Chapter 1 Linear Equations and Graphs
... the independent variable t represents time, are often used to model population growth and radioactive decay. Note that if t = 0, then y = c. So, the constant c represents the initial population (or initial amount.) The constant k is called the relative growth rate. If the relative growth rate is ...
... the independent variable t represents time, are often used to model population growth and radioactive decay. Note that if t = 0, then y = c. So, the constant c represents the initial population (or initial amount.) The constant k is called the relative growth rate. If the relative growth rate is ...
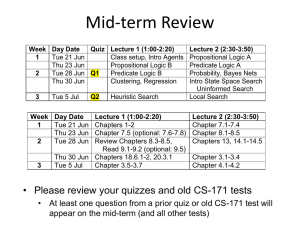
cs-171-09-Midterm-Review_smr16
... environment is completely determined by the current state and the action executed by the agent. (If the environment is deterministic except for the actions of other agents, then the environment is strategic) • Episodic (vs. sequential): An agent’s action is divided into atomic episodes. Decisions do ...
... environment is completely determined by the current state and the action executed by the agent. (If the environment is deterministic except for the actions of other agents, then the environment is strategic) • Episodic (vs. sequential): An agent’s action is divided into atomic episodes. Decisions do ...