Slide 1 - Ursinus College Student, Faculty and Staff Web Pages
... standard exam attained by students from her past classes had a mean of 74 and a standard deviation of 14. The teacher decided to use a new book. Using the new book, a class of 50 students scored a mean of 78 on the standardized exam. Find the probability that a class of 50 students using the new boo ...
... standard exam attained by students from her past classes had a mean of 74 and a standard deviation of 14. The teacher decided to use a new book. Using the new book, a class of 50 students scored a mean of 78 on the standardized exam. Find the probability that a class of 50 students using the new boo ...
04-1-m1
... The arithmetic mean is the most commonly used and readily understood measure of central tendency defined as being equal to the sum of the numerical values of each and every observation divided by the total number of observations. ...
... The arithmetic mean is the most commonly used and readily understood measure of central tendency defined as being equal to the sum of the numerical values of each and every observation divided by the total number of observations. ...
THEMATIC SCHOOL ON MATHEMATICAL BIOLOGY, PARTICLE
... Abstract. Hamilton-Jacobi equations with periodic or random coefficients are used, for instance, in the formalization of fronts propagating in inhomogeneous media. After introducing the notion of viscosity solutions of Hamilton-Jacobi equations, we will discuss homogenization in periodic and random ...
... Abstract. Hamilton-Jacobi equations with periodic or random coefficients are used, for instance, in the formalization of fronts propagating in inhomogeneous media. After introducing the notion of viscosity solutions of Hamilton-Jacobi equations, we will discuss homogenization in periodic and random ...
2005 AP Statistics Free Response
... a two sample t-test or a confidence interval for the difference in two means for two independent samples. (don’t forget to state the inference procedure) b) Matched Pairs – now figure out how to block them so that they are paired on purpose, and the pairs are NOT independent Each participant will be ...
... a two sample t-test or a confidence interval for the difference in two means for two independent samples. (don’t forget to state the inference procedure) b) Matched Pairs – now figure out how to block them so that they are paired on purpose, and the pairs are NOT independent Each participant will be ...
Statistical Computing and Simulation
... Evaluate the following quantities by both numerical and Monte Carlo integration, and compare their errors with respect to the numbers of observations used. Also, propose at least two simulation methods to reduce the variance of Monte Carlo integration and compare their variances. ...
... Evaluate the following quantities by both numerical and Monte Carlo integration, and compare their errors with respect to the numbers of observations used. Also, propose at least two simulation methods to reduce the variance of Monte Carlo integration and compare their variances. ...
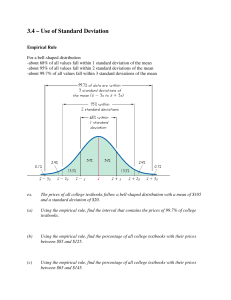
Descriptive Statistics: Central Tendency and Dispersion, Healey Ch
... nominal or ordinal) data are rarely used We will not be covering these in class Omit Formula 4.1 IQV in Healey and Prus 1st Canadian Edition and in Healey 8e Omit Formula 3.1 Variation Ratio in Healey and Prus 2nd Canadian Edition ...
... nominal or ordinal) data are rarely used We will not be covering these in class Omit Formula 4.1 IQV in Healey and Prus 1st Canadian Edition and in Healey 8e Omit Formula 3.1 Variation Ratio in Healey and Prus 2nd Canadian Edition ...
1. Program 9 Instructions, CS101, Prof. Loftin Write a class
... // returns the mean of the values in the array public static double sd (double[] ar) // returns the standard deviation of the values in the array These methods will pass an array of doubles as parameters and will return double values of the mean and standard deviation respectively. Consider x0 , . . ...
... // returns the mean of the values in the array public static double sd (double[] ar) // returns the standard deviation of the values in the array These methods will pass an array of doubles as parameters and will return double values of the mean and standard deviation respectively. Consider x0 , . . ...
ELECTROMAGNETIC ANALOGUE OF A POINT STRUCTURAL
... Since the early studies of Schrödinger [1] on building a classical theory of a particle with spin, a lot of work has been carried out in order to develop models and to analyze physical implications of such particle. The main difficulty of the large number of theoretical studies devoted to this matte ...
... Since the early studies of Schrödinger [1] on building a classical theory of a particle with spin, a lot of work has been carried out in order to develop models and to analyze physical implications of such particle. The main difficulty of the large number of theoretical studies devoted to this matte ...