Some text - (canvas.brown.edu).
... Whenever a cell fires, there will be a little tick-mark on the graph. Each time a cell fires it will release neurotransmitter. ...
... Whenever a cell fires, there will be a little tick-mark on the graph. Each time a cell fires it will release neurotransmitter. ...
Regulation of Astrocyte Plasticity
... It should be noted that these effects are not limited to cerebellar cortex. Kleim et al. (papers and absts) have described synaptogenesis and changes in synapse morphology in association with the same AC motor learning procedure in the somatosensory-somatomotor forelimb cortex of rats. The first mor ...
... It should be noted that these effects are not limited to cerebellar cortex. Kleim et al. (papers and absts) have described synaptogenesis and changes in synapse morphology in association with the same AC motor learning procedure in the somatosensory-somatomotor forelimb cortex of rats. The first mor ...
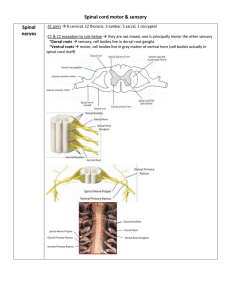
Changes in spinal cord
... *mainly function to control “automatic functions” such as walking or posture -tectospinal *from superior colliculus to ventral horn of cervical region *decussates at level of colliculus *only functions in upper limb/neck *tectum is associated with visual movements also- coordination of muscle with v ...
... *mainly function to control “automatic functions” such as walking or posture -tectospinal *from superior colliculus to ventral horn of cervical region *decussates at level of colliculus *only functions in upper limb/neck *tectum is associated with visual movements also- coordination of muscle with v ...
Anatomy Review - Interactive Physiology
... ________ or __________, and the signal can be modified as it passes from one neuron to the next. a. electrical synapses, excitatory, inhibitory b. chemical synapses, excitatory, inhibitory 29. (Page 7.) Chemical synapses are the most common type of ________, and they are associated with the most com ...
... ________ or __________, and the signal can be modified as it passes from one neuron to the next. a. electrical synapses, excitatory, inhibitory b. chemical synapses, excitatory, inhibitory 29. (Page 7.) Chemical synapses are the most common type of ________, and they are associated with the most com ...
MOTOR SYSTEM – Muscle, LMC, Spinal cord mechanisms of control
... - Both rules lead to increases in force that are smooth 5. - A network of interneurons responsible for generating an automatic rhythmical movement is called central pattern generator (CPG); CPGs are in the spinal cord and brainstem for respiration, chewing, swallowing, and locomotion - once a CPG is ...
... - Both rules lead to increases in force that are smooth 5. - A network of interneurons responsible for generating an automatic rhythmical movement is called central pattern generator (CPG); CPGs are in the spinal cord and brainstem for respiration, chewing, swallowing, and locomotion - once a CPG is ...
Area MST has been thought be involved in heading perception not
... during optic flow (Visual condition), real motion (Vestibular condition) and congruent combinations of the two (Combined condition) using a novel virtual reality system that can move animals along arbitrary paths through a 3D virtual environment. To examine how visual and vestibular signals in MSTd ...
... during optic flow (Visual condition), real motion (Vestibular condition) and congruent combinations of the two (Combined condition) using a novel virtual reality system that can move animals along arbitrary paths through a 3D virtual environment. To examine how visual and vestibular signals in MSTd ...
physiology 1 lab: general cutaneous sensations
... The adaptation appears to happen because the rate of change within the nerve's membrane is inadequate to keep up with continuous stimulation. There are many examples of adaptation in everyday life. For example, our clothing is in constant contact with our skin, which should constantly stimulate touc ...
... The adaptation appears to happen because the rate of change within the nerve's membrane is inadequate to keep up with continuous stimulation. There are many examples of adaptation in everyday life. For example, our clothing is in constant contact with our skin, which should constantly stimulate touc ...
Spinal Cord - Study Windsor
... and progressive weakness of her right lower limb for a period of two months, she contacted her Family physician, Her Family physician referred her to a neurologist. The neurologic evaluation revealed weakness in the right lower limb. This was associated with spasticity (increased tone), hyperrefle ...
... and progressive weakness of her right lower limb for a period of two months, she contacted her Family physician, Her Family physician referred her to a neurologist. The neurologic evaluation revealed weakness in the right lower limb. This was associated with spasticity (increased tone), hyperrefle ...
Leap 2 - Teacher - Teacher Enrichment Initiatives
... 2. be destroyed by chemical reactions that take place in the “receiving” neuron 3. be destroyed by specialized “clean up” glial cells 4. be reabsorbed back into the “sending” neuron - this reabsorption will signal cells to STOP releasing additional neurotransmitter, until the next stimulus occurs. T ...
... 2. be destroyed by chemical reactions that take place in the “receiving” neuron 3. be destroyed by specialized “clean up” glial cells 4. be reabsorbed back into the “sending” neuron - this reabsorption will signal cells to STOP releasing additional neurotransmitter, until the next stimulus occurs. T ...
The vertebrate nervous system is regionally specialized
... Invertebrate nervous systems range in complexity from simple nerve nets to highly centralized nervous systems having complicated brains and ventral nerve cords. In vertebrates, the central nervous system (CNS) consists of the brain and the spinal cord, which is located dorsally. Information processi ...
... Invertebrate nervous systems range in complexity from simple nerve nets to highly centralized nervous systems having complicated brains and ventral nerve cords. In vertebrates, the central nervous system (CNS) consists of the brain and the spinal cord, which is located dorsally. Information processi ...
tractus corticomuscularis
... different physiological processes. That means that nervous system unites, integrates and subordinates all the parts of human body and provides its connection with environment ...
... different physiological processes. That means that nervous system unites, integrates and subordinates all the parts of human body and provides its connection with environment ...
Lecture 11: Chapter 15 Neural Integration I: Sensory
... Incoming information is processed by CNS and distributed by the: 1. The Somatic Nervous System (SNS) 2. Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) SNS also called Somatic motor system controls contraction of skeletal muscle Motor commands control skeletal muscle travel by: ...
... Incoming information is processed by CNS and distributed by the: 1. The Somatic Nervous System (SNS) 2. Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) SNS also called Somatic motor system controls contraction of skeletal muscle Motor commands control skeletal muscle travel by: ...
Division of Informatics, University of Edinburgh
... or the experimenter. However, repeated observation of tool usage (e.g. pliers) has been informally reported to increase the corresponding activation (Rizzolatti and Arbib, 1998). The interacting objects themselves were found to be insignificant: the monkeys respond equally strongly to food as they d ...
... or the experimenter. However, repeated observation of tool usage (e.g. pliers) has been informally reported to increase the corresponding activation (Rizzolatti and Arbib, 1998). The interacting objects themselves were found to be insignificant: the monkeys respond equally strongly to food as they d ...
THE SENSORIMOTOR SYSTEM (p.l) 1. Introduction Like the
... Lesions --- S unable to move one body part without moving other parts (loses the precision of movement) --- astereognosia (difficulty recognizing objects by touch) --- reduced speed, accuracy & force of movement --- but S still above to move (less precise, “clumsy” movements) 6. Cerebellum and Basal ...
... Lesions --- S unable to move one body part without moving other parts (loses the precision of movement) --- astereognosia (difficulty recognizing objects by touch) --- reduced speed, accuracy & force of movement --- but S still above to move (less precise, “clumsy” movements) 6. Cerebellum and Basal ...
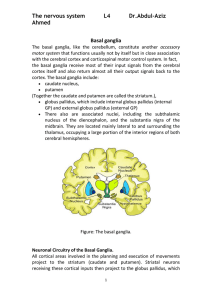
L8 slides
... Basal ganglia, cerebellum and the cortex • Both the cerebellum and basal ganglia have a complex disinhibitory output dynamic, which produces a gating-like effect on the brain areas they control. • For example, the basal ganglia can disinhibit neurons in specific nuclei of the thalamus, which have b ...
... Basal ganglia, cerebellum and the cortex • Both the cerebellum and basal ganglia have a complex disinhibitory output dynamic, which produces a gating-like effect on the brain areas they control. • For example, the basal ganglia can disinhibit neurons in specific nuclei of the thalamus, which have b ...
CRAYFISH DISSECTION - local.brookings.k12.sd.us
... http://biog-101-104.bio.cornell.edu/BioG101_104/tutorials/animals/crayfish.html ...
... http://biog-101-104.bio.cornell.edu/BioG101_104/tutorials/animals/crayfish.html ...
1.In the direct pathway
... 1.the substantia nigra, send Dopamine secreting neuron into the striatum. Dopamine has an excitatory effect upon cells in the striatum that are part of the Direct Pathway. This is via D1 receptors. Dopamine ...
... 1.the substantia nigra, send Dopamine secreting neuron into the striatum. Dopamine has an excitatory effect upon cells in the striatum that are part of the Direct Pathway. This is via D1 receptors. Dopamine ...
Poster No: 1064 - Orthopaedic Research Society
... DISCUSSION. Disturbance of axonal flow therefore threatens the survival of neurons and appears to be one cause of neurological dysfunction. In this study, compression of the peripheral branches of motor neurons in the nerve root led to impairment of axonal flow and central chromatolysis in the neuro ...
... DISCUSSION. Disturbance of axonal flow therefore threatens the survival of neurons and appears to be one cause of neurological dysfunction. In this study, compression of the peripheral branches of motor neurons in the nerve root led to impairment of axonal flow and central chromatolysis in the neuro ...
ppt - Brain Dynamics Laboratory
... • Neural communication depends on the anatomical components that connect individual neurons (structure) and the process of transmitting information (function). Both aspects affect the overall performance of the system. ...
... • Neural communication depends on the anatomical components that connect individual neurons (structure) and the process of transmitting information (function). Both aspects affect the overall performance of the system. ...
Unsupervised models and clustering
... Introduction 1 In order to efficiently mimic the nervous system, it is necessary to get an idea of the nature of the biological processes that actually take place in the brain The only reasonable assumption is that they are driven by mechanisms aimed at optimizing the target they have to pursue E ...
... Introduction 1 In order to efficiently mimic the nervous system, it is necessary to get an idea of the nature of the biological processes that actually take place in the brain The only reasonable assumption is that they are driven by mechanisms aimed at optimizing the target they have to pursue E ...
שקופית 1
... initial values for the first spike are u1 U , R1 1 The parameters U, D, and F were randomly chosen from gaussian distributions that were based on empirically found data for such connections: ◦ If the input was excitatory (E) the mean values of these three parameters (with D, F expressed in secon ...
... initial values for the first spike are u1 U , R1 1 The parameters U, D, and F were randomly chosen from gaussian distributions that were based on empirically found data for such connections: ◦ If the input was excitatory (E) the mean values of these three parameters (with D, F expressed in secon ...
Lecture 19
... fibers. Myelinated nerves, composed mainly of myelinated axons, appear white in the fresh state. The sheath of myelinated fibers is formed by concentric layers of membranes of the Schwann cell (or oligodendrocyte in the CNS) around the axon, which unite to form a lipoprotein complex. This stains bla ...
... fibers. Myelinated nerves, composed mainly of myelinated axons, appear white in the fresh state. The sheath of myelinated fibers is formed by concentric layers of membranes of the Schwann cell (or oligodendrocyte in the CNS) around the axon, which unite to form a lipoprotein complex. This stains bla ...
Threshold Stimulus
... potential • Blocks _______ channels • Sodium cannot flow into the cell, so threshold is not achieved ...
... potential • Blocks _______ channels • Sodium cannot flow into the cell, so threshold is not achieved ...
The biology of time across different scales
... of time that has elapsed since the previous presynaptic action potential, a synapse that was not strong enough to elicit a postsynaptic action potential at time 0 may elicit one at 100 ms. In a circuit, short-term synaptic plasticity occurs at both excitatory and inhibitory synapses; thus, there is ...
... of time that has elapsed since the previous presynaptic action potential, a synapse that was not strong enough to elicit a postsynaptic action potential at time 0 may elicit one at 100 ms. In a circuit, short-term synaptic plasticity occurs at both excitatory and inhibitory synapses; thus, there is ...
Caridoid escape reaction

The caridoid escape reaction, also known as lobstering or tail-flipping, refers to an innate escape mechanism in marine and freshwater crustaceans such as lobsters, krill, shrimp and crayfish.The reaction, most extensively researched in crayfish, allows crustaceans to escape predators through rapid abdominal flexions that produce powerful swimming strokes — thrusting the crustacean backwards through the water and away from danger. The type of response depends on the part of the crustacean stimulated, but this behavior is complex and is regulated both spatially and temporally through the interactions of several neurons.