Lecture - Chapter 4 - Biotic Components of Ecosystems
... Each species produces more offspring than will survive to maturity (David Lack, 1943) ...
... Each species produces more offspring than will survive to maturity (David Lack, 1943) ...
House sparrows from England were released in the US They have
... Strip mining (also known as open cast, mountaintop or surface mining) involves scraping away earth and rocks to get to coal buried near the surface. In many cases, mountains are literally blasted apart to reach thin coal seams within, leaving permanent scars on the landscape as a result. Even though ...
... Strip mining (also known as open cast, mountaintop or surface mining) involves scraping away earth and rocks to get to coal buried near the surface. In many cases, mountains are literally blasted apart to reach thin coal seams within, leaving permanent scars on the landscape as a result. Even though ...
Name: :__
... 31. What term describes the process by which a population becomes better suited to its environment? 32. What happens to two populations of the same species if they are separated from each other for a long time? 33. What are homologous structures? ...
... 31. What term describes the process by which a population becomes better suited to its environment? 32. What happens to two populations of the same species if they are separated from each other for a long time? 33. What are homologous structures? ...
APES Review - Northern Highlands
... Deserts: covers about one fifth of the Earth’s surface and occur where rainfall is less than 50 cm/year. Most deserts occur at low latitudes, have a considerable amount of specialized vegetation, as well as specialized animals. Soils have abundant nutrients, need only water to become productive, and ...
... Deserts: covers about one fifth of the Earth’s surface and occur where rainfall is less than 50 cm/year. Most deserts occur at low latitudes, have a considerable amount of specialized vegetation, as well as specialized animals. Soils have abundant nutrients, need only water to become productive, and ...
Ecosystems
... • Ecosystems can be delicately balanced, so if there is a change, it can affect the animals and other plants in that ecosystem • Cutting down trees could endanger squirrels and other animals that rely on acorns for food. ...
... • Ecosystems can be delicately balanced, so if there is a change, it can affect the animals and other plants in that ecosystem • Cutting down trees could endanger squirrels and other animals that rely on acorns for food. ...
ECOLOGY
... occurs when a disturbance of some kind (fire, land clearing or plowing) changes the community without removing the soil. Begins with grasses and then follows the same pattern as a primary succession. ...
... occurs when a disturbance of some kind (fire, land clearing or plowing) changes the community without removing the soil. Begins with grasses and then follows the same pattern as a primary succession. ...
Check out a Powerpoint slideshow from one of Tao`s presentations
... Dams on southwestern rivers change seasonal flood patterns… ...
... Dams on southwestern rivers change seasonal flood patterns… ...
Chap 4 PowerPoint
... Participants may be benefited, harmed or unaffected by the relationship Result of coevolution ...
... Participants may be benefited, harmed or unaffected by the relationship Result of coevolution ...
Population Biology Chapter 4 Section 1
... 4. Carrying Capacity is the number of organisms of one species an environment can support. ...
... 4. Carrying Capacity is the number of organisms of one species an environment can support. ...
Biodiversity and conservation in Pakistan
... Department of Plant Sciences, Quiad-i-Azam University Islamabad, Pakistan ...
... Department of Plant Sciences, Quiad-i-Azam University Islamabad, Pakistan ...
The Needs of Living Things
... need to get food from somewhere other than themselves. THEY EAT!! – Example: All animals are Heterotrophs as well as mushrooms and slime molds. ...
... need to get food from somewhere other than themselves. THEY EAT!! – Example: All animals are Heterotrophs as well as mushrooms and slime molds. ...
Chp7
... – Identify the physiological tolerance range of the organism for this life cycle phase – Show that the temperature or moisture range in the microclimate where the organism lives is permissible for sites within the geographical range, and lethal for sites outside the normal geographic range ...
... – Identify the physiological tolerance range of the organism for this life cycle phase – Show that the temperature or moisture range in the microclimate where the organism lives is permissible for sites within the geographical range, and lethal for sites outside the normal geographic range ...
Name
... K represents the carrying capacity, which is the maximum number of individuals in a species that the environment can support for an extended time. It is limited by the resources available to individuals in the populations. The graph depicts population growth slows following a period of exponential g ...
... K represents the carrying capacity, which is the maximum number of individuals in a species that the environment can support for an extended time. It is limited by the resources available to individuals in the populations. The graph depicts population growth slows following a period of exponential g ...
Vocabulary List Alien species: Species introduced into ecosystems
... with other species. Food Chain: A group of animals and plants in a community through which energy flows in the form of food. Fossil: The remains or impression of a prehistoric organism preserved in petrified form or as a mold or cast in rock. Foundation species: Species that plays a major role in sh ...
... with other species. Food Chain: A group of animals and plants in a community through which energy flows in the form of food. Fossil: The remains or impression of a prehistoric organism preserved in petrified form or as a mold or cast in rock. Foundation species: Species that plays a major role in sh ...
Dec 8 - PPT: Introduction to Marine Biomes
... • limited ability to move and can migrate vertically through the water from day to night. • Some drifters can photosynthesize while others are consumers. • Plankton is very important as it occupies the first two or three links in the marine food chains. The animal members of the plankton ...
... • limited ability to move and can migrate vertically through the water from day to night. • Some drifters can photosynthesize while others are consumers. • Plankton is very important as it occupies the first two or three links in the marine food chains. The animal members of the plankton ...
Ecology Unit
... Population-a group of organisms of one species living in the same place that interbreed and compete with each other for resources (ex. food, mates, shelter) ...
... Population-a group of organisms of one species living in the same place that interbreed and compete with each other for resources (ex. food, mates, shelter) ...
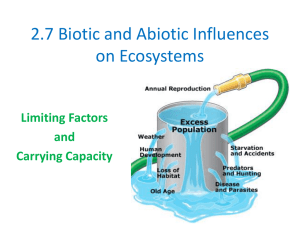
2.7 Biotic and Abiotic Influences on Ecosystems
... that a given ecosystem can sustain. • As population's size increases, the demand for resources, such as food, water, shelter, and space also increase. • Eventually, there will not be enough resources for ...
... that a given ecosystem can sustain. • As population's size increases, the demand for resources, such as food, water, shelter, and space also increase. • Eventually, there will not be enough resources for ...
Chapter 4: Ecosystems and Communities
... 5. Become extinct in that area What type of species overcome this more easily? ...
... 5. Become extinct in that area What type of species overcome this more easily? ...
Animal Kingdom Notes
... abdomen. All have 4 pairs of legs, no antennae • Scorpions have poisonous stingers and pincers • Spiders release enzymes into their food and suck out the liquids. ...
... abdomen. All have 4 pairs of legs, no antennae • Scorpions have poisonous stingers and pincers • Spiders release enzymes into their food and suck out the liquids. ...
Habitat
A habitat is an ecological or environmental area that is inhabited by human, a particular species of animal, plant, or other type of organism.A place where a living thing lives is its habitat. It is a place where it can find food, shelter, protection and mates for reproduction. It is the natural environment in which an organism lives, or the physical environment that surrounds a species population.A habitat is made up of physical factors such as soil, moisture, range of temperature, and availability of light as well as biotic factors such as the availability of food and the presence of predators. A habitat is not necessarily a geographic area—for a parasitic organism it is the body of its host, part of the host's body such as the digestive tract, or a cell within the host's body.