solutions activity 5 - Penn State Department of Statistics
... e. What is the probability that a randomly selected student will have spent between $300 and $535? Show work. [Note: You’ll be able to utilize information from parts c and d.] Find as difference in cumulative probabilities from parts c and d: = 0.974049 – 0.252493 = ...
... e. What is the probability that a randomly selected student will have spent between $300 and $535? Show work. [Note: You’ll be able to utilize information from parts c and d.] Find as difference in cumulative probabilities from parts c and d: = 0.974049 – 0.252493 = ...
Probability
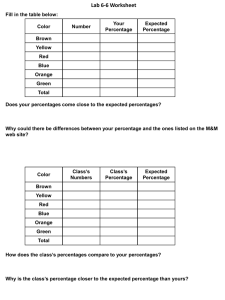
... Another person in the group will then put in 8 green M&Ms and 2 blue M&Ms. Ask the group to predict which color you are more likely to pull out, least likely, unlikely, or equally likely to pull out. The last person in the group will make up his/her own problem with the M&Ms. ...
... Another person in the group will then put in 8 green M&Ms and 2 blue M&Ms. Ask the group to predict which color you are more likely to pull out, least likely, unlikely, or equally likely to pull out. The last person in the group will make up his/her own problem with the M&Ms. ...
5.3 Conditional Probability, Dependent Events, Multiplication Rule
... If small random samples are taken from large populations without replacement, it is reasonable to assume independence of the events. As a general rule, if the sample size is less than 5% of the population, then treat the events as independent. Find the probability that at least 1 male out of 100 ...
... If small random samples are taken from large populations without replacement, it is reasonable to assume independence of the events. As a general rule, if the sample size is less than 5% of the population, then treat the events as independent. Find the probability that at least 1 male out of 100 ...
Supplementary Methods
... We measured the average proportion of all conservation features (species, habitats, bioregions) represented by each of the three results: the Marxan 16% target scenario, the Marxan 30% target scenario, and the large closures categorical classification result. To measure average proportion represente ...
... We measured the average proportion of all conservation features (species, habitats, bioregions) represented by each of the three results: the Marxan 16% target scenario, the Marxan 30% target scenario, and the large closures categorical classification result. To measure average proportion represente ...
Form groups of two or three and discuss the following questions
... (x+1) divided by the total number who lived to age x, is denoted qx. It is the estimated probability of dying aged x”. In demographic jargon this is called the age-specific mortality rate. Note that in this example we have mortality rates for some wider age-ranges. ...
... (x+1) divided by the total number who lived to age x, is denoted qx. It is the estimated probability of dying aged x”. In demographic jargon this is called the age-specific mortality rate. Note that in this example we have mortality rates for some wider age-ranges. ...
Section 1: Basic Probability Concepts
... If S has finitely many points, say S = {a1 , a2 , . . . , ak }, then a probability function P is uniform if P[ai ] = k1 . This says that each outcome is equally (or uniformly) likely to occur. When rolling a fair six-sided die, each side is equally likely to come up. In fact, the probability of get ...
... If S has finitely many points, say S = {a1 , a2 , . . . , ak }, then a probability function P is uniform if P[ai ] = k1 . This says that each outcome is equally (or uniformly) likely to occur. When rolling a fair six-sided die, each side is equally likely to come up. In fact, the probability of get ...
MTAT.03.227 Machine Learning Spring 2016 / Exercise session I
... The aim of this exercise is to study whether strategy is reasonable. Let X be the set of consecutive numbers {1, 2, . . . , 10000}. Study what happens if we compute minimum and mean on based on a small random sample S instead of computing it over the entire dataset X . (a) Write a function that draw ...
... The aim of this exercise is to study whether strategy is reasonable. Let X be the set of consecutive numbers {1, 2, . . . , 10000}. Study what happens if we compute minimum and mean on based on a small random sample S instead of computing it over the entire dataset X . (a) Write a function that draw ...
Muthuvel
... such as simple, compound or continuous compound interest, ordinary annuities, finding the maximum or minimum for quantities which are quadratic functions, and finding break even points, solving systems of linear equations. Use geometric method to solve linear programming problems. Interpret inform ...
... such as simple, compound or continuous compound interest, ordinary annuities, finding the maximum or minimum for quantities which are quadratic functions, and finding break even points, solving systems of linear equations. Use geometric method to solve linear programming problems. Interpret inform ...
Probability box
),steps=500.png?width=300)
A probability box (or p-box) is a characterization of an uncertain number consisting of both aleatoric and epistemic uncertainties that is often used in risk analysis or quantitative uncertainty modeling where numerical calculations must be performed. Probability bounds analysis is used to make arithmetic and logical calculations with p-boxes.An example p-box is shown in the figure at right for an uncertain number x consisting of a left (upper) bound and a right (lower) bound on the probability distribution for x. The bounds are coincident for values of x below 0 and above 24. The bounds may have almost any shapes, including step functions, so long as they are monotonically increasing and do not cross each other. A p-box is used to express simultaneously incertitude (epistemic uncertainty), which is represented by the breadth between the left and right edges of the p-box, and variability (aleatory uncertainty), which is represented by the overall slant of the p-box.