Nervous system Lab - Sonoma Valley High School
... 2) The releaser stands facing the subject and holds the release end of the ruler at his/her eye level. 3) The subject positions the thumb and first finger over the “thumb line”. The distance between the thumb and the first finger should be 1inch. 4) when ready the subject tells the releaser to “star ...
... 2) The releaser stands facing the subject and holds the release end of the ruler at his/her eye level. 3) The subject positions the thumb and first finger over the “thumb line”. The distance between the thumb and the first finger should be 1inch. 4) when ready the subject tells the releaser to “star ...
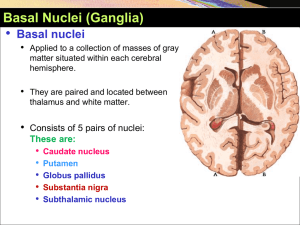
Basal Ganglia YAYDAR 2012-2013
... extent the movement will be fast, and how long it will last. Storage of motor programs of familiar motor actions: e.g. signature. ...
... extent the movement will be fast, and how long it will last. Storage of motor programs of familiar motor actions: e.g. signature. ...
Neurobiology of Behaviour
... An animals response to the environment will be influenced by their underlying nervous system ...
... An animals response to the environment will be influenced by their underlying nervous system ...
what is a seizure? - Patient Focused Neurology!
... "Atonic" means "without tone"— in these seizures, the muscles lose all strength instead of becoming stiff. The person remains conscious but may fall to the ground without warning. In a milder form, the person's head may droop or he may drop things. These seizures last only seconds and the person rec ...
... "Atonic" means "without tone"— in these seizures, the muscles lose all strength instead of becoming stiff. The person remains conscious but may fall to the ground without warning. In a milder form, the person's head may droop or he may drop things. These seizures last only seconds and the person rec ...
Functional Disconnectivities in Autistic Spectrum
... This spectrum of childhood disorders that we are discussing generally relates to an increase or decrease in activation of the brain and the balance of activation between brain regions. These conditions result from two primary system effects: 1) primary arousal deficit or imbalance, and 2) a specific ...
... This spectrum of childhood disorders that we are discussing generally relates to an increase or decrease in activation of the brain and the balance of activation between brain regions. These conditions result from two primary system effects: 1) primary arousal deficit or imbalance, and 2) a specific ...
KLRL1, a novel killer cell lectinlike receptor, inhibits
... expression is up-regulated by antiviral CD8⫹ T cells during acute polyoma infection; this is responsible for down-regulating their antigen-specific cytotoxicity during both viral clearance and virusinduced oncogenesis.12 CD94/NKG2 expression is also observed on antigen (Ag)–specific CD8⫹ T cells fol ...
... expression is up-regulated by antiviral CD8⫹ T cells during acute polyoma infection; this is responsible for down-regulating their antigen-specific cytotoxicity during both viral clearance and virusinduced oncogenesis.12 CD94/NKG2 expression is also observed on antigen (Ag)–specific CD8⫹ T cells fol ...
Psychology, 4/e by Saul Kassin Behavioral Neuroscience The
... The Neuron How Neurons Communicate Impulse releases neurotransmitter from axon terminals. Neurotransmitter enters synaptic gap. Neurotransmitter binds to receptors on the receiving neuron. Psychology, 4/e by Saul Kassin ©2004 Prentice Hall ...
... The Neuron How Neurons Communicate Impulse releases neurotransmitter from axon terminals. Neurotransmitter enters synaptic gap. Neurotransmitter binds to receptors on the receiving neuron. Psychology, 4/e by Saul Kassin ©2004 Prentice Hall ...
medical management: portosystemic vascular anomalies (psva)
... portosystemic shunting in causing hyperammonemia. In PSVA, the extent of hepatofugal circulation (i.e. the magnitude of shunt flow) determines the severity of clinical signs, hyperammonemia, and delivery of enteric toxins to the systemic circulation. Earlier presentation of dogs with I-PSVA is cons ...
... portosystemic shunting in causing hyperammonemia. In PSVA, the extent of hepatofugal circulation (i.e. the magnitude of shunt flow) determines the severity of clinical signs, hyperammonemia, and delivery of enteric toxins to the systemic circulation. Earlier presentation of dogs with I-PSVA is cons ...
5211: Session 1 Hypothalamus and its regulation of anterior and
... leuteinizing hormone, follicle stimulating hormone, thyroid stimulating hormone, adrenocorticotropic hormone. Infundibulum contains axons from hypothalamic neurons that project into the posterior pituitary where they terminate near capillaries. These terminals contain hormones oxytocin and vasopress ...
... leuteinizing hormone, follicle stimulating hormone, thyroid stimulating hormone, adrenocorticotropic hormone. Infundibulum contains axons from hypothalamic neurons that project into the posterior pituitary where they terminate near capillaries. These terminals contain hormones oxytocin and vasopress ...
PTA 106 Unit 1 Lecture 1B Structural and Functional areas of the
... stored in the brain. It is thought that this determination is based on how huge an emotional response an event invokes. Believed to act as an interface between limibic system, cerebum, and other sensory areas. – Clinical concerns: Autism, Depression, Narcolepsy, Posttraumatic stress disorder, and Ph ...
... stored in the brain. It is thought that this determination is based on how huge an emotional response an event invokes. Believed to act as an interface between limibic system, cerebum, and other sensory areas. – Clinical concerns: Autism, Depression, Narcolepsy, Posttraumatic stress disorder, and Ph ...
Leader The molecular basis of disorders of red cell enzymes
... causing chronic haemolysis are restricted to a small number of changes that can produce an enzyme with low red cell activity but considerable activity in other tissues. Three dimensional models of human G6PD have allowed some insight into how mutations can cause clinical disease.16 In the sporadic f ...
... causing chronic haemolysis are restricted to a small number of changes that can produce an enzyme with low red cell activity but considerable activity in other tissues. Three dimensional models of human G6PD have allowed some insight into how mutations can cause clinical disease.16 In the sporadic f ...
CBNS 106 Review
... • Shunting Inhibition: Inhibiting current flow from soma to axon hillock (a) Stimulation of the excitatory input causes inward postsynaptic current that spreads to the soma, where it can be recorded as an EPSP. (b) When the inhibitory and excitatory inputs are stimulated together, the depolarizing c ...
... • Shunting Inhibition: Inhibiting current flow from soma to axon hillock (a) Stimulation of the excitatory input causes inward postsynaptic current that spreads to the soma, where it can be recorded as an EPSP. (b) When the inhibitory and excitatory inputs are stimulated together, the depolarizing c ...
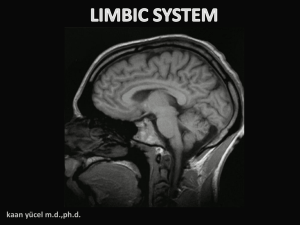
Brain days-Part V-Limbic
... It is possible that the altered emotional regulation or cognition found in all of these syndromes involves aberrant function of these circuits, but perhaps with different patterns on a molecular level. Phillips et al. 2003 ...
... It is possible that the altered emotional regulation or cognition found in all of these syndromes involves aberrant function of these circuits, but perhaps with different patterns on a molecular level. Phillips et al. 2003 ...
Measurement of Enzymes and Their Clinical Significance
... Alkaline Phosphatase (ALP) • ALP frees inorganic phosphate from an organic phosphate monoester, resulting in the production of an alcohol at an alkaline pH • Maximum activity at pH of 9.0- 10.0 ...
... Alkaline Phosphatase (ALP) • ALP frees inorganic phosphate from an organic phosphate monoester, resulting in the production of an alcohol at an alkaline pH • Maximum activity at pH of 9.0- 10.0 ...
Phineas Gage Reading Guide Directions: After you read each
... same effects. During a seizure, his brain shuts down circulation to his feet and hands, then skin, and finally organ by organ until his heart stops. 4. How old was Phineas when he died? Phineas was 36, he died 27 days short of this 37 birthday. 5. Who was Paul Broca? What is Broca's area? Paul Broca ...
... same effects. During a seizure, his brain shuts down circulation to his feet and hands, then skin, and finally organ by organ until his heart stops. 4. How old was Phineas when he died? Phineas was 36, he died 27 days short of this 37 birthday. 5. Who was Paul Broca? What is Broca's area? Paul Broca ...
Protein mteabolism
... I- Removal of α-amino group: The removal of amino group takes place in two steps which are Transamination (that produce glutamate) followed by oxidative deamination of the produced glutamate to give ammonia. Transamination: is the transfer of α-amino group from α-amino acid to α-keto acid to yield ...
... I- Removal of α-amino group: The removal of amino group takes place in two steps which are Transamination (that produce glutamate) followed by oxidative deamination of the produced glutamate to give ammonia. Transamination: is the transfer of α-amino group from α-amino acid to α-keto acid to yield ...
Optogenetics Review1 - Department Of Biological Sciences
... electrical stimulation methods: finer spatiotemporal resolution and parallel stimulations at multiple sites (Callaway €ck 2004). These methods are & Yuste 2002; Miesenbo also less harmful and more convenient than electrical stimulation methods. Another breakthrough combined optical stimulation with ...
... electrical stimulation methods: finer spatiotemporal resolution and parallel stimulations at multiple sites (Callaway €ck 2004). These methods are & Yuste 2002; Miesenbo also less harmful and more convenient than electrical stimulation methods. Another breakthrough combined optical stimulation with ...
another study guide
... The focus of this perspective is on behaviour, although a basic understanding of physiology is needed. Until the middle of the 19th century, most humans regarded themselves as very distinct from animals. Since Darwin's discoveries there has been a general acceptance that humans have evolved from ani ...
... The focus of this perspective is on behaviour, although a basic understanding of physiology is needed. Until the middle of the 19th century, most humans regarded themselves as very distinct from animals. Since Darwin's discoveries there has been a general acceptance that humans have evolved from ani ...
Candidate Genes Predicting Health Vulnerabilities In Families
... 1. Samples may be made up of distinct genetic groups or they have been genetic mixing of groups in recent past (i.e., racial admixture). 2. Groups may differ in allelic distributions and outcomes 3. Creating spurious associations between alleles and outcomes 4. Classic Study: Knowler et al. General ...
... 1. Samples may be made up of distinct genetic groups or they have been genetic mixing of groups in recent past (i.e., racial admixture). 2. Groups may differ in allelic distributions and outcomes 3. Creating spurious associations between alleles and outcomes 4. Classic Study: Knowler et al. General ...
FlyEM`s formal project plan
... three months and only stop when the sample imaging has been completed. This required addressing a variety of interrupt issues: ion source reheat, utility failure (water, power, air, and temperature fluctuation), and microscope failure (focus, electrical, software, vacuum). With improvements and back ...
... three months and only stop when the sample imaging has been completed. This required addressing a variety of interrupt issues: ion source reheat, utility failure (water, power, air, and temperature fluctuation), and microscope failure (focus, electrical, software, vacuum). With improvements and back ...
Thoracic Spine CT
... Presents with new signs or symptoms (e.g., laboratory and/or imaging findings) of new tumor or change in tumor. Presents with radiculopathy, muscle weakness, abnormal reflexes, and/or sensory changes along a particular dermatome (nerve distribution). With an abnormal electromyography (EMG) or ...
... Presents with new signs or symptoms (e.g., laboratory and/or imaging findings) of new tumor or change in tumor. Presents with radiculopathy, muscle weakness, abnormal reflexes, and/or sensory changes along a particular dermatome (nerve distribution). With an abnormal electromyography (EMG) or ...
Lecture 6 - School of Computing | University of Leeds
... complexity at every level, from the sub-cellular to the entire brain. We realised that even with a limited understanding, cartoon models can be derived for some functions of neurons (action potentials, synaptic transmission, neuronal computation and coding). Despite (or perhaps because of) their sim ...
... complexity at every level, from the sub-cellular to the entire brain. We realised that even with a limited understanding, cartoon models can be derived for some functions of neurons (action potentials, synaptic transmission, neuronal computation and coding). Despite (or perhaps because of) their sim ...
B130_Immunohistochemical identification of PAPP-A in
... is notebly expressed in unstable atherosclerotic plaques. It was shown that dPAPP-A is produced by activated cells of the immune system in unstable plaques and is released into the extracellular matrix. Also it was suggested that dPAPP-A could be involved in weakening of the fibrous cap. However, th ...
... is notebly expressed in unstable atherosclerotic plaques. It was shown that dPAPP-A is produced by activated cells of the immune system in unstable plaques and is released into the extracellular matrix. Also it was suggested that dPAPP-A could be involved in weakening of the fibrous cap. However, th ...
Lecture #13 – Animal Nervous Systems
... • Neuron resting potential is ~ -70mV At resting potential the neuron is NOT actively transmitting signals Maintained largely because cell membranes are more permeable to K+ than to Na+; more K+ leaves the cell than Na+ enters An ATP powered K+/Na+ pump continually restores the concentration grad ...
... • Neuron resting potential is ~ -70mV At resting potential the neuron is NOT actively transmitting signals Maintained largely because cell membranes are more permeable to K+ than to Na+; more K+ leaves the cell than Na+ enters An ATP powered K+/Na+ pump continually restores the concentration grad ...
The Nervous System Introducion
... • Bones - skull protects brain; vertebrae protect spinal cord • Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF) - watery fluid formed from plasma that circulates through the central nervous system and function as a shock absorber ...
... • Bones - skull protects brain; vertebrae protect spinal cord • Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF) - watery fluid formed from plasma that circulates through the central nervous system and function as a shock absorber ...
Clinical neurochemistry

Clinical neurochemistry is the field of neurological biochemistry which relates biochemical phenomena to clinical symptomatic manifestations in humans. While neurochemistry is mostly associated with the effects of neurotransmitters and similarly-functioning chemicals on neurons themselves, clinical neurochemistry relates these phenomena to system-wide symptoms. Clinical neurochemistry is related to neurogenesis, neuromodulation, neuroplasticity, neuroendocrinology, and neuroimmunology in the context of associating neurological findings at both lower and higher level organismal functions.