A Summary of Stages
... dwarfs) will be dim and cool and, as they grow older, will only grow dimmer and cooler, ultimately becoming black dwarfs (see STAGE 14). Astronomers have identified several brown dwarf candidates, and even have evidence for the presence of Jupiter-like planets in orbit around several nearby stars. R ...
... dwarfs) will be dim and cool and, as they grow older, will only grow dimmer and cooler, ultimately becoming black dwarfs (see STAGE 14). Astronomers have identified several brown dwarf candidates, and even have evidence for the presence of Jupiter-like planets in orbit around several nearby stars. R ...
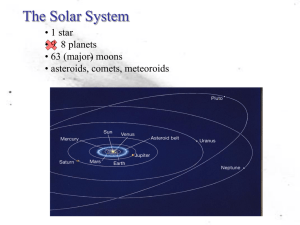
Solar.System
... Mars and Jupiter but a few have orbits that cross Earth’s path. Three asteroids hit the Earth every 1 million years! ...
... Mars and Jupiter but a few have orbits that cross Earth’s path. Three asteroids hit the Earth every 1 million years! ...
absolute magnitude
... magnitude will be a bigger number, i.e. it is intrinsically dimmer than it appears – If a star is farther than 10pc, its absolute magnitude will be a smaller number, i.e. it is intrinsically brighter than it appears ...
... magnitude will be a bigger number, i.e. it is intrinsically dimmer than it appears – If a star is farther than 10pc, its absolute magnitude will be a smaller number, i.e. it is intrinsically brighter than it appears ...
Week 11 Concept Summary
... arms rotate around the galaxy slower than individual stars due. The sun has moved in and out of spiral arms many times during its life. 4. Rotation Curves: Plotting the velocity stuff moves around the galaxy versus its distance for just about all spiral galaxies show flat rotation curves, i.e. every ...
... arms rotate around the galaxy slower than individual stars due. The sun has moved in and out of spiral arms many times during its life. 4. Rotation Curves: Plotting the velocity stuff moves around the galaxy versus its distance for just about all spiral galaxies show flat rotation curves, i.e. every ...
October 2011
... A Nobel Prize for the discovery of Dark Energy! When Einstein postulated his general theory of Relativity he only assumed that physics on earth should be the same as on an accelerating platform in space. The result was four second order differential equations. Any solution which satisfies these equa ...
... A Nobel Prize for the discovery of Dark Energy! When Einstein postulated his general theory of Relativity he only assumed that physics on earth should be the same as on an accelerating platform in space. The result was four second order differential equations. Any solution which satisfies these equa ...
Finish up Sun and begin Stars of the Sun Test 1 Study
... Distances to Stars • Important as determines actual brightness but hard to measure as stars are so far away Closest Alpha Centauri 4.3 light years = 4 x 1013 km (1 AU = distance Earth to Sun = 8 light minutes) • Close stars use stellar parallax (heliocentric parallax or triangulation same meaning ...
... Distances to Stars • Important as determines actual brightness but hard to measure as stars are so far away Closest Alpha Centauri 4.3 light years = 4 x 1013 km (1 AU = distance Earth to Sun = 8 light minutes) • Close stars use stellar parallax (heliocentric parallax or triangulation same meaning ...
about Stars
... • Astronomers quantify the “color” of a star by using the difference in brightness between the brightness in the B and V spectral regions • The B-V color is related to the slope of the ...
... • Astronomers quantify the “color” of a star by using the difference in brightness between the brightness in the B and V spectral regions • The B-V color is related to the slope of the ...
Asteroids powerpoint - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... • (a) orbits the Sun inside the orbit of Jupiter • (b) does not have sufficient mass for its self-gravity to overcome rigid body forces so that it assumes a hydrostatic equilibrium shape (it is not round shaped), • (c) has not cleared the neighborhood around its orbit, and • (d) is not a satellite. ...
... • (a) orbits the Sun inside the orbit of Jupiter • (b) does not have sufficient mass for its self-gravity to overcome rigid body forces so that it assumes a hydrostatic equilibrium shape (it is not round shaped), • (c) has not cleared the neighborhood around its orbit, and • (d) is not a satellite. ...
SAMPLE TEST: Stars and Galaxies Multiple Choice Identify the letter
... 47. The most basic way to measure the distance to a star is ____________________. 48. A light-year is the distance ____________________ travels in a year. 49. Apparent magnitude refers to a star’s ____________________ as it appears from ____________________. 50. Some stars, called _________________ ...
... 47. The most basic way to measure the distance to a star is ____________________. 48. A light-year is the distance ____________________ travels in a year. 49. Apparent magnitude refers to a star’s ____________________ as it appears from ____________________. 50. Some stars, called _________________ ...
The Sun and planets
... structure, called granulation, is caused by convective motion: columns of hot gas coming from the centre of the Sun reach the surface and then sink towards the interior. Also in the photosphere, groups of sunspots can be observed. These areas appear darker than the surrounding area because within th ...
... structure, called granulation, is caused by convective motion: columns of hot gas coming from the centre of the Sun reach the surface and then sink towards the interior. Also in the photosphere, groups of sunspots can be observed. These areas appear darker than the surrounding area because within th ...
I Might Be a Planet If--
... • Larger and farther from the Sun than Pluto • Publicized at first as the 10th planet • More and more objects discovered beyond Pluto ...
... • Larger and farther from the Sun than Pluto • Publicized at first as the 10th planet • More and more objects discovered beyond Pluto ...
Diffuse Ultraviolet Emission in Galaxies
... source of unexplained ultraviolet (UV) emission, diffusely distributed in NGC 1313 and other spiral galaxies, which had been observed in the 1990s. We discovered that the likely source is a particular population of apparently isolated, hot, massive, young stars. To an astronomer, a star is “massive” ...
... source of unexplained ultraviolet (UV) emission, diffusely distributed in NGC 1313 and other spiral galaxies, which had been observed in the 1990s. We discovered that the likely source is a particular population of apparently isolated, hot, massive, young stars. To an astronomer, a star is “massive” ...
Astronomy 103: Midterm 2 Answers Correct answer in bold
... 34. Two clouds of interstellar gas contract to form stars. Suppose that no mass is lost in the contraction and that when they stop contracting, cloud A is a type A star and cloud K is a type K star. What stops the contraction of each star? ...
... 34. Two clouds of interstellar gas contract to form stars. Suppose that no mass is lost in the contraction and that when they stop contracting, cloud A is a type A star and cloud K is a type K star. What stops the contraction of each star? ...
Chapter 13
... • In a matter of seconds the Earth-sized iron core is transformed into a 10-km, extremely dense ball of neutrons • The outer layers of the star, now not supported as well, collapse and heat to billions of degrees as they slam into the ...
... • In a matter of seconds the Earth-sized iron core is transformed into a 10-km, extremely dense ball of neutrons • The outer layers of the star, now not supported as well, collapse and heat to billions of degrees as they slam into the ...
Space Exploration Review Notes
... planets are small, rocky (terrestrial), dense, few or no moons. The outer planets are large, gaseous (gas giants or Jovian), low density, numerous moons, most have rings. Planetary data tables like the one on the next page compare planet criteria such as period of rotation (day), distance from the ...
... planets are small, rocky (terrestrial), dense, few or no moons. The outer planets are large, gaseous (gas giants or Jovian), low density, numerous moons, most have rings. Planetary data tables like the one on the next page compare planet criteria such as period of rotation (day), distance from the ...
JWST Update
... A lot of misinformation (or disinformation) on the web. To help solve this there will be a webinar on Wednesday 21th at 2pm. Speakers: Matt M., Rick Howard and Eric Smith (HQ), John Mather, Julianne Dalcanton and Roberto Abraham. ...
... A lot of misinformation (or disinformation) on the web. To help solve this there will be a webinar on Wednesday 21th at 2pm. Speakers: Matt M., Rick Howard and Eric Smith (HQ), John Mather, Julianne Dalcanton and Roberto Abraham. ...
Movements of Objects in Space
... the Sun, all in the same direction, and all in roughly the same plane (i.e. it's like they are all laid out on a large dinner plate with the Sun at the center). The outer planets orbit more slowly than the inner planets. 4. The stars appear stationary. (They do, in fact, move very quickly. But they ...
... the Sun, all in the same direction, and all in roughly the same plane (i.e. it's like they are all laid out on a large dinner plate with the Sun at the center). The outer planets orbit more slowly than the inner planets. 4. The stars appear stationary. (They do, in fact, move very quickly. But they ...
Kepler Notes
... • The semi-major axis is a planets average distance from the SUN. • P=period of revolution • A=average distance measured in AU ...
... • The semi-major axis is a planets average distance from the SUN. • P=period of revolution • A=average distance measured in AU ...
– 1 – 1. Historical Notes for Ay 123 1.1.
... We now introduce the concept of proper motion, as stellar positions change through both parallax and proper motion, and astrometric programs seek to measure both of these.. Since stars move around with random motions within our Galaxy as well as rotate around its center, there are two components to ...
... We now introduce the concept of proper motion, as stellar positions change through both parallax and proper motion, and astrometric programs seek to measure both of these.. Since stars move around with random motions within our Galaxy as well as rotate around its center, there are two components to ...
Lecture 39
... helium. The relationship results from the rate of hydrogen burning: large stars have hot, dense interiors and burn hydrogen much faster than smaller stars. Consequently there is an inverse relationship between the main sequence lifetime of a star and mass. The most massive stars, up to ~100 solar ma ...
... helium. The relationship results from the rate of hydrogen burning: large stars have hot, dense interiors and burn hydrogen much faster than smaller stars. Consequently there is an inverse relationship between the main sequence lifetime of a star and mass. The most massive stars, up to ~100 solar ma ...