Set Prob 7 - Non-Mutually Exclusive
... disjoint) events. Today we will look at how these problems change if the events are not mutually exclusive. ...
... disjoint) events. Today we will look at how these problems change if the events are not mutually exclusive. ...
2.2 Let E and F be two events for which one knows that the
... at least one of them occurs is 3/4. What is the probability that neither E nor F occurs? Hint: use one of DeMorgan’s laws: E c ∩ F c = (E ∪ F )c . 2.3 Let C and D be two events for which one knows that P(C) = 0.3, P(D) = 0.4, and P(C ∩ D) = 0.2. What is P(C c ∩ D)? 2.4 ! We consider events A, B, and ...
... at least one of them occurs is 3/4. What is the probability that neither E nor F occurs? Hint: use one of DeMorgan’s laws: E c ∩ F c = (E ∪ F )c . 2.3 Let C and D be two events for which one knows that P(C) = 0.3, P(D) = 0.4, and P(C ∩ D) = 0.2. What is P(C c ∩ D)? 2.4 ! We consider events A, B, and ...
Foundations of Cryptography Lecture 2
... • Alice would want to send a message m {0,1}n to Bob – Set-up phase is secret ...
... • Alice would want to send a message m {0,1}n to Bob – Set-up phase is secret ...
ESI 6325: Applied Probability Methods in Engineering (APME) Fall
... Make-up Exam Policy: You are expected to be present without exception and to plan any travel around these dates accordingly. Medical emergencies are of course excluded if accompanied by a doctor's note. A note indicating that you were seen at the health center the day of the exam is not sufficient d ...
... Make-up Exam Policy: You are expected to be present without exception and to plan any travel around these dates accordingly. Medical emergencies are of course excluded if accompanied by a doctor's note. A note indicating that you were seen at the health center the day of the exam is not sufficient d ...
Laws of Probability
... flip resulted in a Tail. The probability of getting both a Head and a Tail in the same flip is evidently 0 (under normal conditions!). ...
... flip resulted in a Tail. The probability of getting both a Head and a Tail in the same flip is evidently 0 (under normal conditions!). ...
Conditional Probability
... Suppose that 60% of all customers of a large insurance agency have automobile policies with the agency, 40% have homeowner’s policies, and 25% have both types of policies. If a customer is randomly selected, what is the probability that he or she has at least one of these two types of policies with ...
... Suppose that 60% of all customers of a large insurance agency have automobile policies with the agency, 40% have homeowner’s policies, and 25% have both types of policies. If a customer is randomly selected, what is the probability that he or she has at least one of these two types of policies with ...
NegetiveReads1
... Operation of the LPA-1 analyzer and its operational statistics Zero measurements and negative values XRF analysis, like all other methods of measurements, is influenced by both random and systematic errors. The random errors are those that their magnitude can be reduced but not eliminated such as th ...
... Operation of the LPA-1 analyzer and its operational statistics Zero measurements and negative values XRF analysis, like all other methods of measurements, is influenced by both random and systematic errors. The random errors are those that their magnitude can be reduced but not eliminated such as th ...
Homework 3
... (c) Give an A and B that are neither mututally exclusive nor mutually independent. (d) Give an A and B that are both mutually exclusive and mututally independent. 3. Show that for finite sample spaces, giving the probability of all of the elementary events is sufficient to determine the probabilitie ...
... (c) Give an A and B that are neither mututally exclusive nor mutually independent. (d) Give an A and B that are both mutually exclusive and mututally independent. 3. Show that for finite sample spaces, giving the probability of all of the elementary events is sufficient to determine the probabilitie ...
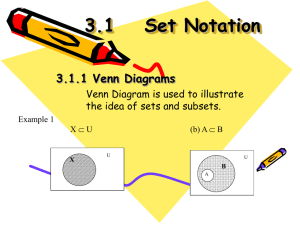
3.1 Set Notation
... – If the letters of the word “MINIMUM” are arranged in a line at random, what is the probability that the three M’s are together at the beginning of the arrangement? – Ten pupils are placed at random in a line. What is the probability that the two youngest pupils are separated? – If a four-digit num ...
... – If the letters of the word “MINIMUM” are arranged in a line at random, what is the probability that the three M’s are together at the beginning of the arrangement? – Ten pupils are placed at random in a line. What is the probability that the two youngest pupils are separated? – If a four-digit num ...
489f10h5.pdf
... the outcomes of the game. Save your chart as you will use this random record several times later in the course to test and illustrate some of the theorems. Each “gambler” flips the coin, and records a +1 (gains $1) if the coin comes up “Heads” and records −1 (loses $1) if the coin comes up “Tails”. ...
... the outcomes of the game. Save your chart as you will use this random record several times later in the course to test and illustrate some of the theorems. Each “gambler” flips the coin, and records a +1 (gains $1) if the coin comes up “Heads” and records −1 (loses $1) if the coin comes up “Tails”. ...
Stat
... - Conduct the necessary data analysis using software of your choice. - Submit a report, written or typed, hard copy or email. If you choose to e-mail the report, send it to both [email protected] and [email protected]. - In the report, describe every step of your analysis: method, reasons, and r ...
... - Conduct the necessary data analysis using software of your choice. - Submit a report, written or typed, hard copy or email. If you choose to e-mail the report, send it to both [email protected] and [email protected]. - In the report, describe every step of your analysis: method, reasons, and r ...
Probability box
),steps=500.png?width=300)
A probability box (or p-box) is a characterization of an uncertain number consisting of both aleatoric and epistemic uncertainties that is often used in risk analysis or quantitative uncertainty modeling where numerical calculations must be performed. Probability bounds analysis is used to make arithmetic and logical calculations with p-boxes.An example p-box is shown in the figure at right for an uncertain number x consisting of a left (upper) bound and a right (lower) bound on the probability distribution for x. The bounds are coincident for values of x below 0 and above 24. The bounds may have almost any shapes, including step functions, so long as they are monotonically increasing and do not cross each other. A p-box is used to express simultaneously incertitude (epistemic uncertainty), which is represented by the breadth between the left and right edges of the p-box, and variability (aleatory uncertainty), which is represented by the overall slant of the p-box.