radio telescope - TorquayCollege56
... name of this category of star cluster is derived from the Latin globulus—a small sphere. A globular cluster is sometimes known more simply as a globular. ...
... name of this category of star cluster is derived from the Latin globulus—a small sphere. A globular cluster is sometimes known more simply as a globular. ...
Kuiper Belt - Shades of Blue
... Exoplanet 55 Cancri e twice Earth’s Size – and made largely of diamond Oct 12, 2012 – Wired UK ...
... Exoplanet 55 Cancri e twice Earth’s Size – and made largely of diamond Oct 12, 2012 – Wired UK ...
Place the stars in the proper sequence, following the
... Along the main sequence, stars of greater magnitude are hotter (have more energy) c. How is a star’s luminosity related to its energy? For main-sequence stars, the luminosity increases with temperature. For the giants and super-giants, large (high magnitude) and luminous stars are actually quite coo ...
... Along the main sequence, stars of greater magnitude are hotter (have more energy) c. How is a star’s luminosity related to its energy? For main-sequence stars, the luminosity increases with temperature. For the giants and super-giants, large (high magnitude) and luminous stars are actually quite coo ...
Wrongway Planets_Do Gymnastics
... responsible f or the planets' behavior. "Their data isn't that definitive to eliminate any other possibilities," Adam Burrows told Science News. Burrows is a scientist at Princeton University. Astronomers have identified more than 400 exoplanets, and most of them are gas giants, like the hot Jupiter ...
... responsible f or the planets' behavior. "Their data isn't that definitive to eliminate any other possibilities," Adam Burrows told Science News. Burrows is a scientist at Princeton University. Astronomers have identified more than 400 exoplanets, and most of them are gas giants, like the hot Jupiter ...
Lecture 31 - 2 The Death of Stars: Stellar Recycling Phase 3 -
... • Helium core shrinks by a factor of ~30 to a size approximately that of the Earth • Hydrogen “burning” (i.e. H→He+energy release) continues in a thin shell just outside collapsing He core. • total luminosity of star increases by 100 to 1000 due to renewed H burning + heating of collapsing core. • o ...
... • Helium core shrinks by a factor of ~30 to a size approximately that of the Earth • Hydrogen “burning” (i.e. H→He+energy release) continues in a thin shell just outside collapsing He core. • total luminosity of star increases by 100 to 1000 due to renewed H burning + heating of collapsing core. • o ...
SISTERS OF THE SUN
... “Nothing lasts forever… Even the stars die” [If time permits, please review Symphony of Science’s Glorious Dawn.] 1. We pulled the stars from the skies and brought them down to Earth. But when we turned on all these lights, we lost something precious: 2. Humans were not the fastest or strongest of t ...
... “Nothing lasts forever… Even the stars die” [If time permits, please review Symphony of Science’s Glorious Dawn.] 1. We pulled the stars from the skies and brought them down to Earth. But when we turned on all these lights, we lost something precious: 2. Humans were not the fastest or strongest of t ...
Chapter 17 Science Class 8
... 4. The Moon and Venus appear to change phases, because from Earth only part of the reflected sunlight can be seen as these two move in their orbit. The Earth has many man made or artificial satellites that are nearer than the Moon , and therefore, do not reflect sunlight regularly. They can seen for ...
... 4. The Moon and Venus appear to change phases, because from Earth only part of the reflected sunlight can be seen as these two move in their orbit. The Earth has many man made or artificial satellites that are nearer than the Moon , and therefore, do not reflect sunlight regularly. They can seen for ...
lecture 32 orbits
... even move backwards with respect to the surrounding stars (retrograde motion). During a planet’s retrograde motion, it appeared brighter than at other times. This suggested to the Greeks that the planet was closer to Earth during its retrograde motion. ...
... even move backwards with respect to the surrounding stars (retrograde motion). During a planet’s retrograde motion, it appeared brighter than at other times. This suggested to the Greeks that the planet was closer to Earth during its retrograde motion. ...
Class Notes for Monday, Feb 20th
... – Our star (Sun) and everything that orbits around it (planets, asteroids, comets, etc.) • Galaxy – Huge collection of stars bound together by gravity (the Sun is 1 star among 100400 billion stars in the Milky Way galaxy) • Universe – Everything (~100 billion galaxies) ...
... – Our star (Sun) and everything that orbits around it (planets, asteroids, comets, etc.) • Galaxy – Huge collection of stars bound together by gravity (the Sun is 1 star among 100400 billion stars in the Milky Way galaxy) • Universe – Everything (~100 billion galaxies) ...
Early history of astronomy
... • The motion of a body, such as a planet or moon, along a path around some point in space • Earth's orbit is elliptical • Earth is closest to the Sun (perihelion) in January • Earth is farthest from the Sun (aphelion) in July • The plane of the ecliptic is an imaginary plane that connects Earth's or ...
... • The motion of a body, such as a planet or moon, along a path around some point in space • Earth's orbit is elliptical • Earth is closest to the Sun (perihelion) in January • Earth is farthest from the Sun (aphelion) in July • The plane of the ecliptic is an imaginary plane that connects Earth's or ...
Slide 1
... it will become a red giant fairly quickly. • When its fusion stops, a central iron core remains. • The temperature heats up dramatically and causes a supernova. • A neutron star is the mass that remains. ...
... it will become a red giant fairly quickly. • When its fusion stops, a central iron core remains. • The temperature heats up dramatically and causes a supernova. • A neutron star is the mass that remains. ...
A stars
... The size and location of the HZ depends on the nature of the star The situation becomes even more extreme in the case of a red dwarf, such as Barnard's Star (M4: about 2,000 times less luminous than the Sun), the HZ of which would extend only between about 750,000 and 2 million km (0.02 to 0.06 AU) ...
... The size and location of the HZ depends on the nature of the star The situation becomes even more extreme in the case of a red dwarf, such as Barnard's Star (M4: about 2,000 times less luminous than the Sun), the HZ of which would extend only between about 750,000 and 2 million km (0.02 to 0.06 AU) ...
Starry Starry Night Vocabulary
... Protostar: The hot core at the center of the collapsing cloud of gas and dust that one day becomes a star. This is the early stage in the process of star formation. Solar flare: A sudden, rapid, and intense variation in brightness on the sun or other star. A solar flare occurs when magnetic energy t ...
... Protostar: The hot core at the center of the collapsing cloud of gas and dust that one day becomes a star. This is the early stage in the process of star formation. Solar flare: A sudden, rapid, and intense variation in brightness on the sun or other star. A solar flare occurs when magnetic energy t ...
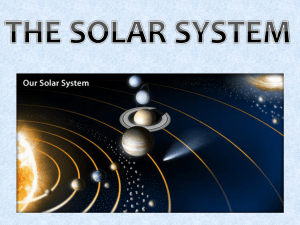
Solar System - Spring Branch ISD
... belt are Jupiter called gas giants. These planets are _______, Neptune These planets ________, Saturn _________, Uranus and ________. are gaseous in nature, composed of mostly hydrogen and helium ____________________. ...
... belt are Jupiter called gas giants. These planets are _______, Neptune These planets ________, Saturn _________, Uranus and ________. are gaseous in nature, composed of mostly hydrogen and helium ____________________. ...
Stellar Classification Worksheet 2
... Explain how each of the 5 characteristics in the boxes below is used to classify stars. In each box, give 2 examples of stars and their specific characteristics. Use pages 127-129 in the textbook and the examples below to complete the worksheet. ...
... Explain how each of the 5 characteristics in the boxes below is used to classify stars. In each box, give 2 examples of stars and their specific characteristics. Use pages 127-129 in the textbook and the examples below to complete the worksheet. ...
View Presentation Slides
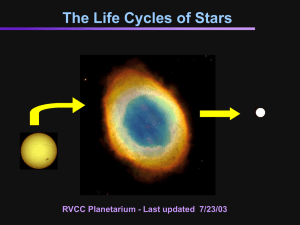
... Stars have “life cycles”. They are “born” and they “die” but are not alive like us. Stars like the Sun “die” by “puffing” off their outer layers of gas and dust. This process creates a beautiful variety of NEBULAE in the Milky Way GALAXY. ...
... Stars have “life cycles”. They are “born” and they “die” but are not alive like us. Stars like the Sun “die” by “puffing” off their outer layers of gas and dust. This process creates a beautiful variety of NEBULAE in the Milky Way GALAXY. ...
Life Cycles of Stars
... Fate of High Mass Stars • After Helium is exhausted, core collapses again until it becomes hot enough to fuse Carbon into Magnesium or Oxygen. • Through a combination of processes, successively heavier elements are formed and burned. ...
... Fate of High Mass Stars • After Helium is exhausted, core collapses again until it becomes hot enough to fuse Carbon into Magnesium or Oxygen. • Through a combination of processes, successively heavier elements are formed and burned. ...