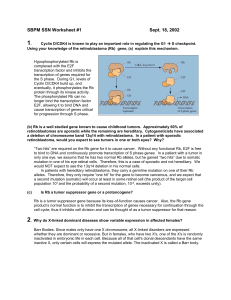
31.1 The Neuron Functions of the Nervous System and external
... At the end of the axon, impulses can be transmitted to the next neuron. The point at which a neuron transfers an impulse to another cell is called a synapse. When an impulse arrives ves at the synapse, neurotransmitters,, chemicals that transmit an impulse across a synapse to another cell, are relea ...
... At the end of the axon, impulses can be transmitted to the next neuron. The point at which a neuron transfers an impulse to another cell is called a synapse. When an impulse arrives ves at the synapse, neurotransmitters,, chemicals that transmit an impulse across a synapse to another cell, are relea ...
control systems of the body - chapter 11
... Neurons are separated by a gap, a synapse, which is the small space between two neurons or the space between a neuron and a muscle cell, gland, or organ. In a typical synapse between two neurons the neuron before the synapse is called the presynaptic neuron and the neuron after the synapse is called ...
... Neurons are separated by a gap, a synapse, which is the small space between two neurons or the space between a neuron and a muscle cell, gland, or organ. In a typical synapse between two neurons the neuron before the synapse is called the presynaptic neuron and the neuron after the synapse is called ...
The Nervous System: Neural Tissue
... causes Na ion gates to open and local __________________ to occur. 3. Neurotransmitters – two classes 1. __________________: Acetylcholine (_______), Norepinephrine, Dopamine, etc. 2. __________________: Gamma-aminobutyric acid (________), Glycine, etc. C. Termination & reabsorption of neurotransmit ...
... causes Na ion gates to open and local __________________ to occur. 3. Neurotransmitters – two classes 1. __________________: Acetylcholine (_______), Norepinephrine, Dopamine, etc. 2. __________________: Gamma-aminobutyric acid (________), Glycine, etc. C. Termination & reabsorption of neurotransmit ...
Cell Communication
... Ion Channel Receptors • Ligand-Gated Ion Channel: contains a “gated” region that allows or blocks ions from entering cell (Na+, Ca2+) ▫ When signal (ligand) binds, gate opens & ions enter ▫ When ligand absent, gate is closed ▫ Play role in nervous system (neurotransmitters act as ligands) ...
... Ion Channel Receptors • Ligand-Gated Ion Channel: contains a “gated” region that allows or blocks ions from entering cell (Na+, Ca2+) ▫ When signal (ligand) binds, gate opens & ions enter ▫ When ligand absent, gate is closed ▫ Play role in nervous system (neurotransmitters act as ligands) ...
afaf-el-ansary-king-saud-university-saudi
... enriched content of unsaturated lipids, as well as to its elevated rate of free radical generation derived from neurotransmitters metabolism, and poor radical scavenging mechanisms. It is also hypothesized that autistic patients as poor detoxifiers have reduced ability to eliminate mercury. Higher ...
... enriched content of unsaturated lipids, as well as to its elevated rate of free radical generation derived from neurotransmitters metabolism, and poor radical scavenging mechanisms. It is also hypothesized that autistic patients as poor detoxifiers have reduced ability to eliminate mercury. Higher ...
Questions with Answers
... a second mutation (somatic) will occur at least in some retinal cell (the product of the target cell population 107 and the probability of a second mutation, 10-6, exceeds unity). (c) ...
... a second mutation (somatic) will occur at least in some retinal cell (the product of the target cell population 107 and the probability of a second mutation, 10-6, exceeds unity). (c) ...
The Human Brain
... by incredibly quick chemical reactions. Different neurons can have different types of chemical transmitters which allow the messages to be passed from neuron to neuron. You may have heard of some of these, serotonin, noradrenaline, dopamine etc. So throughout your life, even when you are sleeping, t ...
... by incredibly quick chemical reactions. Different neurons can have different types of chemical transmitters which allow the messages to be passed from neuron to neuron. You may have heard of some of these, serotonin, noradrenaline, dopamine etc. So throughout your life, even when you are sleeping, t ...
DMPK Scientist
... ESSENTIAL DUTIES AND RESPONSIBILITIES: Responsible for in vitro assays including metabolic stability, reaction phenotype, CYP inhibition, protein binding and drug transporters. The candidates must have demonstrated skills in at least in one of the followings: (i) Caco-2 cell model as applied to drug ...
... ESSENTIAL DUTIES AND RESPONSIBILITIES: Responsible for in vitro assays including metabolic stability, reaction phenotype, CYP inhibition, protein binding and drug transporters. The candidates must have demonstrated skills in at least in one of the followings: (i) Caco-2 cell model as applied to drug ...
Human Anatomy, First Edition McKinley&O'Loughlin
... Detect stimuli from the external environment. Special senses are considered exteroceptors because they usually interpret external stimuli. Also found in the mucous membranes that open to the outside of the body, such as the nasal cavity, oral cavity, vagina, and anal canal. ...
... Detect stimuli from the external environment. Special senses are considered exteroceptors because they usually interpret external stimuli. Also found in the mucous membranes that open to the outside of the body, such as the nasal cavity, oral cavity, vagina, and anal canal. ...
Nervous System webquest……
... http://www.pbs.org/wnet/brain 1. Click on “mind illusions” and try one the illusions. Explain how it works. 2. Click on “teenage Brain” and explore why teens sleep more than adults. 3. Explore the link about desire and addictions. Briefly explain what causes addictions. Part 9: Genes to Cognition ht ...
... http://www.pbs.org/wnet/brain 1. Click on “mind illusions” and try one the illusions. Explain how it works. 2. Click on “teenage Brain” and explore why teens sleep more than adults. 3. Explore the link about desire and addictions. Briefly explain what causes addictions. Part 9: Genes to Cognition ht ...
Module 22
... Promising people a reward for a task they already enjoy can backfire. If children enjoy doing something because it is fun (intrinsic motivation), they may lose interest in the task if they are promised a reward for it (extrinsic motivation). Thus, in some circumstances, offering material gains (a re ...
... Promising people a reward for a task they already enjoy can backfire. If children enjoy doing something because it is fun (intrinsic motivation), they may lose interest in the task if they are promised a reward for it (extrinsic motivation). Thus, in some circumstances, offering material gains (a re ...
FOCUS ON VOCABULARY AND LANGUAGE Biology, Cognition
... Promising people a reward for a task they already enjoy can backfire. If children enjoy doing something because it is fun (intrinsic motivation), they may lose interest in the task if they are promised a reward for it (extrinsic motivation). Thus, in some circumstances, offering material gains (a re ...
... Promising people a reward for a task they already enjoy can backfire. If children enjoy doing something because it is fun (intrinsic motivation), they may lose interest in the task if they are promised a reward for it (extrinsic motivation). Thus, in some circumstances, offering material gains (a re ...
Ch. 48 - 49
... Name the three types of neurons and their functions. Which make up the CNS and the PNS? Describe the main parts of a neuron. ...
... Name the three types of neurons and their functions. Which make up the CNS and the PNS? Describe the main parts of a neuron. ...
File
... V. Sleep and Dreams • A. Biological Rhythms – 1. Biological Rhythms = patterns associated with our biological clock. These patterns can span days, hours or even minutes. – 2. Circadian Rhythms = Biological cycles that occur about every 24 hours. For example or sleep, blood pressure, body temperatu ...
... V. Sleep and Dreams • A. Biological Rhythms – 1. Biological Rhythms = patterns associated with our biological clock. These patterns can span days, hours or even minutes. – 2. Circadian Rhythms = Biological cycles that occur about every 24 hours. For example or sleep, blood pressure, body temperatu ...
The human brain
... We are born with a complete set of neurons. What changes in maturation is the connections between the neurons. On average, we lose about 20% of our neurons by the time we die. ...
... We are born with a complete set of neurons. What changes in maturation is the connections between the neurons. On average, we lose about 20% of our neurons by the time we die. ...
Module 4 ap questions
... (E) Sensory and motor connections to other brain Regions 4 or 3 44. Dopamine, norepinephrine, and acetylcholine are all (AP94) (A) Hormones excreted by the endocrine glands (B) Secretions of the exocrine glands (C) Drugs used in the therapeutic treatment of memory disorders (D) Enzymes involved with ...
... (E) Sensory and motor connections to other brain Regions 4 or 3 44. Dopamine, norepinephrine, and acetylcholine are all (AP94) (A) Hormones excreted by the endocrine glands (B) Secretions of the exocrine glands (C) Drugs used in the therapeutic treatment of memory disorders (D) Enzymes involved with ...
Chapter 2 Vocabulary
... 48. __________________ __________________ , located in the left frontal lobe, is involved in controlling the motor ability to produce speech. (p. 69) 49. __________________ __________________ , located in the left temporal lobe, is involved in language comprehension. (p. 69) 50. __________________ i ...
... 48. __________________ __________________ , located in the left frontal lobe, is involved in controlling the motor ability to produce speech. (p. 69) 49. __________________ __________________ , located in the left temporal lobe, is involved in language comprehension. (p. 69) 50. __________________ i ...
here - TurkoTek
... ---Lesions to this cause the removal of personality. Parietal-Temporal-Occipital Association Cortex- involved in integrating sensory perception. Subcortical Structures- not really part of cortex. a.) Basal Nuclei- (Basal Ganglia) inhibition of muscle contraction ---if don’t have this, will have con ...
... ---Lesions to this cause the removal of personality. Parietal-Temporal-Occipital Association Cortex- involved in integrating sensory perception. Subcortical Structures- not really part of cortex. a.) Basal Nuclei- (Basal Ganglia) inhibition of muscle contraction ---if don’t have this, will have con ...
Read the perspective by Temel and Jahanshahi here.
... for the successful application of deep brain stimulation of the subthalamic nucleus in patients with Parkinson’s disease. In contrast to earlier techniques of electrical stimulation in which electrodes are placed temporarily in the brain and stimulated by external devices to simply drive neuronal ac ...
... for the successful application of deep brain stimulation of the subthalamic nucleus in patients with Parkinson’s disease. In contrast to earlier techniques of electrical stimulation in which electrodes are placed temporarily in the brain and stimulated by external devices to simply drive neuronal ac ...
The Body and the Brain neurons first
... Others, like the neurons that run through our legs, can be several feet long. Myelin is a white fatty substance that insulates and protects the axon. The myelin casing also helps to speed up the transmission of the message. The fibers at the end of the axon are called axon terminals. Messages are se ...
... Others, like the neurons that run through our legs, can be several feet long. Myelin is a white fatty substance that insulates and protects the axon. The myelin casing also helps to speed up the transmission of the message. The fibers at the end of the axon are called axon terminals. Messages are se ...
DOPAMINE
... and loss of satisfaction. When dopamine levels are elevated symptoms may manifest in the form of anxiety or hyperactivity. ...
... and loss of satisfaction. When dopamine levels are elevated symptoms may manifest in the form of anxiety or hyperactivity. ...
Clinical neurochemistry

Clinical neurochemistry is the field of neurological biochemistry which relates biochemical phenomena to clinical symptomatic manifestations in humans. While neurochemistry is mostly associated with the effects of neurotransmitters and similarly-functioning chemicals on neurons themselves, clinical neurochemistry relates these phenomena to system-wide symptoms. Clinical neurochemistry is related to neurogenesis, neuromodulation, neuroplasticity, neuroendocrinology, and neuroimmunology in the context of associating neurological findings at both lower and higher level organismal functions.