Cycle of Renewal Drawings 4-4
... Cycle: an interval of time in which a repeated sequence of events is completed Habitat area: a natural area that provides habitat for plants and animals Washington State EALRs Science 1.1 Categorize plants and animals into groups according to how they accomplish life processes. 1.2 Describe the life ...
... Cycle: an interval of time in which a repeated sequence of events is completed Habitat area: a natural area that provides habitat for plants and animals Washington State EALRs Science 1.1 Categorize plants and animals into groups according to how they accomplish life processes. 1.2 Describe the life ...
Chapter 53 - Canyon ISD
... Disturbance and Community Structure • Disturbances: events such as storms, fire, floods, drought, overgrazing, or human activities that damage communities, remove organisms from them, and alter resource availability • Humans are the most widespread agents of disturbance – Logging and clearing, mini ...
... Disturbance and Community Structure • Disturbances: events such as storms, fire, floods, drought, overgrazing, or human activities that damage communities, remove organisms from them, and alter resource availability • Humans are the most widespread agents of disturbance – Logging and clearing, mini ...
Biotic and Abiotic Factors in an Ecosystem
... The first panel below shows an area covered with rock and ash from a volcanic eruption. When organisms begin to colonize an area such as this, they appear in a predictable order. This is called ecological succession. The first species to colonize this area are called pioneer species. The panels foll ...
... The first panel below shows an area covered with rock and ash from a volcanic eruption. When organisms begin to colonize an area such as this, they appear in a predictable order. This is called ecological succession. The first species to colonize this area are called pioneer species. The panels foll ...
Ecological Pyramids
... There are three types of ecological pyramids, energy, numbers and biomass. When energy is passed along a food chain there are substantial energy losses that occur during each transfer. When an organism consumes another organism it will obtain both physical matter and chemical energy from that organi ...
... There are three types of ecological pyramids, energy, numbers and biomass. When energy is passed along a food chain there are substantial energy losses that occur during each transfer. When an organism consumes another organism it will obtain both physical matter and chemical energy from that organi ...
ecology ppt
... Species/ Organism - individual living thing Population – group of organisms of same species in same area Community – many populations or organisms living close enough for interaction Ecosystem – include biotic & abiotic components in an environment Biome – group of ecosystems with same climate Biosp ...
... Species/ Organism - individual living thing Population – group of organisms of same species in same area Community – many populations or organisms living close enough for interaction Ecosystem – include biotic & abiotic components in an environment Biome – group of ecosystems with same climate Biosp ...
wetland values
... approximately one year of it juvenile life cycle in fresh and brackish wetlands, and also for maintaining wetland processes – for example, physical features such as Riparian areas are necessary for proper function of riverine Ecosystems because they provide habitat for aquatic macroinverbrates, and ...
... approximately one year of it juvenile life cycle in fresh and brackish wetlands, and also for maintaining wetland processes – for example, physical features such as Riparian areas are necessary for proper function of riverine Ecosystems because they provide habitat for aquatic macroinverbrates, and ...
Main page ==> oil-refining http://www.ycysoft.com Copyright ycysoft
... trees, eat nuts, or hoard for the winter so this creates… Competition – When species, or individuals, attempt to use the same limited resource Sometimes species don’t even recognize their competition! Indirect Competition – Occurs even when the species may never come into direct contact Ex: An aphid ...
... trees, eat nuts, or hoard for the winter so this creates… Competition – When species, or individuals, attempt to use the same limited resource Sometimes species don’t even recognize their competition! Indirect Competition – Occurs even when the species may never come into direct contact Ex: An aphid ...
Main page ==> oil-refining http://www.ycysoft.com Copyright ycysoft
... trees, eat nuts, or hoard for the winter so this creates… Competition – When species, or individuals, attempt to use the same limited resource Sometimes species don’t even recognize their competition! Indirect Competition – Occurs even when the species may never come into direct contact Ex: An aphid ...
... trees, eat nuts, or hoard for the winter so this creates… Competition – When species, or individuals, attempt to use the same limited resource Sometimes species don’t even recognize their competition! Indirect Competition – Occurs even when the species may never come into direct contact Ex: An aphid ...
Final – Day 2 – Written Guide
... species may have on the food web and the organisms in the ecosystem. C5 – On some isolated islands, some species of birds have evolved that are unable to fly. Why do you think this occurred? C5 – Where would you expect to find a greater proportion of specialized species – on a large continent or a s ...
... species may have on the food web and the organisms in the ecosystem. C5 – On some isolated islands, some species of birds have evolved that are unable to fly. Why do you think this occurred? C5 – Where would you expect to find a greater proportion of specialized species – on a large continent or a s ...
Brokenhead Wetland Ecological Reserve
... rare in North America. A calcareous fen is a kind of wetland characterized by a fluctuating water table. Groundwater and surface-water movement is a common characteristic of fens and can be observed in the channels and pools in the Brokenhead wetland. The water is rich in calcium carbonate. Fens are ...
... rare in North America. A calcareous fen is a kind of wetland characterized by a fluctuating water table. Groundwater and surface-water movement is a common characteristic of fens and can be observed in the channels and pools in the Brokenhead wetland. The water is rich in calcium carbonate. Fens are ...
Invasive species
... • The abundance term is often greatest at lower trophic positions – Producers and primary consumers vs. predators – Becomes impactful when IS becomes dominant ...
... • The abundance term is often greatest at lower trophic positions – Producers and primary consumers vs. predators – Becomes impactful when IS becomes dominant ...
Lecture 37 - Ecology - Chapter 46 Niche Community
... Plants partitioning prairie soil with roots of different lengths ...
... Plants partitioning prairie soil with roots of different lengths ...
Life Science SOL Review Packet
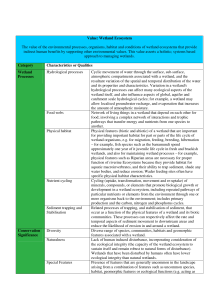
... oxygen and give off carbon dioxide, and plants use the animals’ carbon dioxide. 74. The nitrogen cycle where plants use nitrogen, animals eat the plants (, bacteria on plants fix nitrogen and change it to a usable form) animals and plants die and decompose and animals produce fecal matter replenishi ...
... oxygen and give off carbon dioxide, and plants use the animals’ carbon dioxide. 74. The nitrogen cycle where plants use nitrogen, animals eat the plants (, bacteria on plants fix nitrogen and change it to a usable form) animals and plants die and decompose and animals produce fecal matter replenishi ...
Predators and Wild Turkeys
... controversial issue. There are situations where it may have a place, such as an area with a newly established population of a rare species. However, making an impact on a predator population is ...
... controversial issue. There are situations where it may have a place, such as an area with a newly established population of a rare species. However, making an impact on a predator population is ...
Why does it matter- what are the benefits of biodiversity?
... ecological complexes in which they occur. Diversity can be defined as the number of different items and their relative frequency. For biodiversity, these items are organised at many levels, ranging from complete ecosystems to the chemical structures that are the molecular basis of heredity. Thus, th ...
... ecological complexes in which they occur. Diversity can be defined as the number of different items and their relative frequency. For biodiversity, these items are organised at many levels, ranging from complete ecosystems to the chemical structures that are the molecular basis of heredity. Thus, th ...
oregon forest-pacific sb snail po draft fullsize
... Risk in the Coastal Lowlands. BC Ministry of Environment. In draft 2007 (Available by request from the regional Species at Risk Biologist). Determine the full range extent and potential presence/habitat suitability of these species within BC, especially in areas under pressure from development or ...
... Risk in the Coastal Lowlands. BC Ministry of Environment. In draft 2007 (Available by request from the regional Species at Risk Biologist). Determine the full range extent and potential presence/habitat suitability of these species within BC, especially in areas under pressure from development or ...
otter
... Otters ate members of the weasel family, the Mustelidae, which also includes badgers, mink, polecates and martens. Otters are semi-aquatic carnivores which obtain most if not all their food in the water. In appearance they are small to medum sized animals with short legs, long slender bodies and a l ...
... Otters ate members of the weasel family, the Mustelidae, which also includes badgers, mink, polecates and martens. Otters are semi-aquatic carnivores which obtain most if not all their food in the water. In appearance they are small to medum sized animals with short legs, long slender bodies and a l ...
Ecosystems Unit Review
... chemicals that break down the rock and release nutrients. Along with these chemical changes are physical changes as the rock is exposed and wears away and more nutrients are released. Changes in biotic and abiotic conditions create changes in plant life and then changes in animal life as plants attr ...
... chemicals that break down the rock and release nutrients. Along with these chemical changes are physical changes as the rock is exposed and wears away and more nutrients are released. Changes in biotic and abiotic conditions create changes in plant life and then changes in animal life as plants attr ...
Class Results: Kite graphs showing distribution of species from low
... covered by sea water longer than the other zones. They live just below the mud/sand surface. The deepest we found them was 10 cm. Cockles need food and oxygen to carry out their life processes to survive. They have adaptations to carry out gas exchange and feed. They have gills that carry out gas ex ...
... covered by sea water longer than the other zones. They live just below the mud/sand surface. The deepest we found them was 10 cm. Cockles need food and oxygen to carry out their life processes to survive. They have adaptations to carry out gas exchange and feed. They have gills that carry out gas ex ...
Evolution Quiz #1
... S7L4: Students will examine the dependence of organisms on one another and their environments. d. Categorize relationships between organisms that are competitive or mutually beneficial. Answer the following questions by bubbling in the correct answer on your answer document. 1. Two populations with ...
... S7L4: Students will examine the dependence of organisms on one another and their environments. d. Categorize relationships between organisms that are competitive or mutually beneficial. Answer the following questions by bubbling in the correct answer on your answer document. 1. Two populations with ...
Unit 5
... Events that occur in the frame of what is sometimes called ecological time translate into effects over the longer scale of evolutionary time. 3. Explain the importance of temperature, water, light, soil, and wind to living organisms. Temperature – important because most organisms are unable to moder ...
... Events that occur in the frame of what is sometimes called ecological time translate into effects over the longer scale of evolutionary time. 3. Explain the importance of temperature, water, light, soil, and wind to living organisms. Temperature – important because most organisms are unable to moder ...
Extinction, Colonization, and Metapopulations: Environmental
... extinctions of any but the smallest populations are determined by persistent changes in the local environm e n t (Harrison 1991; C.D. Thomas 1993, 1994), and large populations are not i m m u n e to these changes (J. A. Thomas 1991). For British butterflies, almost all local extinctions can be attri ...
... extinctions of any but the smallest populations are determined by persistent changes in the local environm e n t (Harrison 1991; C.D. Thomas 1993, 1994), and large populations are not i m m u n e to these changes (J. A. Thomas 1991). For British butterflies, almost all local extinctions can be attri ...
Sclerocactus mesae-verdae - Navajo Nation Department of Fish and
... formations. It also grows in Menefee Formation soils near Sheep Springs, NM, but in that case the plant is rooted in Mancos Shale, which closely underlies the soil surface. Soil surfaces within appropriate habitat can have a cover of gravel or cobbles ranging from 0% to 100%. Gravel composition is v ...
... formations. It also grows in Menefee Formation soils near Sheep Springs, NM, but in that case the plant is rooted in Mancos Shale, which closely underlies the soil surface. Soil surfaces within appropriate habitat can have a cover of gravel or cobbles ranging from 0% to 100%. Gravel composition is v ...
Habitat
A habitat is an ecological or environmental area that is inhabited by human, a particular species of animal, plant, or other type of organism.A place where a living thing lives is its habitat. It is a place where it can find food, shelter, protection and mates for reproduction. It is the natural environment in which an organism lives, or the physical environment that surrounds a species population.A habitat is made up of physical factors such as soil, moisture, range of temperature, and availability of light as well as biotic factors such as the availability of food and the presence of predators. A habitat is not necessarily a geographic area—for a parasitic organism it is the body of its host, part of the host's body such as the digestive tract, or a cell within the host's body.