The Cl Area of the Brainstem in Tonic and Reflex
... ventrolateral medulla. In rat, the critical zone corresponds to a small region containing a subpopulation of the adrenergic Cl group, defined imnmnocytochemlcally by the presence of the epinephrinesyntheslzing enzyme phenylethanolamlne iV-methyltransferase. Neurons of this region (the Cl area), poss ...
... ventrolateral medulla. In rat, the critical zone corresponds to a small region containing a subpopulation of the adrenergic Cl group, defined imnmnocytochemlcally by the presence of the epinephrinesyntheslzing enzyme phenylethanolamlne iV-methyltransferase. Neurons of this region (the Cl area), poss ...
Calcium-activated chloride channels: a new target to
... neurons, which might be assisted by the outwardly rectifying characteristic of the ANO2 channels. This phenotype was also observed in the knockdown of ANO2 in CA1 hippocampal neurons, providing further evidence that Ca2+-activated Cl− conductance via ANO2 channels hyperpolarizes the membrane potenti ...
... neurons, which might be assisted by the outwardly rectifying characteristic of the ANO2 channels. This phenotype was also observed in the knockdown of ANO2 in CA1 hippocampal neurons, providing further evidence that Ca2+-activated Cl− conductance via ANO2 channels hyperpolarizes the membrane potenti ...
Introduction
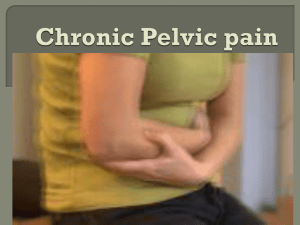
... Patients with chronic pelvic pain are frequently anxious and depressed. Their marital, social, and occupational lives have usually been disrupted. About 12% to 19% of hysterectomies are performed for pelvic pain, and 30% of patients who present to pain clinics have already had a hysterectomy Approxi ...
... Patients with chronic pelvic pain are frequently anxious and depressed. Their marital, social, and occupational lives have usually been disrupted. About 12% to 19% of hysterectomies are performed for pelvic pain, and 30% of patients who present to pain clinics have already had a hysterectomy Approxi ...
Nervous System: Nervous Tissue (Chapter 12) Lecture Materials for
... Relative Refractory Period = +30mV to ! ! -70mV (return to resting potential), Na+ ! ! channels closed, membrane capable of ! ! second action potential but requires ! ! larger/longer stimulus (threshold elevated)! Amy Warenda Czura, Ph.D. ...
... Relative Refractory Period = +30mV to ! ! -70mV (return to resting potential), Na+ ! ! channels closed, membrane capable of ! ! second action potential but requires ! ! larger/longer stimulus (threshold elevated)! Amy Warenda Czura, Ph.D. ...
Chemicals in and Around the Cell.
... describe and explain the importance of the blood–brain barrier. 3. Briefly describe the neural circuitry responsible for a withdrawal reflex and its inhibition by neurons in the brain. 4. Describe the measurement of the action potential and explain how the balance between the forces of diffusion and ...
... describe and explain the importance of the blood–brain barrier. 3. Briefly describe the neural circuitry responsible for a withdrawal reflex and its inhibition by neurons in the brain. 4. Describe the measurement of the action potential and explain how the balance between the forces of diffusion and ...
Parkinson`s Disease
... clear consciousness (i.e., in the absence of delirium). Dementia consists of a variety of symptoms that suggest chronic and widespread dysfunction. Global impairment of intellect is the essential feature, manifested as difficulty with memory, attention, thinking, and comprehension. Other mental func ...
... clear consciousness (i.e., in the absence of delirium). Dementia consists of a variety of symptoms that suggest chronic and widespread dysfunction. Global impairment of intellect is the essential feature, manifested as difficulty with memory, attention, thinking, and comprehension. Other mental func ...
Sample
... describe and explain the importance of the blood–brain barrier. 3. Briefly describe the neural circuitry responsible for a withdrawal reflex and its inhibition by neurons in the brain. 4. Describe the measurement of the action potential and explain how the balance between the forces of diffusion and ...
... describe and explain the importance of the blood–brain barrier. 3. Briefly describe the neural circuitry responsible for a withdrawal reflex and its inhibition by neurons in the brain. 4. Describe the measurement of the action potential and explain how the balance between the forces of diffusion and ...
Introduction to electrophysiological recordings
... Intracell recording shows membrane depolarization and thus the amplitude is in millivolt, whereas for extracell recording, the amplitude is in microvolt. More importantly, the intracell recording signal is always positive whereas the extracell recording shows different polarities according to the el ...
... Intracell recording shows membrane depolarization and thus the amplitude is in millivolt, whereas for extracell recording, the amplitude is in microvolt. More importantly, the intracell recording signal is always positive whereas the extracell recording shows different polarities according to the el ...
Understanding Opioid Reward Howard L. Fields and Elyssa B
... that selective activation of dopamine neurons can produce positive reinforcement has recently been provided using rodents that express Cre recombinase under the tyrosine hydroxylase (TH) promoter (TH is currently the most reliable identifier of dopamine neurons in the VTA). In these rodents, express ...
... that selective activation of dopamine neurons can produce positive reinforcement has recently been provided using rodents that express Cre recombinase under the tyrosine hydroxylase (TH) promoter (TH is currently the most reliable identifier of dopamine neurons in the VTA). In these rodents, express ...
Photon Microscopy in Living Brain Tissue
... Encephalitogenic T cells invade the brain during neuroinflammation such as multiple sclerosis (MS), inducing damage to myelin sheaths and oligodendrocytes. Only recently, neuronal structures were reported to be a crucial target in the disease. Here, two-photon microscopy using ion-sensitive dyes rev ...
... Encephalitogenic T cells invade the brain during neuroinflammation such as multiple sclerosis (MS), inducing damage to myelin sheaths and oligodendrocytes. Only recently, neuronal structures were reported to be a crucial target in the disease. Here, two-photon microscopy using ion-sensitive dyes rev ...
Linear associator
... receive input from the auditory system, and neurons of layer g receive input from the olfactory system. We know if a tone is consistently presented at the same time as food, the dog will eventually become conditioned to respond by salivating to the tone alone. In the previous lab, we hypothesized th ...
... receive input from the auditory system, and neurons of layer g receive input from the olfactory system. We know if a tone is consistently presented at the same time as food, the dog will eventually become conditioned to respond by salivating to the tone alone. In the previous lab, we hypothesized th ...
The Anatomy of Language Sydney Lamb Rice University, Houston
... maps of the momentary electric activity on the scalp Also permits study of the time series of these maps with millisecond resolution ...
... maps of the momentary electric activity on the scalp Also permits study of the time series of these maps with millisecond resolution ...
Neural Axis Representing Target Range in the Auditory
... tones, FM sounds, and combinations of them that mimicked the biosonar signalecho pair in the search, approach, and terminal phases of echolocation in this species (9). The stimuli were delivered from a loudspeaker 73 cm in front of the animal in a soundproof, echo-suppressed room. For details of the ...
... tones, FM sounds, and combinations of them that mimicked the biosonar signalecho pair in the search, approach, and terminal phases of echolocation in this species (9). The stimuli were delivered from a loudspeaker 73 cm in front of the animal in a soundproof, echo-suppressed room. For details of the ...
autonomic nervous system i
... SUMMARY OF FUNCTION OF ANS • Exerts overall control of function of visceral organs – key contribution to homeostasis • Produces important adaptations to environmental stimuli: • Level of illumination ...
... SUMMARY OF FUNCTION OF ANS • Exerts overall control of function of visceral organs – key contribution to homeostasis • Produces important adaptations to environmental stimuli: • Level of illumination ...
May 21, 04.doc
... SI of rats. The effects were larger in supragranular deprived layers II/III than in deprived layer IV for all paradigms. For α1-GABAA receptor subunit immunoreactivity the decrease in layers II/III was 6% ± 0.6, P<0.001, and decrease in layer IV was 3.3% ± 0.9, P<0.001. For [3H]muscimol binding the ...
... SI of rats. The effects were larger in supragranular deprived layers II/III than in deprived layer IV for all paradigms. For α1-GABAA receptor subunit immunoreactivity the decrease in layers II/III was 6% ± 0.6, P<0.001, and decrease in layer IV was 3.3% ± 0.9, P<0.001. For [3H]muscimol binding the ...
optional biology 1 study packet the brain
... motor fibers extending from the cerebrum. These fibers cross each other in this area of the brain stem and results in the right half of the brain controlling the left side of the body and the left half of the brain controlling the right side of the body. The Medulla Oblongata contains vital clusters ...
... motor fibers extending from the cerebrum. These fibers cross each other in this area of the brain stem and results in the right half of the brain controlling the left side of the body and the left half of the brain controlling the right side of the body. The Medulla Oblongata contains vital clusters ...
ALS, MS AND MD - ALS Society of Canada
... initial symptoms in one side more than the other, both sides are involved and the effects usually become more symmetrical as the disorder progresses. Sensation is not affected. Approximately 3,000 Canadians live with ALS. Two to three Canadians a day die of ALS. Less than 10 per cent of all cases of ...
... initial symptoms in one side more than the other, both sides are involved and the effects usually become more symmetrical as the disorder progresses. Sensation is not affected. Approximately 3,000 Canadians live with ALS. Two to three Canadians a day die of ALS. Less than 10 per cent of all cases of ...
Dear Notetaker:
... Superior and inferior parietal lobules are separated by intraparietal sulcus Inferior lobule of posterior parietal cortex is where dorsal pathway comes to an end Characteristics of Dorsal Pathway Neurons o Receives visual information and transform it into the control of action o The dorsal pathw ...
... Superior and inferior parietal lobules are separated by intraparietal sulcus Inferior lobule of posterior parietal cortex is where dorsal pathway comes to an end Characteristics of Dorsal Pathway Neurons o Receives visual information and transform it into the control of action o The dorsal pathw ...
FOLINIC ACID
... Folinic acid is a B vitamin that is used to decrease the harmful effects of different drugs, such as pyrimethamine (Daraprim) or trimetrexate (Neutrexin). It is also used to treat certain types of anemias and cancers. HOW should this drug be taken? Folinic acid comes as a 5 mg tablet that can be t ...
... Folinic acid is a B vitamin that is used to decrease the harmful effects of different drugs, such as pyrimethamine (Daraprim) or trimetrexate (Neutrexin). It is also used to treat certain types of anemias and cancers. HOW should this drug be taken? Folinic acid comes as a 5 mg tablet that can be t ...
THE CEREBRUM (sah REB brum) LOCATION The cerebrum is the
... contraction that restores balance. Maintenance of muscle tone. The cerebellum transmits nerve impulses to the red nucleus ...
... contraction that restores balance. Maintenance of muscle tone. The cerebellum transmits nerve impulses to the red nucleus ...
Nervous and Endocrine System
... • At the end of class you should be able to: – Understand the various parts of the nervous system and explain their functions. – Understand how the hormones of the endocrine system differ from the nervous system? ...
... • At the end of class you should be able to: – Understand the various parts of the nervous system and explain their functions. – Understand how the hormones of the endocrine system differ from the nervous system? ...
Buzsaki and Draguhn (2004), Neuronal Oscillations in Cortical
... strengths across the assemblies, a process that would require energy-demanding biochemical steps. An alternative mechanism is oscillatory synchrony (13, 15). Transient assembly synchronization by oscillation is cost effective. The ability of neuronal assemblies to synchronize depends on the coupling ...
... strengths across the assemblies, a process that would require energy-demanding biochemical steps. An alternative mechanism is oscillatory synchrony (13, 15). Transient assembly synchronization by oscillation is cost effective. The ability of neuronal assemblies to synchronize depends on the coupling ...
a comparative study of the histological changes in cerebral
... level of Ca pump and channels and that’s how the lead induces its toxicity leading to the disturbance in the cellular homeostasis. The clinical manifestation of the lead toxicity popularly known as plumbism depends on the level of exposure, affinity of various tissues and the route of intake. As a c ...
... level of Ca pump and channels and that’s how the lead induces its toxicity leading to the disturbance in the cellular homeostasis. The clinical manifestation of the lead toxicity popularly known as plumbism depends on the level of exposure, affinity of various tissues and the route of intake. As a c ...
Clinical neurochemistry

Clinical neurochemistry is the field of neurological biochemistry which relates biochemical phenomena to clinical symptomatic manifestations in humans. While neurochemistry is mostly associated with the effects of neurotransmitters and similarly-functioning chemicals on neurons themselves, clinical neurochemistry relates these phenomena to system-wide symptoms. Clinical neurochemistry is related to neurogenesis, neuromodulation, neuroplasticity, neuroendocrinology, and neuroimmunology in the context of associating neurological findings at both lower and higher level organismal functions.