LiuPoster - Department of Mathematics
... • the synchrony of the inhibitory neuron increases (or standard deviation decreases), (see figure 8, right). Increasing the synchrony of the inhibitory neurons is important because this balances out the effect of decreasing thalamic synchrony, which decreases the synchrony of the inhibitory neurons. ...
... • the synchrony of the inhibitory neuron increases (or standard deviation decreases), (see figure 8, right). Increasing the synchrony of the inhibitory neurons is important because this balances out the effect of decreasing thalamic synchrony, which decreases the synchrony of the inhibitory neurons. ...
9.01 Introduction to Neuroscience MIT OpenCourseWare Fall 2007
... Lower motor neurons • ventral horn of spinal cord • motor nuclei of brainstem • send axons to muscles – spinal and cranial nerves ...
... Lower motor neurons • ventral horn of spinal cord • motor nuclei of brainstem • send axons to muscles – spinal and cranial nerves ...
Chapter 15 - Las Positas College
... thought. You involuntarily experience countless smooth muscle and cardiac muscle contractions and gland secretions that provide a stable internal environment for you. Some of the important visceral functions under the regulation of the ANS are maintenance of heart rate and blood pressure, digestion, ...
... thought. You involuntarily experience countless smooth muscle and cardiac muscle contractions and gland secretions that provide a stable internal environment for you. Some of the important visceral functions under the regulation of the ANS are maintenance of heart rate and blood pressure, digestion, ...
Autonomic Nervous System
... brain and spinal cord Consists of: – 31 Spinal nerves Carry info to and from the spinal cord – 12 Cranial nerves Carry info to and from the brain ...
... brain and spinal cord Consists of: – 31 Spinal nerves Carry info to and from the spinal cord – 12 Cranial nerves Carry info to and from the brain ...
Nerve Tissue
... – more and more Na+ channels open in in the trigger zone in a positive feedback cycle creating a rapid rise in membrane voltage – spike ...
... – more and more Na+ channels open in in the trigger zone in a positive feedback cycle creating a rapid rise in membrane voltage – spike ...
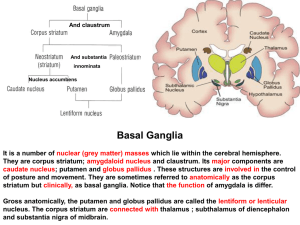
17-Basal ganglion
... It is an autosomal dominant inherited disease with the onset occurring in adult life. Within the striatum, there is particular attrition of the cells that project to the lateral segment of the globus pallidus ( indirect segment ). This leads to disinhibition of the lateral pallidal neurons and inhib ...
... It is an autosomal dominant inherited disease with the onset occurring in adult life. Within the striatum, there is particular attrition of the cells that project to the lateral segment of the globus pallidus ( indirect segment ). This leads to disinhibition of the lateral pallidal neurons and inhib ...
Impact of Correlated inputs on Simple Neural Models
... of the recipient neuron The effect is qualitatively independent of the neural model The neurons have specific preferences to certain levels of correlations in input trains The temporal correlation can dramatically modulate the neural responsiveness ...
... of the recipient neuron The effect is qualitatively independent of the neural model The neurons have specific preferences to certain levels of correlations in input trains The temporal correlation can dramatically modulate the neural responsiveness ...
Chapter 16: Neural Integration II: The Autonomic Nervous System
... stretch to reach target organs • Single preganglionic fiber may innervate 2 dozen or more ganglionic neurons in different ganglia ...
... stretch to reach target organs • Single preganglionic fiber may innervate 2 dozen or more ganglionic neurons in different ganglia ...
Neural Pascal
... driving such a network will take advantage of the structuring of the net, or of the properties of neurons when performing calculations or when updating states of neurons. It seems highly desirable to translate this view of a network into an executable program as directly as possible with the actual ...
... driving such a network will take advantage of the structuring of the net, or of the properties of neurons when performing calculations or when updating states of neurons. It seems highly desirable to translate this view of a network into an executable program as directly as possible with the actual ...
CH 8 Nervous System - Belle Vernon Area School District
... 12. Below are given the steps of the patellar reflex arc. What is the correct order of events from the time the hammer taps the patellar ligament to the knee jerk response? 1) The leg extends at the knee. 2) Sensory neurons conduct the action potentials to the spinal cord. 3) Motor neurons are stimu ...
... 12. Below are given the steps of the patellar reflex arc. What is the correct order of events from the time the hammer taps the patellar ligament to the knee jerk response? 1) The leg extends at the knee. 2) Sensory neurons conduct the action potentials to the spinal cord. 3) Motor neurons are stimu ...
Review of Thoracic and Abdominal Autonomics
... from the T1-T4 chain ganglia—some pass through cervical ganglia on their way to the heart. It may seem odd that some of the pathways to the heart start in the thoracic spinal cord, run all the way up to the superior cervical ganglion, synapse, and then descend again into the thorax. This is a holdov ...
... from the T1-T4 chain ganglia—some pass through cervical ganglia on their way to the heart. It may seem odd that some of the pathways to the heart start in the thoracic spinal cord, run all the way up to the superior cervical ganglion, synapse, and then descend again into the thorax. This is a holdov ...
Biology and Behavior note frame
... a. The “_______________ _______________” during which a neuron, after firing, cannot _______________ another _______________ _______________ b. Once the refractory period is complete the neuron can _______________ _______________ 3. Resting Potential a. The state of a neuron when it is at _________ ...
... a. The “_______________ _______________” during which a neuron, after firing, cannot _______________ another _______________ _______________ b. Once the refractory period is complete the neuron can _______________ _______________ 3. Resting Potential a. The state of a neuron when it is at _________ ...
Examination of sensory physiology Obgective:To determine the
... the midline and ascend in the medial lemniscus to nucleus of thalamus . this is called dorsal column pathway . other touch fibers (crud) with those mediating temperature and pain synapse on neuron in the dorsal horn. The second order neurons cross the midline and ascend in the ventral and lateral sp ...
... the midline and ascend in the medial lemniscus to nucleus of thalamus . this is called dorsal column pathway . other touch fibers (crud) with those mediating temperature and pain synapse on neuron in the dorsal horn. The second order neurons cross the midline and ascend in the ventral and lateral sp ...
PDF
... behaviors and their mechanisms of central pattern generation. General mechanisms that contribute to central pattern generator function in other animal groups, such as reciprocal inhibition, postinhibitory rebound, multi-component synaptic potentials, delayed excitation, and extrinsic modulation (to ...
... behaviors and their mechanisms of central pattern generation. General mechanisms that contribute to central pattern generator function in other animal groups, such as reciprocal inhibition, postinhibitory rebound, multi-component synaptic potentials, delayed excitation, and extrinsic modulation (to ...
Orbitofrontal Cortex and Its Contribution to Decision
... cognitive measures correlate expected reward while driving neuronal response. ...
... cognitive measures correlate expected reward while driving neuronal response. ...
Chapter 16: Basal Ganglia
... further integrates the already highly integrated signals from the visual areas of the cortex, such as MT and V5. The parietal lobes are themselves closely interconnected with the prefrontal areas, and together these two regions represent the highest level of integration in the motor control hierarch ...
... further integrates the already highly integrated signals from the visual areas of the cortex, such as MT and V5. The parietal lobes are themselves closely interconnected with the prefrontal areas, and together these two regions represent the highest level of integration in the motor control hierarch ...
Neural Cell Assemblies for Practical
... the relationships between the sub-patterns. These relationships may be based on semantics or on some arbitrary concept. This kind of system can be used to build large LAMs. For example, consider the situation where a person cannot remember the name of the band who sang the song ‘Satisfaction’, but c ...
... the relationships between the sub-patterns. These relationships may be based on semantics or on some arbitrary concept. This kind of system can be used to build large LAMs. For example, consider the situation where a person cannot remember the name of the band who sang the song ‘Satisfaction’, but c ...
CNS II
... - Impulse may be changed from a single impulse into repetitive impulses - Impulse may be integrated with impulses from other neurons to cause highly intricate patterns of impulses • Types of synapses – chemical and electrical – Chemical synapses • Almost all synapses are chemical • Neurotransmitter ...
... - Impulse may be changed from a single impulse into repetitive impulses - Impulse may be integrated with impulses from other neurons to cause highly intricate patterns of impulses • Types of synapses – chemical and electrical – Chemical synapses • Almost all synapses are chemical • Neurotransmitter ...
Glossary of commonly used Occupational Therapy terms
... Tactile Sense: The sensory system that receives sensations of pressure, vibration, movement, temperature and pain, primarily through receptors in the skin. Tracking: Following a moving object or a line of print with the eyes. Vestibular: Refers to our sense of movement and the pull of gravity, relat ...
... Tactile Sense: The sensory system that receives sensations of pressure, vibration, movement, temperature and pain, primarily through receptors in the skin. Tracking: Following a moving object or a line of print with the eyes. Vestibular: Refers to our sense of movement and the pull of gravity, relat ...
Attack and Escape Behaviors
... • Emotional experiences arouse many areas of the brain. • The limbic system has traditionally been regarded as critical for emotion. • PET and fMRI studies also suggest many other areas of the cerebral cortex, especially the frontal and temporal lobes, are activated during an emotional experience. ...
... • Emotional experiences arouse many areas of the brain. • The limbic system has traditionally been regarded as critical for emotion. • PET and fMRI studies also suggest many other areas of the cerebral cortex, especially the frontal and temporal lobes, are activated during an emotional experience. ...
The Autonomic Nervous System
... 3) pass through the chain in the thoracic portion of the trunk without synapsing, form the splanchnic nerves 4) pass through the sympathetic chain and synapse in the adrenal medulla (T10, 11) ( SPECIAL!) ...
... 3) pass through the chain in the thoracic portion of the trunk without synapsing, form the splanchnic nerves 4) pass through the sympathetic chain and synapse in the adrenal medulla (T10, 11) ( SPECIAL!) ...
Cortical Control of Motor Function-L18
... Primary motor cortex - loss of voluntary control of discrete movement of the distal segments of the ...
... Primary motor cortex - loss of voluntary control of discrete movement of the distal segments of the ...
Neural networks
... • Motivation: the simulation of the neuo system (human brain)’s information processing mechanisms • Structure: huge amount of densely connected, mutally operating processing units (neurons) • It learns from experiences (training instances) ...
... • Motivation: the simulation of the neuo system (human brain)’s information processing mechanisms • Structure: huge amount of densely connected, mutally operating processing units (neurons) • It learns from experiences (training instances) ...
Caridoid escape reaction

The caridoid escape reaction, also known as lobstering or tail-flipping, refers to an innate escape mechanism in marine and freshwater crustaceans such as lobsters, krill, shrimp and crayfish.The reaction, most extensively researched in crayfish, allows crustaceans to escape predators through rapid abdominal flexions that produce powerful swimming strokes — thrusting the crustacean backwards through the water and away from danger. The type of response depends on the part of the crustacean stimulated, but this behavior is complex and is regulated both spatially and temporally through the interactions of several neurons.