Fibrinogen
... Clinical features & treatment • Variable, generally mild bleeding tendency – Bleeding after trauma & surgery – Spontaneous bleeding uncommon – Bleeding risk does not correlate well with XI level ...
... Clinical features & treatment • Variable, generally mild bleeding tendency – Bleeding after trauma & surgery – Spontaneous bleeding uncommon – Bleeding risk does not correlate well with XI level ...
Chapter 12 Lecture Outline
... the body and external environment, and transmit coded messages to the brain and spinal cord (CNS: central nervous system) • CNS processes this information, relates it to past experiences, and determines appropriate response • CNS issues commands to muscles and gland cells to carry out such a respons ...
... the body and external environment, and transmit coded messages to the brain and spinal cord (CNS: central nervous system) • CNS processes this information, relates it to past experiences, and determines appropriate response • CNS issues commands to muscles and gland cells to carry out such a respons ...
CHAPTER 12: THE CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM MODULE 12.1
... Amygdala – anterior to hippocampus; involved in behavior and expression of emotion, especially fear ...
... Amygdala – anterior to hippocampus; involved in behavior and expression of emotion, especially fear ...
In general terms, pharmacology is the
... How can knowledge of the structure of a macromolecule be used to design (intelligently) new more effective drugs? Example: Can HIV proteins be targeted with specific Inhibitory molecules? Can we predict protein mutation? How do organisms develop increased or decreased sensitivity to drugs? Exampl ...
... How can knowledge of the structure of a macromolecule be used to design (intelligently) new more effective drugs? Example: Can HIV proteins be targeted with specific Inhibitory molecules? Can we predict protein mutation? How do organisms develop increased or decreased sensitivity to drugs? Exampl ...
Development of glutamatergic and GABAergic synapses
... L1 immunoglobulin family, along the PC soma-AIS axis, and such gradient requires ankyrinG, a membrane adaptor protein that recruits neurofascin (Ango et al. 2004). Interestingly, another member of the same family of adhesion molecules, CHL1, is localized along Bergmann glia fibers and stellate cells ...
... L1 immunoglobulin family, along the PC soma-AIS axis, and such gradient requires ankyrinG, a membrane adaptor protein that recruits neurofascin (Ango et al. 2004). Interestingly, another member of the same family of adhesion molecules, CHL1, is localized along Bergmann glia fibers and stellate cells ...
Artificial Intelligence Methods
... Desire to understand the brain and to imitate some of its strength Traditional computers implement a sequence of logical and arithmetic operations but don’t have the ability to adapt their structure or learn Learn from examples, Generalisation ...
... Desire to understand the brain and to imitate some of its strength Traditional computers implement a sequence of logical and arithmetic operations but don’t have the ability to adapt their structure or learn Learn from examples, Generalisation ...
Michael Arbib: CS564 - Brain Theory and Artificial Intelligence
... Michael Arbib CS564 - Brain Theory and Artificial Intelligence, USC, Fall 2001. Lecture 20. Schemas 1 ...
... Michael Arbib CS564 - Brain Theory and Artificial Intelligence, USC, Fall 2001. Lecture 20. Schemas 1 ...
PDF
... enough to fulfill the switching role we seek. As a result, neuromodulation is not generally considered to be a candidate mechanism for rapid and precise switching of complex neural circuits and responses. Nevertheless, it is good to keep in mind that this standard wisdom may be wrong (see Sherman an ...
... enough to fulfill the switching role we seek. As a result, neuromodulation is not generally considered to be a candidate mechanism for rapid and precise switching of complex neural circuits and responses. Nevertheless, it is good to keep in mind that this standard wisdom may be wrong (see Sherman an ...
B. Oral hypoglycemic drugs
... hunger, weakenss, tachycardia, blurred vision, headache, etc.), treated with 50% glucose ...
... hunger, weakenss, tachycardia, blurred vision, headache, etc.), treated with 50% glucose ...
ANS notes filled
... Sympathetic division of the ANS has its preganglionic somas in the... thoracolumbar regions of the cord helps body respond to stress This division of the ANS is called the “fight or flight’ division. If the body is under some threat or stress, the sympathetic stimulation goes up. This causes an incr ...
... Sympathetic division of the ANS has its preganglionic somas in the... thoracolumbar regions of the cord helps body respond to stress This division of the ANS is called the “fight or flight’ division. If the body is under some threat or stress, the sympathetic stimulation goes up. This causes an incr ...
Thalamus 1
... Superiorly- transverse cerebral fissure, floor of 3rd ventricle Inferiorly- hypothalamic sulcus Posteriorly- overlaps midbrain ...
... Superiorly- transverse cerebral fissure, floor of 3rd ventricle Inferiorly- hypothalamic sulcus Posteriorly- overlaps midbrain ...
Pharmacology 13a – Atherosclerosis and Lipid Metabolism
... - LDL (low density lipoprotein) cholesterol levels in the blood are strongly associated with atherosclerosis risk. - A 10% increase in LDL results in a 20% increase in atherosclerosis risk. - It is modified by other risk factors such as smoking, hypertension and diabetes. HDL Cholesterol - HDL chole ...
... - LDL (low density lipoprotein) cholesterol levels in the blood are strongly associated with atherosclerosis risk. - A 10% increase in LDL results in a 20% increase in atherosclerosis risk. - It is modified by other risk factors such as smoking, hypertension and diabetes. HDL Cholesterol - HDL chole ...
Monkey social depriv-brain I - University of Illinois Archives
... movements, self-directed behaviors, and psychosocial abnormalities, but neurobiological mechanisms underlying the behaviors of socially deprived (SD) monkeys are unknown. Monkeys were reared in total social deprivation for the first 9 months of life; control monkeys were reared socially (SR) with mo ...
... movements, self-directed behaviors, and psychosocial abnormalities, but neurobiological mechanisms underlying the behaviors of socially deprived (SD) monkeys are unknown. Monkeys were reared in total social deprivation for the first 9 months of life; control monkeys were reared socially (SR) with mo ...
NIH Public Access
... Pursuant to our previously reported finding that 12-Lox deficient neurons are resistant to glutamate-induced death and that 12-Lox represents a key target for α-tocotrienol action 7, we observed that 12-Lox deficient mice were resistant to stroke injury (Fig. 4). The compelling neuroprotective effec ...
... Pursuant to our previously reported finding that 12-Lox deficient neurons are resistant to glutamate-induced death and that 12-Lox represents a key target for α-tocotrienol action 7, we observed that 12-Lox deficient mice were resistant to stroke injury (Fig. 4). The compelling neuroprotective effec ...
Validation of In Vivo Mouse Brain Fiber Tracking
... positioning, the thalamocortical projections reconstructed in our study with in-vivo tractography and with axonal tracing were distorted, less compacted and thinner than normal. The fiber tracking pictorials (Fig. 1-B) are in agreement with our histological observation of poorly compacted axonal pro ...
... positioning, the thalamocortical projections reconstructed in our study with in-vivo tractography and with axonal tracing were distorted, less compacted and thinner than normal. The fiber tracking pictorials (Fig. 1-B) are in agreement with our histological observation of poorly compacted axonal pro ...
Reaching for the brain: stimulating neural activity as the big leap in
... increasing electrical activity of retinal ganglion cells to enhance regrowth of their axons. This builds upon a large body of evidence—both from preclinical work and clinical trials—for its success in peripheral nerve regeneration, where electrical stimulation is a well-known treatment to promote ne ...
... increasing electrical activity of retinal ganglion cells to enhance regrowth of their axons. This builds upon a large body of evidence—both from preclinical work and clinical trials—for its success in peripheral nerve regeneration, where electrical stimulation is a well-known treatment to promote ne ...
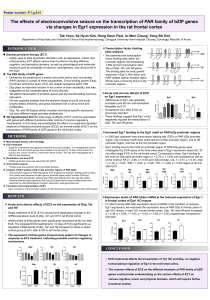
The effects of electroconvulsive seizure on the transcription
... (PAR) domain is consist of three polypeptides, D-box binding protein (Dbp), thyrotroph embryonic factor (Tef), and hepatic leukaemia factor (Hlf) • Dbp plays an important function in the control of brain excitability, and was suggested as the candidate gene of mood disorder • Tef affects transcripti ...
... (PAR) domain is consist of three polypeptides, D-box binding protein (Dbp), thyrotroph embryonic factor (Tef), and hepatic leukaemia factor (Hlf) • Dbp plays an important function in the control of brain excitability, and was suggested as the candidate gene of mood disorder • Tef affects transcripti ...
Lecture-4b
... The effect is all via the peripheral chemoreceptors Stimulated only when arterial PO2 falls to low levels (<8.0 kPa) Is not important in normal respiration May become important in patients with chronic CO2 retention (e.g. patients with COPD) It is important at high altitudes ...
... The effect is all via the peripheral chemoreceptors Stimulated only when arterial PO2 falls to low levels (<8.0 kPa) Is not important in normal respiration May become important in patients with chronic CO2 retention (e.g. patients with COPD) It is important at high altitudes ...
Dissipation of dark energy by cortex in knowledge retrieval
... and carbon dioxide production. The sensory receptors in the body and on the body surface provide the information by absorbing energy of various types impinging from the internal and external environments (Laughlin et al., 1998). The role of each sensory receptor is selectively to convert a microscop ...
... and carbon dioxide production. The sensory receptors in the body and on the body surface provide the information by absorbing energy of various types impinging from the internal and external environments (Laughlin et al., 1998). The role of each sensory receptor is selectively to convert a microscop ...
Summary Antipsychotic medications are overused in Australia as a
... treatment may result in progressive damage to the brain. Antipsychotic medications were originally developed in the 1950s for treatment of psychotic illnesses such as schizophrenia and bipolar disorder. However, they have increasingly been used ‘off-label’ to treat a range of child and adult mental ...
... treatment may result in progressive damage to the brain. Antipsychotic medications were originally developed in the 1950s for treatment of psychotic illnesses such as schizophrenia and bipolar disorder. However, they have increasingly been used ‘off-label’ to treat a range of child and adult mental ...
Neurogenesis
... Support for Adult Neurogenesis o3H- Thymidine Autoradiography o Technique used to identify proliferating cells ...
... Support for Adult Neurogenesis o3H- Thymidine Autoradiography o Technique used to identify proliferating cells ...
CNS - FIU
... The basic role of nerve cells is to conduct electrical signals from one place to another. The nervous system can be divided anatomically into a central nervous system consisting of the brain and spinal cord, and a peripheral nervous system consisting of (1) the nerves projecting from the CNS (crania ...
... The basic role of nerve cells is to conduct electrical signals from one place to another. The nervous system can be divided anatomically into a central nervous system consisting of the brain and spinal cord, and a peripheral nervous system consisting of (1) the nerves projecting from the CNS (crania ...
Synchrony Unbound: Review A Critical Evaluation of
... is that populations of cells that represent low-level features (for example, neurons in primary visual cortex) synchronize their activity when they respond to different elements that are to be linked in the analysis of a scene. Singer’s laboratory and others have presented supporting evidence, discu ...
... is that populations of cells that represent low-level features (for example, neurons in primary visual cortex) synchronize their activity when they respond to different elements that are to be linked in the analysis of a scene. Singer’s laboratory and others have presented supporting evidence, discu ...
Clinical neurochemistry

Clinical neurochemistry is the field of neurological biochemistry which relates biochemical phenomena to clinical symptomatic manifestations in humans. While neurochemistry is mostly associated with the effects of neurotransmitters and similarly-functioning chemicals on neurons themselves, clinical neurochemistry relates these phenomena to system-wide symptoms. Clinical neurochemistry is related to neurogenesis, neuromodulation, neuroplasticity, neuroendocrinology, and neuroimmunology in the context of associating neurological findings at both lower and higher level organismal functions.