Peer Instruction/Active Learning
... a) HST is closer to planets & stars. b) HST uses a larger primary mirror. c) it gathers X-‐ray light. d) HST orbits above the atmosphere. e) it stays on the night-‐
... a) HST is closer to planets & stars. b) HST uses a larger primary mirror. c) it gathers X-‐ray light. d) HST orbits above the atmosphere. e) it stays on the night-‐
Astronomical Ideas Fall 2012 Homework 4 Solutions 1. Two stars
... Convert the white dwarf radius into meters: 104 km = 107 m, and plug numbers into the above equation. 106 K: L ~ 7 * 1031 W. The Sunʼs luminosity is ~4 * 1026 , so this hot white dwarf is about 100,000 times the luminosity of the Sun. 104 K: L ~ 7 * 1024 W. The Sunʼs luminosity is ~4 * 1026 , so thi ...
... Convert the white dwarf radius into meters: 104 km = 107 m, and plug numbers into the above equation. 106 K: L ~ 7 * 1031 W. The Sunʼs luminosity is ~4 * 1026 , so this hot white dwarf is about 100,000 times the luminosity of the Sun. 104 K: L ~ 7 * 1024 W. The Sunʼs luminosity is ~4 * 1026 , so thi ...
Exam2 Review Slides
... The length of time a star spends fusing hydrogen into helium is called its main sequence lifetime – Stars spend most of their lives on the main sequence – Lifetime depends on the star’s mass and luminosity – More luminous stars burn their energy more rapidly than less luminous stars. – High-mass sta ...
... The length of time a star spends fusing hydrogen into helium is called its main sequence lifetime – Stars spend most of their lives on the main sequence – Lifetime depends on the star’s mass and luminosity – More luminous stars burn their energy more rapidly than less luminous stars. – High-mass sta ...
ASTRONOMY 1102 1
... *1) Why are SN of type Ia good standard candles? Because they [ ] have the same apparent magnitude. [ ] have the same absolute magnitude. [ ] have the same luminosity. [ ] obey the Period{Luminosity relation for Cepheid Variables. [ ] result from the collapse and detonation of the same mass. 5) What ...
... *1) Why are SN of type Ia good standard candles? Because they [ ] have the same apparent magnitude. [ ] have the same absolute magnitude. [ ] have the same luminosity. [ ] obey the Period{Luminosity relation for Cepheid Variables. [ ] result from the collapse and detonation of the same mass. 5) What ...
What Can We See in the Night Sky?
... • Groups of stars that are close together and travel together are known as star clusters • Star clusters are part of galaxies • Open clusters – contain about 50 to 1000 stars – dispersed along the Milky Way’s main band ...
... • Groups of stars that are close together and travel together are known as star clusters • Star clusters are part of galaxies • Open clusters – contain about 50 to 1000 stars – dispersed along the Milky Way’s main band ...
How do we know how the Solar System is
... Copernicus, a Polish astronomer, suggested a dramatically different model of the Solar System, a heliocentric model, with the Sun at the center Copernicus preserved the idea that planets orbited in circular orbits around the Sun, however. Big debate ensued, between geocentric and heliocentric mode ...
... Copernicus, a Polish astronomer, suggested a dramatically different model of the Solar System, a heliocentric model, with the Sun at the center Copernicus preserved the idea that planets orbited in circular orbits around the Sun, however. Big debate ensued, between geocentric and heliocentric mode ...
CURRICULUM COMMITTEE COURSE PROPOSAL FORM
... Comprehend how diffraction blurring places a fundamental limit on how sharp an image we can get from a telescope, even in outer space. ...
... Comprehend how diffraction blurring places a fundamental limit on how sharp an image we can get from a telescope, even in outer space. ...
18.3 NOTES What is magnitude? Objective: Compare apparent
... Without a telescope, you can see about 2000 stars in the night sky. Some appear brighter than others. One way to measure a star’s brightness is by magnitude. The brightness of a star depends on its temperature, size, and distance from Earth. A hot star is usually brighter than a cool star. A large s ...
... Without a telescope, you can see about 2000 stars in the night sky. Some appear brighter than others. One way to measure a star’s brightness is by magnitude. The brightness of a star depends on its temperature, size, and distance from Earth. A hot star is usually brighter than a cool star. A large s ...
Space – Astronomy Review
... The Universe is everything that exists, including all matter and energy everywhere. The study of what is beyond Earth is called Astronomy. Groups of stars that form shapes or patterns are called constellations. The Solar System consists of our Sun and all the objects that travel around it. Objects t ...
... The Universe is everything that exists, including all matter and energy everywhere. The study of what is beyond Earth is called Astronomy. Groups of stars that form shapes or patterns are called constellations. The Solar System consists of our Sun and all the objects that travel around it. Objects t ...
pptx
... Ncivil = N* fp np fl fi fc fL Now make your best guess at each number and multiply them. What do you get? N* = the number of stars in the Milky Way = 200,000,000,000 fp = the fraction of stars that have “habitable planets” = 0.5 np = the number of habitable planets per system = 2 fl = t ...
... Ncivil = N* fp np fl fi fc fL Now make your best guess at each number and multiply them. What do you get? N* = the number of stars in the Milky Way = 200,000,000,000 fp = the fraction of stars that have “habitable planets” = 0.5 np = the number of habitable planets per system = 2 fl = t ...
Today`s Powerpoint
... Suppose two stars (star A and star B) appeared equally bright but we knew that star A was 10 times further away, what do we know about the luminosity of star A? A: The two stars have equal luminosity. ...
... Suppose two stars (star A and star B) appeared equally bright but we knew that star A was 10 times further away, what do we know about the luminosity of star A? A: The two stars have equal luminosity. ...
Overview and status of the Kepler Mission - Harvard
... Presently we know of more than one-hundred planets1 orbiting other stars with orbital periods from about one day to a few years. All of these planets are known or presumed to be gas-giants with minimum masses typically greater than that of Saturn, except for a few Earth-mass planets that are known t ...
... Presently we know of more than one-hundred planets1 orbiting other stars with orbital periods from about one day to a few years. All of these planets are known or presumed to be gas-giants with minimum masses typically greater than that of Saturn, except for a few Earth-mass planets that are known t ...
Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram
... A star has a high luminosity (100 solar luminosities) and a surface temperature of 3500 K. What type of star is it? ...
... A star has a high luminosity (100 solar luminosities) and a surface temperature of 3500 K. What type of star is it? ...
Brichler-powerpoint
... fuel – it either becomes a What white dwarf, a neutron happens star, or a supernova. when a star • Small to medium sized dies? stars like our sun will burn out leaving only the bluewhite core called a white dwarf. When the white dwarf stops glowing it will become a black dwarf. ...
... fuel – it either becomes a What white dwarf, a neutron happens star, or a supernova. when a star • Small to medium sized dies? stars like our sun will burn out leaving only the bluewhite core called a white dwarf. When the white dwarf stops glowing it will become a black dwarf. ...
H-R Diagram - Faculty Website Listing
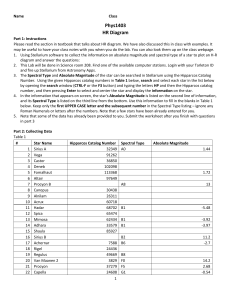
... Please read the section in textbook that talks about HR diagram. We have also discussed this in class with examples. It may be useful to have your class notes with you when you do the lab. You can also look them up on the class webpage. 1. Using Stellarium software to collect the information on abso ...
... Please read the section in textbook that talks about HR diagram. We have also discussed this in class with examples. It may be useful to have your class notes with you when you do the lab. You can also look them up on the class webpage. 1. Using Stellarium software to collect the information on abso ...
Planet formation - problems and future
... IV. Our future research description In our mind, existing investigations do not ansuer all of questions about origin and starting evolution of planetary systems. The most of the authors pay attention on interaction between solid bodies (planetesimals) and gas arround existing stars. In many used met ...
... IV. Our future research description In our mind, existing investigations do not ansuer all of questions about origin and starting evolution of planetary systems. The most of the authors pay attention on interaction between solid bodies (planetesimals) and gas arround existing stars. In many used met ...
Stars Chapter 21
... Measuring Distance to Stars • Light Year- Astronomers use light years to measure the distances between stars –A light year is the distance that light travels in one year • 9,460,730,472,580.8 km • 5,878,630,000,000 miles ...
... Measuring Distance to Stars • Light Year- Astronomers use light years to measure the distances between stars –A light year is the distance that light travels in one year • 9,460,730,472,580.8 km • 5,878,630,000,000 miles ...
Physics@Brock - Brock University
... Big Bang created hydrogen and some helium, along with a slew of other subatomic particles and electromagnetic radiation, but all the heavier elements were created inside stars. When the early massive stars “died” (their lifetimes were very short due to their enormous mass) the resulting explosions ( ...
... Big Bang created hydrogen and some helium, along with a slew of other subatomic particles and electromagnetic radiation, but all the heavier elements were created inside stars. When the early massive stars “died” (their lifetimes were very short due to their enormous mass) the resulting explosions ( ...
Earth in Space and Time: SC.5.E.5.1
... 4) Brandon has learned that many stars are actually larger than the Sun. If this is true, why do these stars appear like points of light in the sky? A. These stars are hotter than the Sun. B. These stars have less mass than the Sun. C. These stars are farther away from Earth than the Sun is. D. Thes ...
... 4) Brandon has learned that many stars are actually larger than the Sun. If this is true, why do these stars appear like points of light in the sky? A. These stars are hotter than the Sun. B. These stars have less mass than the Sun. C. These stars are farther away from Earth than the Sun is. D. Thes ...
4. How can we select stars whose planets are likely homes for life?
... Travel to distance stars and planets Travel between stars is nearly impossible because the distances are too great and nature has imposed a very real speed limit that we can not exceed. Nothing can travel faster than the speed of light, and human travel can not be expected to exceed even a small fra ...
... Travel to distance stars and planets Travel between stars is nearly impossible because the distances are too great and nature has imposed a very real speed limit that we can not exceed. Nothing can travel faster than the speed of light, and human travel can not be expected to exceed even a small fra ...
`A ship flying in space:` Earth seen through the eyes of an astronaut
... complete an orbit. Scientists want to see at least three transits to be able to rule out other explanations for fluctuations in a star’s light, such as small companion stars. Results also are verified by ground and other space telescopes. ...
... complete an orbit. Scientists want to see at least three transits to be able to rule out other explanations for fluctuations in a star’s light, such as small companion stars. Results also are verified by ground and other space telescopes. ...