Origins of the Universe
... • A major object which orbits around a star • In our solar system, there are eight such objects which are traditionally called “planets” ...
... • A major object which orbits around a star • In our solar system, there are eight such objects which are traditionally called “planets” ...
Variable and Binary Stars
... If two stars coalesce out of a globule near enough to each other but with sufficient relative velocity, they will orbit about their common center AKA Barycenter ...
... If two stars coalesce out of a globule near enough to each other but with sufficient relative velocity, they will orbit about their common center AKA Barycenter ...
Astronomy 360 Physics/Geology 360
... Pleiades has several meanings in different cultures and traditions. The cluster is dominated by hot blue and extremely luminous stars that have formed within the last 100 million years. Dust that forms a faint reflection nebulosity around the brightest stars was thought at first to be left over from ...
... Pleiades has several meanings in different cultures and traditions. The cluster is dominated by hot blue and extremely luminous stars that have formed within the last 100 million years. Dust that forms a faint reflection nebulosity around the brightest stars was thought at first to be left over from ...
For each statement or question, select the word or expression that
... D. Their brightness cannot be compare without more data. ____ 14. Most stars are composed mainly of A. iron and titanium B. titanium and hydrogen C. hydrogen and helium D. helium and iron ____ 15. Red giants that lose their atmospheres leave faint, Earth-sized stars called A. Cepheid variables B. bl ...
... D. Their brightness cannot be compare without more data. ____ 14. Most stars are composed mainly of A. iron and titanium B. titanium and hydrogen C. hydrogen and helium D. helium and iron ____ 15. Red giants that lose their atmospheres leave faint, Earth-sized stars called A. Cepheid variables B. bl ...
Our Universe - Etiwanda E
... What happens to comets after they pass the sun several times? Most asteroids are between the orbits of what two planets? ...
... What happens to comets after they pass the sun several times? Most asteroids are between the orbits of what two planets? ...
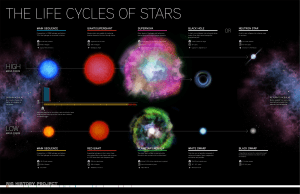
SES4U Life Cycle of a Star
... the protostar becomes a brown dwarf and never reaches star status If critical temperature is reached, nuclear fusion begins (H fuses into He for the first time) ...
... the protostar becomes a brown dwarf and never reaches star status If critical temperature is reached, nuclear fusion begins (H fuses into He for the first time) ...
Intro L4 IQ
... the apparent (observed) motion of planets are the “geocentric” (Earth-centered) and “heliocentric” (Suncentered) models. The accepted model today is: ...
... the apparent (observed) motion of planets are the “geocentric” (Earth-centered) and “heliocentric” (Suncentered) models. The accepted model today is: ...
The most accepted theory of the origin of the solar system is the
... Space Telescope discovered many examples of disks around newly formed stars in the great nebula in Orion. As the name suggests, protoplanetary disks (proplyds) are thought to contain the material from which planets form around stars. ...
... Space Telescope discovered many examples of disks around newly formed stars in the great nebula in Orion. As the name suggests, protoplanetary disks (proplyds) are thought to contain the material from which planets form around stars. ...
Unit 10 H-R Diagram Worksheet
... _______________________________________________________________ 9. About how many times brighter than the Sun is Betelgeuse? _________________________________ 10. If Betelgeuse is so bright, why does the Sun appear brighter to us? _____________________________________________________________ 11. Whi ...
... _______________________________________________________________ 9. About how many times brighter than the Sun is Betelgeuse? _________________________________ 10. If Betelgeuse is so bright, why does the Sun appear brighter to us? _____________________________________________________________ 11. Whi ...
Chapter 28 Vocabulary
... Neutron star – The superdense remains of a massive star that collapsed with enough force to push all of its electrons into the nuclei they orbit, resulting in a mass of ...
... Neutron star – The superdense remains of a massive star that collapsed with enough force to push all of its electrons into the nuclei they orbit, resulting in a mass of ...
Stars - TeacherWeb
... here on Earth, they can be many different sizes. • Neutron Stars are the smallest. They are made of the material left behind after a larger star explodes; about 20 kilometers in diameter. ...
... here on Earth, they can be many different sizes. • Neutron Stars are the smallest. They are made of the material left behind after a larger star explodes; about 20 kilometers in diameter. ...
StarType
... When you look at the stars you’ll notice that some are white, some are yellow, and some are red. Stars are classified according to their colors, ranging from electric blue for the hottest stars to dull red for the coolest stars. Early spectrometers identified emission lines in the stars’ spectrum fo ...
... When you look at the stars you’ll notice that some are white, some are yellow, and some are red. Stars are classified according to their colors, ranging from electric blue for the hottest stars to dull red for the coolest stars. Early spectrometers identified emission lines in the stars’ spectrum fo ...
Unit 12 Guide: Concepts of Earth Science Stars, Galaxies, and the
... Be able to use an H-R diagram to determine the stage in stellar evolution of a given star. 11. What are the stages in the life of a high mass star? A low mass star? Be able to give characteristics of stars at each stage. 12. Be able to label and describe the three layers of the Sun’s interior: core, ...
... Be able to use an H-R diagram to determine the stage in stellar evolution of a given star. 11. What are the stages in the life of a high mass star? A low mass star? Be able to give characteristics of stars at each stage. 12. Be able to label and describe the three layers of the Sun’s interior: core, ...
Sammy Nagel · Annie Jump Cannon
... What were the contribution(s) that this individual made to science and/or a related field? She classified over 350000 stars.1.She also classified over 300 rare types of stars.2.Annie organized and collected photos for Harvard.3.She added over 300000 photos to their collection.4.Harvard had 200000 ph ...
... What were the contribution(s) that this individual made to science and/or a related field? She classified over 350000 stars.1.She also classified over 300 rare types of stars.2.Annie organized and collected photos for Harvard.3.She added over 300000 photos to their collection.4.Harvard had 200000 ph ...
File
... 6. How would you classify the sun based on each of these characteristics? Building Vocabulary From the list below, choose the term that best completes each sentence and then write the entire sentence in your notebook. spectrograph constellation light-year ...
... 6. How would you classify the sun based on each of these characteristics? Building Vocabulary From the list below, choose the term that best completes each sentence and then write the entire sentence in your notebook. spectrograph constellation light-year ...
C472 Continuous Assessment: Essay #2
... conference. The now famous Drake Equation considers, amongst others, the factors discussed by Wallace, as a series of diminishing probabilities in an attempt to quantify the number of stars in the Milky Way galaxy, the fraction of stars with orbiting planets, the number of planets per star capable o ...
... conference. The now famous Drake Equation considers, amongst others, the factors discussed by Wallace, as a series of diminishing probabilities in an attempt to quantify the number of stars in the Milky Way galaxy, the fraction of stars with orbiting planets, the number of planets per star capable o ...
Exploring Space
... Star Birth When the core of the Protostar reaches 10 million K, pressure is so great that nuclear fusion occurs- a star is born Heat from fusion of hydrogen is released When balance is maintained from inward pressure (gravity) and outward pressure (heat) the Main-Sequence stage is ...
... Star Birth When the core of the Protostar reaches 10 million K, pressure is so great that nuclear fusion occurs- a star is born Heat from fusion of hydrogen is released When balance is maintained from inward pressure (gravity) and outward pressure (heat) the Main-Sequence stage is ...