09 Pop Fluc-Struct rubric
... Graph 1: Most species have very small ranges. Graph 2: Range size increases with increasing latitude. B. Propose a hypothesis to explain the range size at high latitudes. 1. Few species exert low competition and allow range expansion to large sizes in high latitudes. 2. Species adapted to high latit ...
... Graph 1: Most species have very small ranges. Graph 2: Range size increases with increasing latitude. B. Propose a hypothesis to explain the range size at high latitudes. 1. Few species exert low competition and allow range expansion to large sizes in high latitudes. 2. Species adapted to high latit ...
Outline 7
... H. Succession types I. Successional processes (three processes) J. Richness changes during succession ...
... H. Succession types I. Successional processes (three processes) J. Richness changes during succession ...
biodiversity
... 2. What is the disadvantage of a rapid growth in human population? 3. Explain the relationship and trend between predator and prey population in an ecosystem. ...
... 2. What is the disadvantage of a rapid growth in human population? 3. Explain the relationship and trend between predator and prey population in an ecosystem. ...
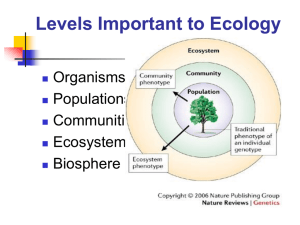
Community Ecology
... • Secondary – Review of primary literature • Ter/ary– excerpt of primary literature, worded for a broader audience • Opinion – subjec2ve interpreta2on of primary research findings • Most websites, commentaries, ...
... • Secondary – Review of primary literature • Ter/ary– excerpt of primary literature, worded for a broader audience • Opinion – subjec2ve interpreta2on of primary research findings • Most websites, commentaries, ...
Outline and important questions to know for the exam
... 9. What are some human activities that can alter the carbon and nitrogen cycle? 10. What is nitrification? 11. What are negative effects of human interference in the nitrogen cycle? 12. Where do carnivores get the majority of their nitrogen? 13. Where does most terrestrial phosphate come from? 14. W ...
... 9. What are some human activities that can alter the carbon and nitrogen cycle? 10. What is nitrification? 11. What are negative effects of human interference in the nitrogen cycle? 12. Where do carnivores get the majority of their nitrogen? 13. Where does most terrestrial phosphate come from? 14. W ...
An EMu based electronic monograph of the Brazil nut
... ELECTRONIC KEY FROM THE LECYTHIDACEAE PAGES (prepared using Lucid 3) ...
... ELECTRONIC KEY FROM THE LECYTHIDACEAE PAGES (prepared using Lucid 3) ...
Vocabulary Master List
... Nitrogen fixation – Organisms cannot use nitrogen gas (N2), but the gas can be “fixed” or converted into ammonia by bacteria. Non-native species – A species introduced to a region intentionally or accidentally. Pathway – The geographic path a species follows on its way to an introduction. Perennial ...
... Nitrogen fixation – Organisms cannot use nitrogen gas (N2), but the gas can be “fixed” or converted into ammonia by bacteria. Non-native species – A species introduced to a region intentionally or accidentally. Pathway – The geographic path a species follows on its way to an introduction. Perennial ...
Water Resources - Southgate Community School District
... taxonomic groups, or within a given geographic area. Did You Know? In general, biodiversity increases toward the equator. Orangutan in an Indonesian rain forest ...
... taxonomic groups, or within a given geographic area. Did You Know? In general, biodiversity increases toward the equator. Orangutan in an Indonesian rain forest ...
Questions: Ecological Succession is the natural, gradual changes in
... grow in an ecosystem, beginning a chain of ecological succession. Primary Succession begins in a place without any soil. Starts with bare rock Pioneer Species – Lichen and Moss Secondary Succession begins in a place that already has soil and was once the home of living organisms. Examples: aft ...
... grow in an ecosystem, beginning a chain of ecological succession. Primary Succession begins in a place without any soil. Starts with bare rock Pioneer Species – Lichen and Moss Secondary Succession begins in a place that already has soil and was once the home of living organisms. Examples: aft ...
16.5 Conservation - Brookwood High School
... • The timber industry has started to adopt sustainable practices. • Global fisheries have adopted several sustainable practices. – rotation of catches – fishing gear review – harvest reduction – fishing bans ...
... • The timber industry has started to adopt sustainable practices. • Global fisheries have adopted several sustainable practices. – rotation of catches – fishing gear review – harvest reduction – fishing bans ...
Gause`s competitive exclusion principle and “the
... Gause’s competitive exclusion principle and “the paradox of the plankton” 713/813 Lecture 10 ...
... Gause’s competitive exclusion principle and “the paradox of the plankton” 713/813 Lecture 10 ...
Future KBA Identification
... Candidate KBA Identification: Modeling Techniques for Field Survey Prioritization • Species Distribution Modeling: approximation of species ecological niche projected into geographic space – realized niche may be smaller than fundamental or “theoretical” niche ...
... Candidate KBA Identification: Modeling Techniques for Field Survey Prioritization • Species Distribution Modeling: approximation of species ecological niche projected into geographic space – realized niche may be smaller than fundamental or “theoretical” niche ...
Name
... 2. Define a keystone species in your own words. What happens (at least three possibilities) to the species composition of a community if you remove the keystone species? 3. Why can new species often invade a habitat after a keystone species is removed? 4. Why are sea otters considered "The most pote ...
... 2. Define a keystone species in your own words. What happens (at least three possibilities) to the species composition of a community if you remove the keystone species? 3. Why can new species often invade a habitat after a keystone species is removed? 4. Why are sea otters considered "The most pote ...
04 Climate and Ecosystems
... (soil, rocks, sunlight, wind, rain) •Habitat – The place where a population lives •Tolerance – Each species in an ecosystem has a certain range they can survive under for conditions. – Not all survival is created equal ...
... (soil, rocks, sunlight, wind, rain) •Habitat – The place where a population lives •Tolerance – Each species in an ecosystem has a certain range they can survive under for conditions. – Not all survival is created equal ...
Extinction
... • Unlike other predators, humans exploited the mass flocks of the passenger pigeon ...
... • Unlike other predators, humans exploited the mass flocks of the passenger pigeon ...
glossary
... environmental or ecological factors such as climate change, disease, loss of habitat, or competitive disadvantage in relation to other species. Background extinction occurs at a fairly steady rate over geological time and is the result of normal evolutionary processes, with only a limited number of ...
... environmental or ecological factors such as climate change, disease, loss of habitat, or competitive disadvantage in relation to other species. Background extinction occurs at a fairly steady rate over geological time and is the result of normal evolutionary processes, with only a limited number of ...
NOTES ECOLOGY - Pascack Valley Regional High School District
... I. Populations in Communities INTERACT A. Competition: struggle for resources between living things 1. Example: a. Interspecific competition: competition between species that depend on the same limited resource 2. Competitive exclusion is when 2 species are so similar in their requirements that the ...
... I. Populations in Communities INTERACT A. Competition: struggle for resources between living things 1. Example: a. Interspecific competition: competition between species that depend on the same limited resource 2. Competitive exclusion is when 2 species are so similar in their requirements that the ...
Review 1. What is the niche concept and how is it useful in the study
... 1. What is the niche concept and how is it useful in the study of competition? 2. What did Connel's study, in which he removed each of 2 competing species of barnacles, demonstrate? Remember that he got different results for the two species. 3. Be able to interpret Connel's results in terms of the f ...
... 1. What is the niche concept and how is it useful in the study of competition? 2. What did Connel's study, in which he removed each of 2 competing species of barnacles, demonstrate? Remember that he got different results for the two species. 3. Be able to interpret Connel's results in terms of the f ...
COMMUNITY AND POPULATION ECOLOGY
... Succession in lakes filling in to form bogs and then meadows. ...
... Succession in lakes filling in to form bogs and then meadows. ...
TYPES OF BIRDS
... certain bird species, its not evolving in other species that remain resident, sedentary, year-round. a particular species migrates depends on a number of factors. The climate of the breeding area is important, as few species can with the harsh winters of inland Canada. ...
... certain bird species, its not evolving in other species that remain resident, sedentary, year-round. a particular species migrates depends on a number of factors. The climate of the breeding area is important, as few species can with the harsh winters of inland Canada. ...
power point
... Increasing numbers of species disappearing every day. Extinction of different kinds of organisms has been much greater than before. A variety of human activities are the main causes. ...
... Increasing numbers of species disappearing every day. Extinction of different kinds of organisms has been much greater than before. A variety of human activities are the main causes. ...
Abundance, Diversity, & Invasive Species
... Invasion Nutrient-poor soils more resistant to invasive species Invasives do well in absence of native herbivores, pathogens (e.g., bladder campion) ...
... Invasion Nutrient-poor soils more resistant to invasive species Invasives do well in absence of native herbivores, pathogens (e.g., bladder campion) ...
WUQ – How do zebras and lions interact
... BIG IDEA – Organisms live in a community. Remove one species, and all of the other species are affected. Each species has a habitat and a niche - Habitat – WHERE an animal lives, “address” - Niche – HOW an animal lives, “profession” Organisms interact. They form a variety of relationships: 1. Predat ...
... BIG IDEA – Organisms live in a community. Remove one species, and all of the other species are affected. Each species has a habitat and a niche - Habitat – WHERE an animal lives, “address” - Niche – HOW an animal lives, “profession” Organisms interact. They form a variety of relationships: 1. Predat ...
Stream Fish Diversity Lab
... competitors; they cannot occupy the exact same niche. Niche Separation / Differentiation Competitors use different resources to coexist. Environmental heterogeneity - Creates more niche possibilities; therefore, higher environmental diversity leads to higher species diversity. ...
... competitors; they cannot occupy the exact same niche. Niche Separation / Differentiation Competitors use different resources to coexist. Environmental heterogeneity - Creates more niche possibilities; therefore, higher environmental diversity leads to higher species diversity. ...