Multimodal functional and structural neuroimaging investigation of major depressive
... in the amygdala, dorsal anterior cingulate and insula, but reduced activity in the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex and striatum relative to healthy participants, while measures of resting state have most commonly revealed greater regional cerebral blood flow in the thalamus [5]. Studies have generall ...
... in the amygdala, dorsal anterior cingulate and insula, but reduced activity in the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex and striatum relative to healthy participants, while measures of resting state have most commonly revealed greater regional cerebral blood flow in the thalamus [5]. Studies have generall ...
The Calcium Rationale in Aging and Alzheimer`s Disease
... environmental, or some interaction between the two, has not been definitively established. It has been postulated that excessive influx, raised levels, or poor buffering of intracellular calcium are results, not causes, of the molecular and cellular mechanisms leading to the development of Alzheimer ...
... environmental, or some interaction between the two, has not been definitively established. It has been postulated that excessive influx, raised levels, or poor buffering of intracellular calcium are results, not causes, of the molecular and cellular mechanisms leading to the development of Alzheimer ...
Purification and some characteristics of a calcium
... residues. The molecular mass is consistent with that estimated from SDS-PAGE (Fig. 2). The amino acid composition provides information for comparative studies with calmodulin from bovine brain and protein S from Myxococcus xanthus. Protein S is structurally similar to bovine brain calmodulin, and th ...
... residues. The molecular mass is consistent with that estimated from SDS-PAGE (Fig. 2). The amino acid composition provides information for comparative studies with calmodulin from bovine brain and protein S from Myxococcus xanthus. Protein S is structurally similar to bovine brain calmodulin, and th ...
Sonic Hedgehog Expression in Corticofugal Projection Neurons
... and wild-type control littermates (Figures 3A–3D). We observed significant reductions in the growth and complexity of basal dendrites of layer V neurons in the somatosensory and motor area of Shh conditional null animals (Figure 3E). We also observed a reduction in basal dendritic spine density of l ...
... and wild-type control littermates (Figures 3A–3D). We observed significant reductions in the growth and complexity of basal dendrites of layer V neurons in the somatosensory and motor area of Shh conditional null animals (Figure 3E). We also observed a reduction in basal dendritic spine density of l ...
http://www.utdallas.edu/~tres/papers/Disterhoftetal1994.pdf
... environmental, or some interaction between the two, has not been definitively established. It has been postulated that excessive influx, raised levels, or poor buffering of intracellular calcium are results, not causes, of the molecular and cellular mechanisms leading to the development of Alzheimer ...
... environmental, or some interaction between the two, has not been definitively established. It has been postulated that excessive influx, raised levels, or poor buffering of intracellular calcium are results, not causes, of the molecular and cellular mechanisms leading to the development of Alzheimer ...
Interplay of environmental signals and progenitor diversity on fate
... Parvalbumin– and somatostatin-expressing interneurons are the two most abundant classes of cortical interneurons with non-overlapping molecular identities and relatively large cell bodies (>20µm; DeFelipe, 1993, 1997; Kawaguchi and Kondo, 2002). GABAergic interneurons expressing PV make up ∼40% of a ...
... Parvalbumin– and somatostatin-expressing interneurons are the two most abundant classes of cortical interneurons with non-overlapping molecular identities and relatively large cell bodies (>20µm; DeFelipe, 1993, 1997; Kawaguchi and Kondo, 2002). GABAergic interneurons expressing PV make up ∼40% of a ...
Chemical Transmitters and Modulation of Sleep
... and sleep generation, the neurotransmitter identity and activity ofBF neurons serving these different functions have remained uncertain. Furthermore, few studies have been done to clarify how the wake vs. sleep promoting neurons may be modulated to generate their differential activity and sleep-wake ...
... and sleep generation, the neurotransmitter identity and activity ofBF neurons serving these different functions have remained uncertain. Furthermore, few studies have been done to clarify how the wake vs. sleep promoting neurons may be modulated to generate their differential activity and sleep-wake ...
The therapeutic implications of ketone bodies
... When ketone bodies are metabolized in heart, the mitochondrial NAD couple is reduced while the mitochondrial Q couple is oxidized increasing the redox span, DEQ=NADH ; between site I and site III, making more energy available for the synthesis of ATP, and hence an increase in the DG 0 of ATP hydroly ...
... When ketone bodies are metabolized in heart, the mitochondrial NAD couple is reduced while the mitochondrial Q couple is oxidized increasing the redox span, DEQ=NADH ; between site I and site III, making more energy available for the synthesis of ATP, and hence an increase in the DG 0 of ATP hydroly ...
The columnar organization of the neocortex
... ependymal surface of the neural tube to the pia, attached by endfeet to both surfaces (Sidman and Rakic, 1973). The three phases of interphase of the cell cycle (G1, S and G2) occur with the nuclei in the mid-position of the cells. When cells enter the prophase of mitosis they withdraw their process ...
... ependymal surface of the neural tube to the pia, attached by endfeet to both surfaces (Sidman and Rakic, 1973). The three phases of interphase of the cell cycle (G1, S and G2) occur with the nuclei in the mid-position of the cells. When cells enter the prophase of mitosis they withdraw their process ...
Identified Serotonergic Neurons LCBI and RCBI in the Cerebral
... Are they excited by cutaneous stimuli known to produce dishabituation and sensitization? (3) Does intracellular stimulation of CB 1 cells, in a manner similar to their response to cutaneous stimulation, produce facilitation of EPSPs from LE cells to follower cells? (4) Is this effect direct? (5) Is ...
... Are they excited by cutaneous stimuli known to produce dishabituation and sensitization? (3) Does intracellular stimulation of CB 1 cells, in a manner similar to their response to cutaneous stimulation, produce facilitation of EPSPs from LE cells to follower cells? (4) Is this effect direct? (5) Is ...
14 Regulation by hypothalamo-hypophisial system and adrenal
... (a) Down-regulation occurs when the number of receptors for a hormone decreases within target cells. For example, gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) released from the hypothalamus binds to GnRH receptors in the anterior pituitary. GnRH bound to its receptors causes down-regulation of the GnRH rec ...
... (a) Down-regulation occurs when the number of receptors for a hormone decreases within target cells. For example, gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) released from the hypothalamus binds to GnRH receptors in the anterior pituitary. GnRH bound to its receptors causes down-regulation of the GnRH rec ...
Deep transcranial magnetic stimulation add
... One patient suffered from mild and self-limiting headaches after the first two treatments. She did not use analgesics. Apart from that no side effects were observed. ...
... One patient suffered from mild and self-limiting headaches after the first two treatments. She did not use analgesics. Apart from that no side effects were observed. ...
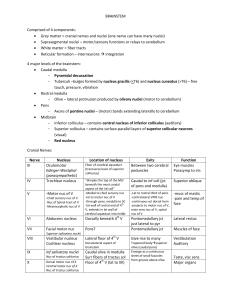
BRAINSTEM Comprised of 4 components: • Grey matter = cranial
... Originate in : Nucleus pontis oralis (rostral pons), nucleus pontis caudalis (caudal pons), gigantocellular reticular nucleus (medulla) - Raphespinal pathway Modulate pain transmission of nocioceptive inputs in the dorsal horn Originate in: Dorsal Raphe, Median Raphe (midbrain and pons) Ascend ...
... Originate in : Nucleus pontis oralis (rostral pons), nucleus pontis caudalis (caudal pons), gigantocellular reticular nucleus (medulla) - Raphespinal pathway Modulate pain transmission of nocioceptive inputs in the dorsal horn Originate in: Dorsal Raphe, Median Raphe (midbrain and pons) Ascend ...
Cholesterol a jeho transport
... LCAT (lecitin cholesterol acyltransferase) - formation of cholesterol esters! ...
... LCAT (lecitin cholesterol acyltransferase) - formation of cholesterol esters! ...
TETHERING: Fragment-Based Drug Discovery
... NON-TETHERING METHODS Detecting fragments that bind a target can be challenging. Traditional high-throughput screening (HTS) typically relies on inhibition assays. But high concentrations of compound may be needed to find weak inhibitors. For example, an inhibitor with an IC50 of 1 mM produces less ...
... NON-TETHERING METHODS Detecting fragments that bind a target can be challenging. Traditional high-throughput screening (HTS) typically relies on inhibition assays. But high concentrations of compound may be needed to find weak inhibitors. For example, an inhibitor with an IC50 of 1 mM produces less ...
Slide 1
... • Action: drug produces a loss of sensation in the specific body part or region • Therapeutic Effect and Clinical Use: – Topical Administration & Transdermal administration – Infiltration anesthesia: injection into local tissues to be numbed – Peripheral nerve block: brachial plexus catheters with r ...
... • Action: drug produces a loss of sensation in the specific body part or region • Therapeutic Effect and Clinical Use: – Topical Administration & Transdermal administration – Infiltration anesthesia: injection into local tissues to be numbed – Peripheral nerve block: brachial plexus catheters with r ...
Cholesterol a jeho transport
... LCAT (lecitin cholesterol acyltransferase) - formation of cholesterol esters! ...
... LCAT (lecitin cholesterol acyltransferase) - formation of cholesterol esters! ...
New dimensions of interneuronal specialization unmasked by
... the excitatory inputs that they receive [9–13]. Such findings suggest that these subpopulations of PCs form distinct excitatory subnetworks that participate in functionally different information-processing streams. How do such excitatory subnetworks formed by PCs with different projection targets in ...
... the excitatory inputs that they receive [9–13]. Such findings suggest that these subpopulations of PCs form distinct excitatory subnetworks that participate in functionally different information-processing streams. How do such excitatory subnetworks formed by PCs with different projection targets in ...
Lecture6 - Part 1 ANS student (2012).
... • Parasympathetic system activities is related to the relaxed state , rest and anabolism • It promotes vegetative functions ( nutritive , body-building , restorative functions & tissue repair ) • Increased secretion of endocrine & exocrine glands . ...
... • Parasympathetic system activities is related to the relaxed state , rest and anabolism • It promotes vegetative functions ( nutritive , body-building , restorative functions & tissue repair ) • Increased secretion of endocrine & exocrine glands . ...
Cholesterol and its transport
... LCAT (lecitin cholesterol acyltransferase) - formation of cholesterol esters! 2. Interaction with other lipoproteins Transfer of apoproteins (Apo C-II, Apo E) and lipids (CETP - cholesterol ester transfer protein) Fate of HDL cholesterol: receptors in the liver, scavenger receptors, transfer t ...
... LCAT (lecitin cholesterol acyltransferase) - formation of cholesterol esters! 2. Interaction with other lipoproteins Transfer of apoproteins (Apo C-II, Apo E) and lipids (CETP - cholesterol ester transfer protein) Fate of HDL cholesterol: receptors in the liver, scavenger receptors, transfer t ...
Molecular Analysis of Developmental Plasticity in Neocortex
... Sretavan and Shatz, 1986). In this context, an appropriate connection is defined as a connection where pre- and postsynaptic activity are correlated—in other words, a Hebbian synapse (Fregnac et al., 1988; Shulz and Fregnac, 1992; Stryker and Strickland, 1984). In principle, the Hebbian synapse hypo ...
... Sretavan and Shatz, 1986). In this context, an appropriate connection is defined as a connection where pre- and postsynaptic activity are correlated—in other words, a Hebbian synapse (Fregnac et al., 1988; Shulz and Fregnac, 1992; Stryker and Strickland, 1984). In principle, the Hebbian synapse hypo ...
hypothalamus, pit..
... The hypothalamus is a small area, weighing about 4 g of the total 1,400 g of adult brain weight, but it is the only 4 g of brain without which life itself is impossible. The hypothalamus is so critical for life because it contains the integrative circuitry that coordinates autonomic, endocrine, and ...
... The hypothalamus is a small area, weighing about 4 g of the total 1,400 g of adult brain weight, but it is the only 4 g of brain without which life itself is impossible. The hypothalamus is so critical for life because it contains the integrative circuitry that coordinates autonomic, endocrine, and ...
OPTOGENETIC STUDY OF THE PROJECTIONS FROM THE BED
... al. 2013). Second, we aimed to minimize use-dependent depression of optogenetically-elicited ...
... al. 2013). Second, we aimed to minimize use-dependent depression of optogenetically-elicited ...
Clinical neurochemistry

Clinical neurochemistry is the field of neurological biochemistry which relates biochemical phenomena to clinical symptomatic manifestations in humans. While neurochemistry is mostly associated with the effects of neurotransmitters and similarly-functioning chemicals on neurons themselves, clinical neurochemistry relates these phenomena to system-wide symptoms. Clinical neurochemistry is related to neurogenesis, neuromodulation, neuroplasticity, neuroendocrinology, and neuroimmunology in the context of associating neurological findings at both lower and higher level organismal functions.