NEUROGENESIS Y PLASTICIDAD DEL HIPOCAMPO ADULTO
... Parallel channeling of information arriving to the dentate gyrus: highly active cohorts of young non-specific GCs and highly input-specific mature GCs ...
... Parallel channeling of information arriving to the dentate gyrus: highly active cohorts of young non-specific GCs and highly input-specific mature GCs ...
Aromatic Amino Acid Hydroxylase Genes and
... K274E mutation. In Family B, the PAH K274E mutation was present in all available family members except for one schizophrenic subject. In all cases, the PAH K274E mutation was observed in the heterozygous state, and was accompanied by the PAH L321L polymorphism, either in the heterozygous or homozygo ...
... K274E mutation. In Family B, the PAH K274E mutation was present in all available family members except for one schizophrenic subject. In all cases, the PAH K274E mutation was observed in the heterozygous state, and was accompanied by the PAH L321L polymorphism, either in the heterozygous or homozygo ...
PPT
... Finding common and different pathway modules (based on multiple samples: – Looking for “differential pathways” - modules that distinguish one group of samples from another – Finding common motifs in a group of pathway modules Inferring patterns of network activity – Identifying causal relation betwe ...
... Finding common and different pathway modules (based on multiple samples: – Looking for “differential pathways” - modules that distinguish one group of samples from another – Finding common motifs in a group of pathway modules Inferring patterns of network activity – Identifying causal relation betwe ...
uncorrected page proofs
... most complex organ in the body and perhaps the most complex natural or artificial structure in the known universe. Its remarkable complexity is largely invisible to the naked eye. You cannot see that it is densely packed with structures, systems, functions, connections and interconnections, many of ...
... most complex organ in the body and perhaps the most complex natural or artificial structure in the known universe. Its remarkable complexity is largely invisible to the naked eye. You cannot see that it is densely packed with structures, systems, functions, connections and interconnections, many of ...
Engines of the brain
... TANs receive inhibitory inputs from striosomes, and provide input to matrisomes. TANs can be thought of as a semi-random or “X” factor affecting matrisomes’ choice of action from a given cortical input. For actions that have a negative expected reward (or a relatively small positive one), the inhibi ...
... TANs receive inhibitory inputs from striosomes, and provide input to matrisomes. TANs can be thought of as a semi-random or “X” factor affecting matrisomes’ choice of action from a given cortical input. For actions that have a negative expected reward (or a relatively small positive one), the inhibi ...
Untitled
... biological tissue. We have developed 2P uncaging methods to reveal the microarchitecture of synaptic connections at a level of single synapses. Recently, we synthesized two novel caged-GABA compounds. 2P excitation of the first caged GABA produced rapid activation of GABAergic currents in neurons in ...
... biological tissue. We have developed 2P uncaging methods to reveal the microarchitecture of synaptic connections at a level of single synapses. Recently, we synthesized two novel caged-GABA compounds. 2P excitation of the first caged GABA produced rapid activation of GABAergic currents in neurons in ...
BOX 30.8 THE ROLE OF THE SUBTHALAMIC NUCLEUS IN
... connect to motor/premotor cortical, lateral prefrontal and cingulate/orbital frontal regions, respectively. It is an open question whether the kind of stopping discussed here could extend, for example, to the limbic domain of the subthalamic nucleus to enable emotional and motivational control. Nota ...
... connect to motor/premotor cortical, lateral prefrontal and cingulate/orbital frontal regions, respectively. It is an open question whether the kind of stopping discussed here could extend, for example, to the limbic domain of the subthalamic nucleus to enable emotional and motivational control. Nota ...
important ascending tracts
... The corticospinal tract is involved in voluntary movement. The majority of fibres of the corticospinal tract cross over in the medulla, resulting in muscles being controlled by the opposite side of the brain. The pyramidal tracts are named because they pass through the pyramids of the medulla. ...
... The corticospinal tract is involved in voluntary movement. The majority of fibres of the corticospinal tract cross over in the medulla, resulting in muscles being controlled by the opposite side of the brain. The pyramidal tracts are named because they pass through the pyramids of the medulla. ...
lect4
... intake leads to the catabolism of amino acids Excess amino acids can be used for energy Insufficient dietary amino acids lead to the catabolism of proteins Insufficient dietary energy leads to the catabolism of proteins ...
... intake leads to the catabolism of amino acids Excess amino acids can be used for energy Insufficient dietary amino acids lead to the catabolism of proteins Insufficient dietary energy leads to the catabolism of proteins ...
PROTEIN ANALYSIS - Farmasi Carbon 2012
... Absorbance values are determined on a spectrophotometer at 750 nm. As little as 0.2 mg protein in a sample can be determined. ...
... Absorbance values are determined on a spectrophotometer at 750 nm. As little as 0.2 mg protein in a sample can be determined. ...
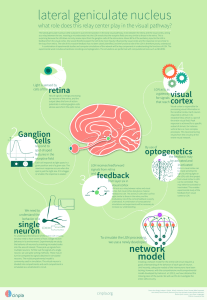
lgn - cinpla
... what role does this relay center play in the visual pathway? The lateral geniculate nucleus (LGN) is placed in a prominent position in the early visual pathway. It sits between the retina and the visual cortex, acting as a relay between the two. Inserting a microelectrode into the LGN reveals that t ...
... what role does this relay center play in the visual pathway? The lateral geniculate nucleus (LGN) is placed in a prominent position in the early visual pathway. It sits between the retina and the visual cortex, acting as a relay between the two. Inserting a microelectrode into the LGN reveals that t ...
Thyroid Hormones
... follicular cell receptors ii. Formation and storage of thyroglobulin 1. Thyroglobulin is synthesized on the ribosomes then sugar residues are attached (glycosylated) in the ER, and molecules are packed into vesicles and then transport to the Golgi. These transport vesicles move to the apex of the fo ...
... follicular cell receptors ii. Formation and storage of thyroglobulin 1. Thyroglobulin is synthesized on the ribosomes then sugar residues are attached (glycosylated) in the ER, and molecules are packed into vesicles and then transport to the Golgi. These transport vesicles move to the apex of the fo ...
Neurological Control of Movement. Chapter 3.
... impulse has been successfully transmitted and the neurotransmitter is then either destroyed by enzymes or actively returned to the presynaptic neuron for future use. ...
... impulse has been successfully transmitted and the neurotransmitter is then either destroyed by enzymes or actively returned to the presynaptic neuron for future use. ...
The Brain of the Planarian as the Ancestor of the Human Brain
... found, and are abundant in other simple species of both vertebrates and invertebrates. Electrophysiology of the planarian brain Vertebrates and invertebrates differ fundamentally in the character of spontaneous electrical activity generated by both individual neurons and by neuronal circuits. Verteb ...
... found, and are abundant in other simple species of both vertebrates and invertebrates. Electrophysiology of the planarian brain Vertebrates and invertebrates differ fundamentally in the character of spontaneous electrical activity generated by both individual neurons and by neuronal circuits. Verteb ...
STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION
... channels and effectively inhibit ammonia uptake. These types of interactions would occur in the event that there are low concentrations of Mg-ATP and 2-KG within the cells, or when the cell does not need nitrogen for biosynthesis. Another reason why you would want to keep ammonia out of the cell wh ...
... channels and effectively inhibit ammonia uptake. These types of interactions would occur in the event that there are low concentrations of Mg-ATP and 2-KG within the cells, or when the cell does not need nitrogen for biosynthesis. Another reason why you would want to keep ammonia out of the cell wh ...
Stress induces atrophy of apical dendrites of hippocampal CA3
... this responsiveness is drastically reduced with the destruction of the mossy fibers 6. CA3 neurons may also be more vulnerable to damage because they lack both calbindin D28k and parvalbumin, calcium-binding proteins that are present in dentate granule neurons as well as in CA1 and CA2 pyramidal neu ...
... this responsiveness is drastically reduced with the destruction of the mossy fibers 6. CA3 neurons may also be more vulnerable to damage because they lack both calbindin D28k and parvalbumin, calcium-binding proteins that are present in dentate granule neurons as well as in CA1 and CA2 pyramidal neu ...
A2.2.1.TheNeuron
... stimuli and make an appropriate response. Electrical signals travel in paths that take information to and from the brain and spinal cord. These signals allow the nervous system to react quickly while at the same time processing a great deal of sensory information. The nervous system interacts with a ...
... stimuli and make an appropriate response. Electrical signals travel in paths that take information to and from the brain and spinal cord. These signals allow the nervous system to react quickly while at the same time processing a great deal of sensory information. The nervous system interacts with a ...
Detection of grey matter loss in mild Alzheimer`s disease
... and entorhinal cortex volumetry and surface measures of the entorhinal cortex are believed to have high sensitivity and specificity in the detection of AD from non-demented elderly controls1 2 and can predict conversion of mild cognitive impairment to AD.3 However, the variability of the measurement ...
... and entorhinal cortex volumetry and surface measures of the entorhinal cortex are believed to have high sensitivity and specificity in the detection of AD from non-demented elderly controls1 2 and can predict conversion of mild cognitive impairment to AD.3 However, the variability of the measurement ...
Fut u re N
... [10]. In this model, activation dynamics driven by theta, as described above, interact with a synaptic modification rule that strengthens strongly active neurons and weakens moderately active neurons [28]. Together, theta and this modification rule have the effect of limiting new strengthening to no ...
... [10]. In this model, activation dynamics driven by theta, as described above, interact with a synaptic modification rule that strengthens strongly active neurons and weakens moderately active neurons [28]. Together, theta and this modification rule have the effect of limiting new strengthening to no ...
Neurotransmitter Profile of Saccadic Omnipause Neurons in
... a strong input from GLY- and GABA-positive terminals on somata and dendrites, whereas GLU-positive puncta were mainly confined to the dendrites. Very few 5-HT and catecholaminergic terminals contacted OPN somata. Our findings suggest that OPNs use GLY as a neurotransmitter, and they receive numerous ...
... a strong input from GLY- and GABA-positive terminals on somata and dendrites, whereas GLU-positive puncta were mainly confined to the dendrites. Very few 5-HT and catecholaminergic terminals contacted OPN somata. Our findings suggest that OPNs use GLY as a neurotransmitter, and they receive numerous ...
Brain Mechanisms of Memory and Cognition
... (see Bourgeois et al., 2000). However, adult cortex is plastic too: visual, auditory, somatotopic, and motor cortical maps can all reorganize. For example, amputation or denervation of a digit leads to loss of its cortical representation and expansion of adjacent somatosensory representations into t ...
... (see Bourgeois et al., 2000). However, adult cortex is plastic too: visual, auditory, somatotopic, and motor cortical maps can all reorganize. For example, amputation or denervation of a digit leads to loss of its cortical representation and expansion of adjacent somatosensory representations into t ...
Presentation 5: The Role of the Nervous System
... Competition between excitation and inhibition occurs Threshold stimulus reached? NMJ or motor end plate ...
... Competition between excitation and inhibition occurs Threshold stimulus reached? NMJ or motor end plate ...
The Biology
... messages to travel through the brain and the body. Psychologists are increasing their understanding of human behaviour and are uncovering important clues in their efforts to cure certain kinds of diseases through their growing knowledge of these neurons and the nervous system. Then a review of the s ...
... messages to travel through the brain and the body. Psychologists are increasing their understanding of human behaviour and are uncovering important clues in their efforts to cure certain kinds of diseases through their growing knowledge of these neurons and the nervous system. Then a review of the s ...
Mathematical neuroscience: from neurons to circuits to systems
... Most observed currents exhibit a constant conductance only within a range of voltages. In fact, some nonlinearity in the current-to-voltage relationship is expected even for completely passive currents. For instance, when the voltage is such that both diffusive and electrical forces are driving ions ...
... Most observed currents exhibit a constant conductance only within a range of voltages. In fact, some nonlinearity in the current-to-voltage relationship is expected even for completely passive currents. For instance, when the voltage is such that both diffusive and electrical forces are driving ions ...
H 2 O 2
... MAO A preferentially metabolizes serotonin. MAO B preferentially metabolizes phenethylamine, dopamine. MAO inhibitor + dietary amines or proprietary drugs MAOB inhibitor deprenyl (selegiline) similar to phenethylamine and increases brain dopamine levels. This is used to treat Parkinson’s disease. Bu ...
... MAO A preferentially metabolizes serotonin. MAO B preferentially metabolizes phenethylamine, dopamine. MAO inhibitor + dietary amines or proprietary drugs MAOB inhibitor deprenyl (selegiline) similar to phenethylamine and increases brain dopamine levels. This is used to treat Parkinson’s disease. Bu ...
Clinical neurochemistry

Clinical neurochemistry is the field of neurological biochemistry which relates biochemical phenomena to clinical symptomatic manifestations in humans. While neurochemistry is mostly associated with the effects of neurotransmitters and similarly-functioning chemicals on neurons themselves, clinical neurochemistry relates these phenomena to system-wide symptoms. Clinical neurochemistry is related to neurogenesis, neuromodulation, neuroplasticity, neuroendocrinology, and neuroimmunology in the context of associating neurological findings at both lower and higher level organismal functions.