1. The Freshwater Biome Ponds and Lakes
... Soil is nutrient poor Canopy is multilayered, little sun gets through One square km could have up to 100 tree species birds, bats, small mammals, and insects ...
... Soil is nutrient poor Canopy is multilayered, little sun gets through One square km could have up to 100 tree species birds, bats, small mammals, and insects ...
Chapter 17 Test Study Guide ( )
... 8. The association of two or more species that live together in a close long-term relationship is called ____________. There are three types of symbiotic relationships _______________, ________________, and ________________. 9. __________________ is a symbiotic relationship where both organisms bene ...
... 8. The association of two or more species that live together in a close long-term relationship is called ____________. There are three types of symbiotic relationships _______________, ________________, and ________________. 9. __________________ is a symbiotic relationship where both organisms bene ...
Ecology Unit
... A niche is determined by the tolerance limitations of an organism, or a limiting factor. Limiting factor- any biotic or abiotic factor that restricts the existence of organisms in a specific environment. ...
... A niche is determined by the tolerance limitations of an organism, or a limiting factor. Limiting factor- any biotic or abiotic factor that restricts the existence of organisms in a specific environment. ...
5-4 Community Stability PowerPoint
... alters a community but does not completely destroy it • Common after disturbances such as fire, logging, or farming • Occurs significantly faster than primary succession QuickTime™ and a decompressor are needed to see this picture. ...
... alters a community but does not completely destroy it • Common after disturbances such as fire, logging, or farming • Occurs significantly faster than primary succession QuickTime™ and a decompressor are needed to see this picture. ...
Chapter 5: “How Ecosystems Work”
... Energy passes from one organism to the next Trophic level: each step in this flow of energy Food chain: straight path Food web Interconnected food chains More realistic than food chain; why? ...
... Energy passes from one organism to the next Trophic level: each step in this flow of energy Food chain: straight path Food web Interconnected food chains More realistic than food chain; why? ...
Ecology - Images
... materials around cells & tissues in the body • Light: required by plants & other organisms to make food through photosynthesis • Living Space: organisms need room to obtain resources & reproduce ...
... materials around cells & tissues in the body • Light: required by plants & other organisms to make food through photosynthesis • Living Space: organisms need room to obtain resources & reproduce ...
Feeding Relationships
... make up an ORGANISM. • All the organ systems work together to serve the organism as a whole. ...
... make up an ORGANISM. • All the organ systems work together to serve the organism as a whole. ...
Competition, Predation, and Symbiosis
... Predators depend on prey to survive When the population of prey is low, the population of predators will go down When the prey population goes up, predator populations tend to go up as well It is a cycle ...
... Predators depend on prey to survive When the population of prey is low, the population of predators will go down When the prey population goes up, predator populations tend to go up as well It is a cycle ...
Ecology Notes
... Relationships in a Community - 2 • Predation - The feeding of one organisms on another – Predator • hunts/eats – Prey • gets eaten ...
... Relationships in a Community - 2 • Predation - The feeding of one organisms on another – Predator • hunts/eats – Prey • gets eaten ...
Understanding Our Environment
... Adaptation - Process where species acquire traits that allow them to survive in their environments. Limited range of physiological modifications. E.g transferring an indoor winter plant outside to outside during spring . Inheritance of specific genetic traits allowing a species to live in a pa ...
... Adaptation - Process where species acquire traits that allow them to survive in their environments. Limited range of physiological modifications. E.g transferring an indoor winter plant outside to outside during spring . Inheritance of specific genetic traits allowing a species to live in a pa ...
Watershed Structure and Function Related to Ecological
... 6. Communities can exist in several stable configurations 7. Keystone species may be essential to a community (species really matter) 8. Natural systems recycle essential nutrients 9. Climates change – communities change 10. Natural systems are products of evolution ...
... 6. Communities can exist in several stable configurations 7. Keystone species may be essential to a community (species really matter) 8. Natural systems recycle essential nutrients 9. Climates change – communities change 10. Natural systems are products of evolution ...
Basic Ecology Notes
... Population-a group of organisms of one species living in the same place at the same time that interbreed and compete with each other for resources (ex. food, mates, shelter) ...
... Population-a group of organisms of one species living in the same place at the same time that interbreed and compete with each other for resources (ex. food, mates, shelter) ...
Ecology - My eCoach
... As soil develops, these organisms are overgrown by grasses, shrubs and trees that are blown in or brought in by animals. Eventually, the area is colonized by plants that become the main form of vegetation. This process can take hundreds to thousands of years. ...
... As soil develops, these organisms are overgrown by grasses, shrubs and trees that are blown in or brought in by animals. Eventually, the area is colonized by plants that become the main form of vegetation. This process can take hundreds to thousands of years. ...
Lecture 8 - Community Interactions and Niche Diversity
... b. Some associations can become obligatory. The only pollinator of the yucca is the yucca moth. Moth's only food source (both adult and larvae) is yucca pollen and seeds. 4. Other mutualistic relationships are symbiotic- i.e. the two organisms live in close contact. a. Lichen - association of fungus ...
... b. Some associations can become obligatory. The only pollinator of the yucca is the yucca moth. Moth's only food source (both adult and larvae) is yucca pollen and seeds. 4. Other mutualistic relationships are symbiotic- i.e. the two organisms live in close contact. a. Lichen - association of fungus ...
Living Under Water
... ECOSYSTEM STABILITY AND INVASIVE SPECIES What are invasive species? A species that is not native to the ecosystem, and whose introduction may cause significantly greater economic, environmental or harm to human health than benefits. Invasive species compete so well in new ecosystems that they displa ...
... ECOSYSTEM STABILITY AND INVASIVE SPECIES What are invasive species? A species that is not native to the ecosystem, and whose introduction may cause significantly greater economic, environmental or harm to human health than benefits. Invasive species compete so well in new ecosystems that they displa ...
Wildlife and Conservation Management
... Management background (cont.) D. Biodiversity: the variety and variability of living organisms and their environments E. Habitat Corridors: habitat tracts in which wildlife can travel safely between sites. ...
... Management background (cont.) D. Biodiversity: the variety and variability of living organisms and their environments E. Habitat Corridors: habitat tracts in which wildlife can travel safely between sites. ...
Wildlife - Southern Oregon Forest Restoration Collaborative
... Use vegetation to increase shading of wetlands and microhabitats Retain water levels in wetlands when controlled by reservoir systems Increase microhabitat structures (e.g., woody ...
... Use vegetation to increase shading of wetlands and microhabitats Retain water levels in wetlands when controlled by reservoir systems Increase microhabitat structures (e.g., woody ...
Roles of Organisms in an Ecosystem PRODUCER
... • Secondary – Eats animals that eat plants • (CARNIVORES eating HERBIVORES) • Tertiary – Eats animals that eat other animals • (CARNIVORES eating CARNIVORES) ...
... • Secondary – Eats animals that eat plants • (CARNIVORES eating HERBIVORES) • Tertiary – Eats animals that eat other animals • (CARNIVORES eating CARNIVORES) ...
ecology
... Population-a group of organisms of one species living in the same place at the same time that interbreed and compete with each other for resources (ex. food, mates, shelter) ...
... Population-a group of organisms of one species living in the same place at the same time that interbreed and compete with each other for resources (ex. food, mates, shelter) ...
Factors that Limit Distribution
... occupy part of the year in which offspring have the greatest chances of survival • Birds in temperate zones use spring time - increasing/longer day length in spring - to begin nesting cycle at a point when adequate food resources will be available for their young in nest and as fledglings. • light a ...
... occupy part of the year in which offspring have the greatest chances of survival • Birds in temperate zones use spring time - increasing/longer day length in spring - to begin nesting cycle at a point when adequate food resources will be available for their young in nest and as fledglings. • light a ...
Intro to Ecology
... Many people believe that the world wide decline in frog populations is an indicator of population declines in other ...
... Many people believe that the world wide decline in frog populations is an indicator of population declines in other ...
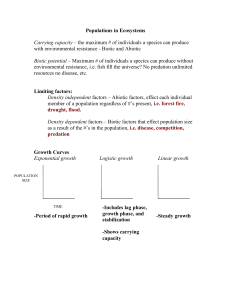
Populations in Ecosystems
... member of a population regardless of #’s present, i.e. forest fire, drought, flood. Density dependent factors – Biotic factors that effect population size as a result of the #’s in the population, i.e. disease, competition, predation ...
... member of a population regardless of #’s present, i.e. forest fire, drought, flood. Density dependent factors – Biotic factors that effect population size as a result of the #’s in the population, i.e. disease, competition, predation ...
Habitat
A habitat is an ecological or environmental area that is inhabited by human, a particular species of animal, plant, or other type of organism.A place where a living thing lives is its habitat. It is a place where it can find food, shelter, protection and mates for reproduction. It is the natural environment in which an organism lives, or the physical environment that surrounds a species population.A habitat is made up of physical factors such as soil, moisture, range of temperature, and availability of light as well as biotic factors such as the availability of food and the presence of predators. A habitat is not necessarily a geographic area—for a parasitic organism it is the body of its host, part of the host's body such as the digestive tract, or a cell within the host's body.