Within each ecosystem, there are habitats which may also vary in size
... the same time. All of the populations interact and form a community. The community of living things interacts with the non-living world around it to form the ecosystem. The habitat must supply the needs of organisms, such as food, water, temperature, oxygen, and minerals. If the population's needs a ...
... the same time. All of the populations interact and form a community. The community of living things interacts with the non-living world around it to form the ecosystem. The habitat must supply the needs of organisms, such as food, water, temperature, oxygen, and minerals. If the population's needs a ...
Overview of Rangeland Animals and Habitat
... Enlarged fermentation organ (cecum) that houses microbes (mostly bacteria and protozoa) that break down cellulose (into Volatile Fatty Acids or VFAs) that can be used as energy Horses, rabbits, and some rodents ...
... Enlarged fermentation organ (cecum) that houses microbes (mostly bacteria and protozoa) that break down cellulose (into Volatile Fatty Acids or VFAs) that can be used as energy Horses, rabbits, and some rodents ...
SPECIES INTERACTIONS
... Succession – gradual change in the composition of species over time; frequently following a disturbance. 1. Primary succession - succession on a new site by pioneer species such as lichens; eventually larger plants replace the pioneer species. Lichen = fungus living with algae or cyanobacteria (mut ...
... Succession – gradual change in the composition of species over time; frequently following a disturbance. 1. Primary succession - succession on a new site by pioneer species such as lichens; eventually larger plants replace the pioneer species. Lichen = fungus living with algae or cyanobacteria (mut ...
Conservation Biology
... Extinctions have occurred since life originated. However, since humans have been on the Earth, many extinctions have occurred as a result of human activities. Biologists are concerned about this trend in extinctions and human presence. Which of the following choices is correct about how biologists e ...
... Extinctions have occurred since life originated. However, since humans have been on the Earth, many extinctions have occurred as a result of human activities. Biologists are concerned about this trend in extinctions and human presence. Which of the following choices is correct about how biologists e ...
Understanding Our Environment
... (refrigeration and industry) - Broken down into active compounds by sunlight at high altitudes • Breakdown products destroy ozone in the ...
... (refrigeration and industry) - Broken down into active compounds by sunlight at high altitudes • Breakdown products destroy ozone in the ...
Sponsor presentation
... • The Grande Ronde Valley once held expansive areas of seasonal wetland; some reports suggest as much as 70,000 acres of the valley was seasonally inundated. • Most of those wetlands were drained to facilitate agricultural development; as little as 1% remained by ...
... • The Grande Ronde Valley once held expansive areas of seasonal wetland; some reports suggest as much as 70,000 acres of the valley was seasonally inundated. • Most of those wetlands were drained to facilitate agricultural development; as little as 1% remained by ...
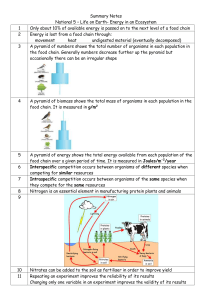
Energy in an Ecosystem Summary Notes
... food chain over a given period of time. It is measured in Joules/m-2/year Interspecific competition occurs between organisms of different species when competing for similar resources Intraspecific competition occurs between organisms of the same species when they compete for the same resources Nitro ...
... food chain over a given period of time. It is measured in Joules/m-2/year Interspecific competition occurs between organisms of different species when competing for similar resources Intraspecific competition occurs between organisms of the same species when they compete for the same resources Nitro ...
Biodiversity is the variety or richness of life at all structural levels
... Biodiversity is the variety or richness of life at all structural levels (molecular/genetic, species, ecosystem). It is an essential renewable resource. It is exploited and depleted as a result of the “Tragedy of the Commons” phenomenon. The current rate of biodiversity loss is comparable to previou ...
... Biodiversity is the variety or richness of life at all structural levels (molecular/genetic, species, ecosystem). It is an essential renewable resource. It is exploited and depleted as a result of the “Tragedy of the Commons” phenomenon. The current rate of biodiversity loss is comparable to previou ...
INTERACTIONS WITHIN COMMUNITIES
... The interaction is beneficial to both species. Ex. Bees and flowers Obligatory mutualism is when neither species can survive without the other (gut bacteria in herbivores, oxpecker birds). ...
... The interaction is beneficial to both species. Ex. Bees and flowers Obligatory mutualism is when neither species can survive without the other (gut bacteria in herbivores, oxpecker birds). ...
Symbiotic Relationships
... Limiting factors – • When one or more of the essential needs of a population (food, water, shelter) becomes scarce then the ecosystem cannot support all organisms of a population, the strongest and smartest will survive . ...
... Limiting factors – • When one or more of the essential needs of a population (food, water, shelter) becomes scarce then the ecosystem cannot support all organisms of a population, the strongest and smartest will survive . ...
(Trench Diagram)
... Extensive planning and hard work went into solving the problems the site was facing and creating this interpretative area. This project was underway in April of 2008 starting with the Environmental Assessment with all licences in place. Work began in the winter of 2008 starting with rock processing. ...
... Extensive planning and hard work went into solving the problems the site was facing and creating this interpretative area. This project was underway in April of 2008 starting with the Environmental Assessment with all licences in place. Work began in the winter of 2008 starting with rock processing. ...
Biology MCAS Prep 12/13 Topic: Evolution and Biodiversity
... the preference of female beetles to mate with only dark-colored male beetles the outbreak of plant diseases that either produce dark spots on leaves or cause leaves to lose their color the removal of almost all the vegetation from the habitat, exposing the light-colored soil underneath the vegetatio ...
... the preference of female beetles to mate with only dark-colored male beetles the outbreak of plant diseases that either produce dark spots on leaves or cause leaves to lose their color the removal of almost all the vegetation from the habitat, exposing the light-colored soil underneath the vegetatio ...
Ecology
... this area begins at the edge of the continental slope and extends from 200 meters to 5000 meters below the surface this zone is in perpetual darkness and supports a limited variety of life nutrients descend from the euphotic zone and permit life to exits in this region. 6. Abyssal zone (deepes ...
... this area begins at the edge of the continental slope and extends from 200 meters to 5000 meters below the surface this zone is in perpetual darkness and supports a limited variety of life nutrients descend from the euphotic zone and permit life to exits in this region. 6. Abyssal zone (deepes ...
LOTL 4 Ecoagriculture 2012
... natural systems to create a new ecosystem, including perennials and native species. By mimicking and re-creating an eco-system, biodiversity, stability, fertility, resilience and resistance are increased, there-by strengthening the overall agricultural system. ...
... natural systems to create a new ecosystem, including perennials and native species. By mimicking and re-creating an eco-system, biodiversity, stability, fertility, resilience and resistance are increased, there-by strengthening the overall agricultural system. ...
ECOSYSTEMS
... Interact- means they affect each other in some way Environment- all the factors in an organism’s life /surroundings that affect it. Habitat- area where animals live ...
... Interact- means they affect each other in some way Environment- all the factors in an organism’s life /surroundings that affect it. Habitat- area where animals live ...
Energy Flow - SchoolRack
... • Community – Several groups of organisms living together – Example: birds, bears, snakes, all living in the forest ...
... • Community – Several groups of organisms living together – Example: birds, bears, snakes, all living in the forest ...
Facts you need to know to pass the Living Environment Regents Exam
... 60.The failure to adapt to a changing environment may result in the extinction or death of a species 61.Extinction is the disappearance of an entire species and can occur if the environment changes 63.Ecology is the study of how organisms interact with the living and nonliving things 64.Biotic facto ...
... 60.The failure to adapt to a changing environment may result in the extinction or death of a species 61.Extinction is the disappearance of an entire species and can occur if the environment changes 63.Ecology is the study of how organisms interact with the living and nonliving things 64.Biotic facto ...
Ecology - Warren County Schools
... Parasitism: one organism lives on or inside another organism and harms it. ...
... Parasitism: one organism lives on or inside another organism and harms it. ...
(Create in Google Drive) Invasive Species Project Student Name Date
... large fishing operations • Increase in fish exports, providing more money and jobs ...
... large fishing operations • Increase in fish exports, providing more money and jobs ...
APES Ecology Lecture - yayscienceclass.com
... barriers that prevent the spread of those distinctive kinds of life to other regions. ...
... barriers that prevent the spread of those distinctive kinds of life to other regions. ...
Species Interactions - Iowa State University
... Draw graphs showing mortality % vs population density for: Natural disasters territorial predator ...
... Draw graphs showing mortality % vs population density for: Natural disasters territorial predator ...
Key Stage 3 Education sessions
... Adaptations for using a food source or against predators Features of predator and prey animals Trophic levels, food chains and webs Toxins in food chains ...
... Adaptations for using a food source or against predators Features of predator and prey animals Trophic levels, food chains and webs Toxins in food chains ...
Ecology Keynote (BIO)2016 copy 2
... liquid “honeydew” from aphids, which are in turn protected by the ants -- also pollination, bees. butterflies and flowering plants Commensalism : a relationship in which one species benefits and the other is neither harmed nor helped ex.clown fish “Nemo” and the sea anemone, the fish gets protection ...
... liquid “honeydew” from aphids, which are in turn protected by the ants -- also pollination, bees. butterflies and flowering plants Commensalism : a relationship in which one species benefits and the other is neither harmed nor helped ex.clown fish “Nemo” and the sea anemone, the fish gets protection ...
Outline Community Ecology and Ecosystems
... water and light, soil pH, and mineral nutrients. 4. Describe the biotic and abiotic factors that affect the distribution of animal species within an environment, including temperature, availability of water and breeding sites, food supply, and territory. Environmental Gradients 5. Describe how abiot ...
... water and light, soil pH, and mineral nutrients. 4. Describe the biotic and abiotic factors that affect the distribution of animal species within an environment, including temperature, availability of water and breeding sites, food supply, and territory. Environmental Gradients 5. Describe how abiot ...
Habitat
A habitat is an ecological or environmental area that is inhabited by human, a particular species of animal, plant, or other type of organism.A place where a living thing lives is its habitat. It is a place where it can find food, shelter, protection and mates for reproduction. It is the natural environment in which an organism lives, or the physical environment that surrounds a species population.A habitat is made up of physical factors such as soil, moisture, range of temperature, and availability of light as well as biotic factors such as the availability of food and the presence of predators. A habitat is not necessarily a geographic area—for a parasitic organism it is the body of its host, part of the host's body such as the digestive tract, or a cell within the host's body.