PPT
... • Using a person’s scores on one or more variables to make a “best guess” of the that person’s score on another variable (the value of which isn’t known) Classification is very similar … • Using a person’s scores on one or more variables to make a “best guess” of the category to which that person be ...
... • Using a person’s scores on one or more variables to make a “best guess” of the that person’s score on another variable (the value of which isn’t known) Classification is very similar … • Using a person’s scores on one or more variables to make a “best guess” of the category to which that person be ...
s - Mrs. Denney
... from 73 home runs to 100 home runs. How is the mean affected? The median? How do the mean and median compare to each other in a symmetric distribution? In a (uni-modal) skewed right distribution? In a (uni-modal) skewed left distribution? ...
... from 73 home runs to 100 home runs. How is the mean affected? The median? How do the mean and median compare to each other in a symmetric distribution? In a (uni-modal) skewed right distribution? In a (uni-modal) skewed left distribution? ...
Review Session 1
... 1. The following are the scores of 25 students who participated in a psychology experiment. The scores represent the number of trials required to complete a memorization test. (Consider the students to be a sample.) ...
... 1. The following are the scores of 25 students who participated in a psychology experiment. The scores represent the number of trials required to complete a memorization test. (Consider the students to be a sample.) ...
confidence intervals
... The value of z is determined by the level of confidence and can be found using normal tables, a graphics calculator or an online statistics program such as Stat Trek: ...
... The value of z is determined by the level of confidence and can be found using normal tables, a graphics calculator or an online statistics program such as Stat Trek: ...
Monte Carlo Simulation Basics
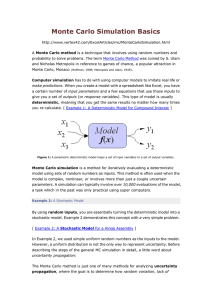
... Although we still need to analyze the data, we have essentially completed a Monte Carlo simulation. Because we have used the volatile RAND() formula, to re-run the simulation all we have to do is recalculate the worksheet (F9 is the shortcut). This may seem like a strange way to implement Monte Carl ...
... Although we still need to analyze the data, we have essentially completed a Monte Carlo simulation. Because we have used the volatile RAND() formula, to re-run the simulation all we have to do is recalculate the worksheet (F9 is the shortcut). This may seem like a strange way to implement Monte Carl ...
Ch03a
... • The weighted mean is the same number you would get if you had totaled all of the original scores and divided by N. • The weighted mean calculation is a shortcut. You can also calculate it by multiplying each sample mean by the proportion of total participants found in each sample. ...
... • The weighted mean is the same number you would get if you had totaled all of the original scores and divided by N. • The weighted mean calculation is a shortcut. You can also calculate it by multiplying each sample mean by the proportion of total participants found in each sample. ...
Unit Operation-II
... Driving forces on Settling and Sedimentation What is the difference between filtration and settling & sedimentation process? FOR FILTRATION – Driving Force is P through a filter medium FOR SETTLING & SEDIMENTATION – Driving Force is gravitational forces ...
... Driving forces on Settling and Sedimentation What is the difference between filtration and settling & sedimentation process? FOR FILTRATION – Driving Force is P through a filter medium FOR SETTLING & SEDIMENTATION – Driving Force is gravitational forces ...
Example
... ***The geometric mean is GM 3 (5)(21)(4) 7.49 The GM gives a more conservative profit figure because it is not heavily weighted by the rate of 21percent. ...
... ***The geometric mean is GM 3 (5)(21)(4) 7.49 The GM gives a more conservative profit figure because it is not heavily weighted by the rate of 21percent. ...