
Invasions
... Invasions are processes of the penetration of alien species into ecosystems located outside their natural areas and their impact to the native communities. Invasions can be caused by: ...
... Invasions are processes of the penetration of alien species into ecosystems located outside their natural areas and their impact to the native communities. Invasions can be caused by: ...
APES_chapter_11_Sust.. - Zamora`s Science Zone
... 1. Modern industrial fishing can deplete 80% of target fish species in just 10–15 years. 2. Overfishing can lead to commercial extinction, which occurs when it is no longer profitable to continue fishing the affected species. 3. Nearly one-third of annual fish catch consists of bycatch—non-target sp ...
... 1. Modern industrial fishing can deplete 80% of target fish species in just 10–15 years. 2. Overfishing can lead to commercial extinction, which occurs when it is no longer profitable to continue fishing the affected species. 3. Nearly one-third of annual fish catch consists of bycatch—non-target sp ...
GARDENING IN THE 21 CENTURY ST
... disturbed areas, day-lighting streams, reintroduction of native species, as well as habitat and range improvement for targeted species. ...
... disturbed areas, day-lighting streams, reintroduction of native species, as well as habitat and range improvement for targeted species. ...
Open House Presentation - Charlotte Teachers Institute
... 2.L.1 Understand animal life cycles. 2.L.1.1 Summarize the life cycle of animals: • Birth • Developing into an adult 2.L.1.2 Compare life cycles of different animals such as, but not limited to, mealworms, ladybugs, crickets, guppies or frogs. ...
... 2.L.1 Understand animal life cycles. 2.L.1.1 Summarize the life cycle of animals: • Birth • Developing into an adult 2.L.1.2 Compare life cycles of different animals such as, but not limited to, mealworms, ladybugs, crickets, guppies or frogs. ...
Prelecture Chapter 53 - Seattle Central College
... 6. Keystone predators maintain species diversity in a community by a. competitively excluding other predators. b. preying on the community's dominant species. c. allowing immigration of other predators. d. reducing the number of disruptions in the community. e. coevolving with their prey. 7. Food c ...
... 6. Keystone predators maintain species diversity in a community by a. competitively excluding other predators. b. preying on the community's dominant species. c. allowing immigration of other predators. d. reducing the number of disruptions in the community. e. coevolving with their prey. 7. Food c ...
A Biodiversity and Conservation Assessment of the Edwards
... too are there unique population, economic, cultural, ...
... too are there unique population, economic, cultural, ...
Chapter 27 Notes
... A particular species that ___________________________________________ __________________________________ Removing the keystone species would ________________________________ ...
... A particular species that ___________________________________________ __________________________________ Removing the keystone species would ________________________________ ...
Protecting, preserving and improving the world around us
... subsist is called biosphere. This includes from some centimeters (or even meters) below the surface of the land and sea's bottom to several kilometres up in the atmosphere. A habitat is the environment in which an animal or plant lives, generally defined in terms of its vegetation and physical featu ...
... subsist is called biosphere. This includes from some centimeters (or even meters) below the surface of the land and sea's bottom to several kilometres up in the atmosphere. A habitat is the environment in which an animal or plant lives, generally defined in terms of its vegetation and physical featu ...
chapter 4
... Distinguish among the following species interactions and give one example of each: interspecific competition, predation, and symbiosis. Distinguish between interference competition and exploitation competition. Summarize the competitive exclusion principle. List two strategies species use to reduce ...
... Distinguish among the following species interactions and give one example of each: interspecific competition, predation, and symbiosis. Distinguish between interference competition and exploitation competition. Summarize the competitive exclusion principle. List two strategies species use to reduce ...
Unit IV Biodiversity
... (autotrophic plants, some protists), and consumers (some protists, fungi, heterotrophic animals). These organisms are the biotic factors, or living things, in an area. These organisms in turn, rely on the abiotic, or non-living factors in an area. Examples of abiotic factors are: salinity, climate/w ...
... (autotrophic plants, some protists), and consumers (some protists, fungi, heterotrophic animals). These organisms are the biotic factors, or living things, in an area. These organisms in turn, rely on the abiotic, or non-living factors in an area. Examples of abiotic factors are: salinity, climate/w ...
Essential Standard 2.1 Analyze the interdependence of living
... Within a population, one individual, that has all the characteristics of life, is called an organism. ...
... Within a population, one individual, that has all the characteristics of life, is called an organism. ...
Ecology Refresher
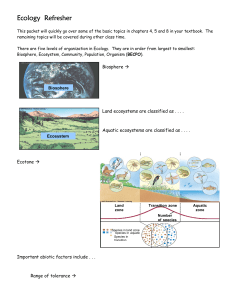
... Ecology Refresher This packet will quickly go over some of the basic topics in chapters 4, 5 and 8 in your textbook. The remaining topics will be covered during other class time. There are five levels of organization in Ecology. They are in order from largest to smallest: Biosphere, Ecosystem, Commu ...
... Ecology Refresher This packet will quickly go over some of the basic topics in chapters 4, 5 and 8 in your textbook. The remaining topics will be covered during other class time. There are five levels of organization in Ecology. They are in order from largest to smallest: Biosphere, Ecosystem, Commu ...
Community Ecology Ch 6 - Pendleton
... in the same habitat with the same requirements for very long. ...
... in the same habitat with the same requirements for very long. ...
biodiversity human health - American Museum of Natural History
... Predators that controlled both pathogens and disease carriers can be killed off, leading to the emergence of new diseases and the resurgence of old diseases that predators previously kept in check. The outbreak of hantavirus in the Southwest occurred when a combination of land use and climatic chang ...
... Predators that controlled both pathogens and disease carriers can be killed off, leading to the emergence of new diseases and the resurgence of old diseases that predators previously kept in check. The outbreak of hantavirus in the Southwest occurred when a combination of land use and climatic chang ...
Examples of Animal Adaptations
... 1.All species have variations (caused by genetic makeup…Mutations can cause variation). 2. Variation is inherited. 3. More species are produced than will live. 4. Those species that survive to reproduce will pass their characteristics (genes) on to the next generation those that don’t become extinct ...
... 1.All species have variations (caused by genetic makeup…Mutations can cause variation). 2. Variation is inherited. 3. More species are produced than will live. 4. Those species that survive to reproduce will pass their characteristics (genes) on to the next generation those that don’t become extinct ...
Glossary Terms
... keystone species. A species whose impact on the community or ecosystem is disproportionately large relative to its abundance. landscape ecology. Focuses on how ecological processes operate across large spatial scales. limiting factors. Environmental features or conditions that exist at a suboptimal ...
... keystone species. A species whose impact on the community or ecosystem is disproportionately large relative to its abundance. landscape ecology. Focuses on how ecological processes operate across large spatial scales. limiting factors. Environmental features or conditions that exist at a suboptimal ...
Which of the following is a commercially used method for harvesting
... d. Increase in gene flow within species e. Increase in population size of top carnivores 10. In general, which of the following is the best long-term method of preventing extinctions? a. Breeding endangered species in captivity. b. Protecting the habitats of endangered species. c. Paying people not ...
... d. Increase in gene flow within species e. Increase in population size of top carnivores 10. In general, which of the following is the best long-term method of preventing extinctions? a. Breeding endangered species in captivity. b. Protecting the habitats of endangered species. c. Paying people not ...
Location and Adjacent Conservation Lands
... Biodiversity Hotspot by FWC. • 122 bird species documented to date • 22 mammals • 18 listed species ...
... Biodiversity Hotspot by FWC. • 122 bird species documented to date • 22 mammals • 18 listed species ...
What is biodiversity? Why is it important? What threatens biodiversity
... more to attain prior levels of species diversity • Homo sapiens (humans) are the cause of a sixth major extinction in history. ...
... more to attain prior levels of species diversity • Homo sapiens (humans) are the cause of a sixth major extinction in history. ...
Global Climate Change
... pyrethrum insecticides. The seeds contain a natural insecticide called pyrethrin, a generic name for six related active compounds. It is one of the safer insecticides for several reasons: it decomposes rapidly in sunlight; it has few known effects on mammals; and insects do not develop resistance to ...
... pyrethrum insecticides. The seeds contain a natural insecticide called pyrethrin, a generic name for six related active compounds. It is one of the safer insecticides for several reasons: it decomposes rapidly in sunlight; it has few known effects on mammals; and insects do not develop resistance to ...
Chapter 6 Humans in the Biosphere
... based variety of all organisms in the biosphere Ecosystem diversity - the variety of habitats, communities, and ecological processes in the living world Species diversity – the number of different species in the biosphere So far, biologists have identified and named about 1.5 million species and est ...
... based variety of all organisms in the biosphere Ecosystem diversity - the variety of habitats, communities, and ecological processes in the living world Species diversity – the number of different species in the biosphere So far, biologists have identified and named about 1.5 million species and est ...
Conservation of natural- and agro-ecosystems - HES-SO
... Bachelor in LS, Agronomy or Natural resource management, or equivalent ...
... Bachelor in LS, Agronomy or Natural resource management, or equivalent ...
Biodiversity action plan

This article is about a conservation biology topic. For other uses of BAP, see BAP (disambiguation).A biodiversity action plan (BAP) is an internationally recognized program addressing threatened species and habitats and is designed to protect and restore biological systems. The original impetus for these plans derives from the 1992 Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD). As of 2009, 191 countries have ratified the CBD, but only a fraction of these have developed substantive BAP documents.The principal elements of a BAP typically include: (a) preparing inventories of biological information for selected species or habitats; (b) assessing the conservation status of species within specified ecosystems; (c) creation of targets for conservation and restoration; and (d) establishing budgets, timelines and institutional partnerships for implementing the BAP.