Integer Programming
... • The objective function value of a solution is obtained by evaluating the objective function at the given point. • An optimal solution (assuming maximization) is one whose objective function value is greater than or equal to that of all other feasible solutions. • There are efficient algorithms for ...
... • The objective function value of a solution is obtained by evaluating the objective function at the given point. • An optimal solution (assuming maximization) is one whose objective function value is greater than or equal to that of all other feasible solutions. • There are efficient algorithms for ...
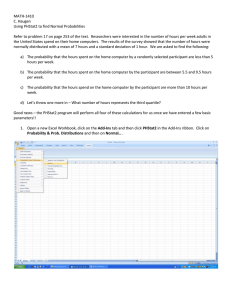
HW3
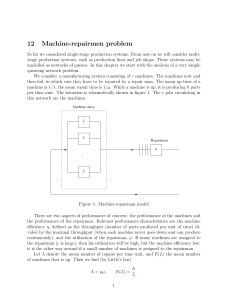
... Here we focus on the distribution for the productivity shock with continuous support. First obtain an approximation for the bond price. In this model the bond price is given by ...
... Here we focus on the distribution for the productivity shock with continuous support. First obtain an approximation for the bond price. In this model the bond price is given by ...