Sensory Pathways (Ascending Tracts)
... • Spinal lemniscus: bundle of fibers that contain lateral spinothalamic tract, anterior spinothalamic tract, Spinotectal tract ...
... • Spinal lemniscus: bundle of fibers that contain lateral spinothalamic tract, anterior spinothalamic tract, Spinotectal tract ...
Supplemental Text
... scavenge NAPQI but to scavenge peroxynitrite. In one of the previous studies,15 we injected GSH at different times after APAP and showed that when GSH is being resynthesized at the time when NAPQI is still formed, there is not only complete protection but also no increase of GSSG formation (indicato ...
... scavenge NAPQI but to scavenge peroxynitrite. In one of the previous studies,15 we injected GSH at different times after APAP and showed that when GSH is being resynthesized at the time when NAPQI is still formed, there is not only complete protection but also no increase of GSSG formation (indicato ...
Optogenetics in a transparent animal: circuit function in the larval
... (OKR) where objects moving across the visual field evoke stereotyped tracking eye movements [6], the optomotor response (OMR) where larvae turn and swim in the direction of perceived whole-field visual motion [7], prey tracking and capture [8–11], as well as associative learning [12], and motor adap ...
... (OKR) where objects moving across the visual field evoke stereotyped tracking eye movements [6], the optomotor response (OMR) where larvae turn and swim in the direction of perceived whole-field visual motion [7], prey tracking and capture [8–11], as well as associative learning [12], and motor adap ...
Nervous Systems
... – others inhibit a receiving cell’s activity by decreasing its ability to develop action potentials. ...
... – others inhibit a receiving cell’s activity by decreasing its ability to develop action potentials. ...
Slide 1
... – others inhibit a receiving cell’s activity by decreasing its ability to develop action potentials. ...
... – others inhibit a receiving cell’s activity by decreasing its ability to develop action potentials. ...
Autonomic nervous system
... 2 neurons in the effector pathway. 1st neuron has its cell body in gray matter of brain or spinal cord. – Preganglionic neuron. ...
... 2 neurons in the effector pathway. 1st neuron has its cell body in gray matter of brain or spinal cord. – Preganglionic neuron. ...
The Retrotrapezoid Nucleus and Central Chemoreception
... is mediated by changes in pH [9]. It is temperaturesensitive (Q10 ∼ 2.5) and robust (2.2 Hz per 0.1 pH unit at 37°C) [10]. In slices, RTN neurons discharge tonically, regardless of the recording temperature [10]. Their pH sensitivity is independent of glutamatergic, GABAergic, glycinergic and purine ...
... is mediated by changes in pH [9]. It is temperaturesensitive (Q10 ∼ 2.5) and robust (2.2 Hz per 0.1 pH unit at 37°C) [10]. In slices, RTN neurons discharge tonically, regardless of the recording temperature [10]. Their pH sensitivity is independent of glutamatergic, GABAergic, glycinergic and purine ...
IGF1
... lacked the sulfation action in its entirety. Furthermore, for some reason it’s activity could not be reconstituted by the addition of further quantities of growth hormone (GH) to the maturation medium, but rather it reappeared after further administration of GH to hypophysectomized rats [1]. The ...
... lacked the sulfation action in its entirety. Furthermore, for some reason it’s activity could not be reconstituted by the addition of further quantities of growth hormone (GH) to the maturation medium, but rather it reappeared after further administration of GH to hypophysectomized rats [1]. The ...
Phenylketonuria in Sohag: A Preliminary Study
... disorder characterized by a mutation in the gene for the hepatic enzyme phenylalanine hydroxylase (PAH), rendering it nonfunctional. The diagnosis of this disorder can be confirmed by analysis of urine components. The present study aimed to assess the prevalence of PKU among children aged 6 months t ...
... disorder characterized by a mutation in the gene for the hepatic enzyme phenylalanine hydroxylase (PAH), rendering it nonfunctional. The diagnosis of this disorder can be confirmed by analysis of urine components. The present study aimed to assess the prevalence of PKU among children aged 6 months t ...
Introduction to the Nervous System and Nervous Tissue Nervous
... 3. Amino acids: (Glutamate – E; GABA- Inhib.) 4. Neuropeptides: E and I (endorphins) ...
... 3. Amino acids: (Glutamate – E; GABA- Inhib.) 4. Neuropeptides: E and I (endorphins) ...
Lecture 12 - Taft College
... discrete pathways (nerves) and local actions. – The effects of nervous stimulation are usually immediate and short lived. • E.g. muscle movement ...
... discrete pathways (nerves) and local actions. – The effects of nervous stimulation are usually immediate and short lived. • E.g. muscle movement ...
Z333 Lecture
... B) Limbic System • Produce emotions; form memories • Hypothalamus: Homeostatic control center • Regulation of temperature; water balance; food intake • Hippocampus: Formation of long-term memory C) Thalamus • Relays information from body to limbic system / cerebral cortex ...
... B) Limbic System • Produce emotions; form memories • Hypothalamus: Homeostatic control center • Regulation of temperature; water balance; food intake • Hippocampus: Formation of long-term memory C) Thalamus • Relays information from body to limbic system / cerebral cortex ...
Article Review - Make up assignment
... 12. In the case of acids what specific chemical causes depolarization? Which type of taste is this phenomenon associated with? ...
... 12. In the case of acids what specific chemical causes depolarization? Which type of taste is this phenomenon associated with? ...
Synaptic Neurotransmission and the Anatomically Addressed
... Neurogenesis begins after conception with embryonic stem cells differentiating into immature neurons (Figures 2-1 and 2-2). In adults, this continues from adult stem cells, but only in two evolutionarily primitive regions: the hippocampal dentate gyrus from neuronal precursors in the subgranular zon ...
... Neurogenesis begins after conception with embryonic stem cells differentiating into immature neurons (Figures 2-1 and 2-2). In adults, this continues from adult stem cells, but only in two evolutionarily primitive regions: the hippocampal dentate gyrus from neuronal precursors in the subgranular zon ...
Alterations of Mitochondria and Golgi Apparatus Are
... are the result of the post-translational proteolysis of the APP [18], by concerted actions of βand γ-secretases [19]. The amyloidogenic pathway for APP is initiated by β- site amyloid precursor proteincleavage enzyme 1 (BACE- 1), resulting in the generation of the intermediate product sAPPβ [20]. γ ...
... are the result of the post-translational proteolysis of the APP [18], by concerted actions of βand γ-secretases [19]. The amyloidogenic pathway for APP is initiated by β- site amyloid precursor proteincleavage enzyme 1 (BACE- 1), resulting in the generation of the intermediate product sAPPβ [20]. γ ...
1 Part 1: The Brain - Sinoe Medical Association TM
... which prevents wide changes in intracranial blood flow. When disorders of CSF flow occur, they may therefore impact not only CSF movement, but also the intracranial blood flow, with subsequent neuronal and glial vulnerabilities. The venous system is also important in this equation. Infants and pat ...
... which prevents wide changes in intracranial blood flow. When disorders of CSF flow occur, they may therefore impact not only CSF movement, but also the intracranial blood flow, with subsequent neuronal and glial vulnerabilities. The venous system is also important in this equation. Infants and pat ...
MUSK Antibody
... activation of ABL1 and Src family kinases which in turn regulate MUSK. DVL1 and PAK1 that form a ternary complex with MUSK are also important for MUSK-dependent regulation of AChR clustering. May positively regulate Rho family GTPases through FNTA. Mediates the phosphorylation of FNTA which promotes ...
... activation of ABL1 and Src family kinases which in turn regulate MUSK. DVL1 and PAK1 that form a ternary complex with MUSK are also important for MUSK-dependent regulation of AChR clustering. May positively regulate Rho family GTPases through FNTA. Mediates the phosphorylation of FNTA which promotes ...
how different levels of organization imply pre
... located at the periphery of the environment. (Os are free to move out of the 20x20 environment even if they can increase their fitness only by remaining in the environment). Os are placed in individual copies in the environment (i.e. they live in isolation) and they do not change during the course o ...
... located at the periphery of the environment. (Os are free to move out of the 20x20 environment even if they can increase their fitness only by remaining in the environment). Os are placed in individual copies in the environment (i.e. they live in isolation) and they do not change during the course o ...
Discontinuity in evolution: how different levels of organization imply
... located at the periphery of the environment. (Os are free to move out of the 20x20 environment even if they can increase their fitness only by remaining in the environment). Os are placed in individual copies in the environment (i.e. they live in isolation) and they do not change during the course o ...
... located at the periphery of the environment. (Os are free to move out of the 20x20 environment even if they can increase their fitness only by remaining in the environment). Os are placed in individual copies in the environment (i.e. they live in isolation) and they do not change during the course o ...
Homework
... Enduring Understandings: 1.The nervous system mediates communication between different parts of the body and the body’s interactions with the environment. 2. Feedback loops in the nervous and endocrine systems regulate conditions in the body. 3. Neurons transmit electrochemical impulses. 4. Sensory ...
... Enduring Understandings: 1.The nervous system mediates communication between different parts of the body and the body’s interactions with the environment. 2. Feedback loops in the nervous and endocrine systems regulate conditions in the body. 3. Neurons transmit electrochemical impulses. 4. Sensory ...
Optimization of neuronal cultures derived from human
... The MANTRA instrumentation (left) consists of integrated 96-well parallel imaging and field stimulation systems. Right, top shows the instrument deck with its multiple technology components. Right, bottom shows the design of the electrode tip module. ...
... The MANTRA instrumentation (left) consists of integrated 96-well parallel imaging and field stimulation systems. Right, top shows the instrument deck with its multiple technology components. Right, bottom shows the design of the electrode tip module. ...
State of the art
... refers to experiences that cause feelings of anxiety and frustration because they push us beyond our ability to successfully cope. “There is so much to do and so little time!” is a common expression. Besides time pressures and daily hassles at work and home, there are stressors related to economic i ...
... refers to experiences that cause feelings of anxiety and frustration because they push us beyond our ability to successfully cope. “There is so much to do and so little time!” is a common expression. Besides time pressures and daily hassles at work and home, there are stressors related to economic i ...
Facioscapulohumeral Muscular Dystrophy: The Molecular Signaling
... The muscle fiber necrosis and degeneration occurs due to activation of transcription of DUX4 gene [8]. Genes FRG1 and FRG2 are adjacent to DUX4 [9,10]. FRG1 activation leads to increased activity of spliceosome. Also, with use of mouse model of FSHD, it was shown that FRG1 reduces the stability of m ...
... The muscle fiber necrosis and degeneration occurs due to activation of transcription of DUX4 gene [8]. Genes FRG1 and FRG2 are adjacent to DUX4 [9,10]. FRG1 activation leads to increased activity of spliceosome. Also, with use of mouse model of FSHD, it was shown that FRG1 reduces the stability of m ...
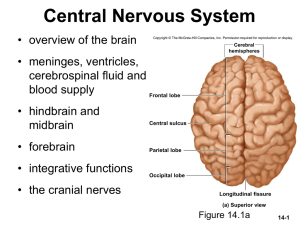
CNS Slide Show
... the “gateway to the cerebral cortex” – nearly all input to the cerebrum passes by way of synapses in the thalamic nuclei, filters information on its way to cerebral cortex – plays key role in motor control by relaying signals from cerebellum to cerebrum and providing feedback loops between the cereb ...
... the “gateway to the cerebral cortex” – nearly all input to the cerebrum passes by way of synapses in the thalamic nuclei, filters information on its way to cerebral cortex – plays key role in motor control by relaying signals from cerebellum to cerebrum and providing feedback loops between the cereb ...
Neurophysiological Aspects of Song Pattern Recognition and Sound
... For assessing the directionality cues present in the spike activity of auditory receptors of L. migratoria we used sawtoothshaped sound pulses (white noise) of 10 ms duration. In order to compare stimuli of equal energy and frequency content, a ramp stimulus and its temporal inverse were used (compa ...
... For assessing the directionality cues present in the spike activity of auditory receptors of L. migratoria we used sawtoothshaped sound pulses (white noise) of 10 ms duration. In order to compare stimuli of equal energy and frequency content, a ramp stimulus and its temporal inverse were used (compa ...
Clinical neurochemistry

Clinical neurochemistry is the field of neurological biochemistry which relates biochemical phenomena to clinical symptomatic manifestations in humans. While neurochemistry is mostly associated with the effects of neurotransmitters and similarly-functioning chemicals on neurons themselves, clinical neurochemistry relates these phenomena to system-wide symptoms. Clinical neurochemistry is related to neurogenesis, neuromodulation, neuroplasticity, neuroendocrinology, and neuroimmunology in the context of associating neurological findings at both lower and higher level organismal functions.