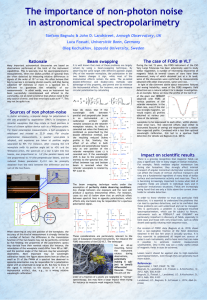
NGC 3370 Spiral Galaxy
... forming. O,B,A,F,G,K,M • Spiral arms barely move, but gas clouds and stars orbit around the galaxy moving in and out of spiral arms • From the HR diagram, by far the most luminous stars are the O-type stars. Their luminosity can be 100,000 times the Sun’s. • Why is the spiral structure in galaxies s ...
... forming. O,B,A,F,G,K,M • Spiral arms barely move, but gas clouds and stars orbit around the galaxy moving in and out of spiral arms • From the HR diagram, by far the most luminous stars are the O-type stars. Their luminosity can be 100,000 times the Sun’s. • Why is the spiral structure in galaxies s ...
Variable star information
... The changes in the observed brightness of an extrinsic variable star are either due to some process that is external to star or the rotation of the star, for example: Most of the stars in the Milky Way are thought to be in binary (or even multiple) star systems. A binary system is where two stars ...
... The changes in the observed brightness of an extrinsic variable star are either due to some process that is external to star or the rotation of the star, for example: Most of the stars in the Milky Way are thought to be in binary (or even multiple) star systems. A binary system is where two stars ...
Folie 1
... Particularly noteworthy is the dredge-up of processed material into the convective envelope by the moving inner boundary of the convective zone. ...
... Particularly noteworthy is the dredge-up of processed material into the convective envelope by the moving inner boundary of the convective zone. ...
A billion pixels, a billion stars
... stars within that telescope’s field of view (figure 1a). However, with two telescopes that are separated by a (very precisely known) large angle, and that each feed light into a single optical camera, it is possible to measure parallaxes absolutely (figure 1b). This two-telescope method of measuring ...
... stars within that telescope’s field of view (figure 1a). However, with two telescopes that are separated by a (very precisely known) large angle, and that each feed light into a single optical camera, it is possible to measure parallaxes absolutely (figure 1b). This two-telescope method of measuring ...
SBA_2 - Armagh Observatory
... Very Large Telescope has been extensively used to study stellar magnetism. A number of interesting discoveries of magnetic fields in several classes of stars have been announced, many of which obtained just at a 3σ level; some of the discoveries were confirmed by measurements obtained with other ins ...
... Very Large Telescope has been extensively used to study stellar magnetism. A number of interesting discoveries of magnetic fields in several classes of stars have been announced, many of which obtained just at a 3σ level; some of the discoveries were confirmed by measurements obtained with other ins ...
Bagnulo_2 - Armagh Observatory
... ESO Very Large Telescope has been extensively used to study stellar magnetism. A number of interesting discoveries of magnetic fields in several classes of stars have been announced, many of which obtained just at a 3σ level; some of the discoveries were confirmed by measurements obtained with other ...
... ESO Very Large Telescope has been extensively used to study stellar magnetism. A number of interesting discoveries of magnetic fields in several classes of stars have been announced, many of which obtained just at a 3σ level; some of the discoveries were confirmed by measurements obtained with other ...
Slide 1
... • As the core of a star collapses to form a neutron star, it spins fasters and faster • Its magnetic field becomes concentrated, and this results in a beam of radio waves coming out of its ...
... • As the core of a star collapses to form a neutron star, it spins fasters and faster • Its magnetic field becomes concentrated, and this results in a beam of radio waves coming out of its ...
DP11 Foundations of Astronomy
... Now that we have seen how we can find out various properties of stars – mass, luminosity, distance, radius – we can start to talk about their lives. The lives of stars are extremely long – millions, billions or even trillions of years. So how can we understand them at all, when the whole of recorded ...
... Now that we have seen how we can find out various properties of stars – mass, luminosity, distance, radius – we can start to talk about their lives. The lives of stars are extremely long – millions, billions or even trillions of years. So how can we understand them at all, when the whole of recorded ...
A brief history of extra-solar planets - X
... – What will happen to the solar system in the future? ...
... – What will happen to the solar system in the future? ...
Scale Model of the Solar System
... – Spectroscopic information (analysis of light from excited atoms) provide insight on atmospheric composition – Radio and infrared measurements collect data on planetary surface temperatures – NASA’s Cassini probe currently in orbit around Saturn – Pluto fly-by mission (NASA’s New Horizons) launched ...
... – Spectroscopic information (analysis of light from excited atoms) provide insight on atmospheric composition – Radio and infrared measurements collect data on planetary surface temperatures – NASA’s Cassini probe currently in orbit around Saturn – Pluto fly-by mission (NASA’s New Horizons) launched ...
The Heliocentric Universe
... calculate planetary orbit distances for the first time. D. placed earth at the center of the solar system and was the first to postulate that planets moved in epicycles. ...
... calculate planetary orbit distances for the first time. D. placed earth at the center of the solar system and was the first to postulate that planets moved in epicycles. ...
The Solar System and its Planets
... Which part of the IAU definition of a dwarf planet does asteroid Vesta not satisfy? (A) is in orbit around the Sun (B) has sufficient mass for its self-gravity to overcome rigid body forces so that it assumes a hydrostatic equilibrium (nearly round) shape (C) has not cleared the neighbourhood aroun ...
... Which part of the IAU definition of a dwarf planet does asteroid Vesta not satisfy? (A) is in orbit around the Sun (B) has sufficient mass for its self-gravity to overcome rigid body forces so that it assumes a hydrostatic equilibrium (nearly round) shape (C) has not cleared the neighbourhood aroun ...
Planets of Our, and Other, Solar Systems
... 2. CAI’s (calcium rich inclusions) within meteorites have a very narrow (~1600K) temperature range within which they solidify, and this corresponds to a very narrow time range when they could incorporate Al-26. Time scale <~20,000 yrs very early in formation. • 3. CAI’s are enriched in Mg-26 relativ ...
... 2. CAI’s (calcium rich inclusions) within meteorites have a very narrow (~1600K) temperature range within which they solidify, and this corresponds to a very narrow time range when they could incorporate Al-26. Time scale <~20,000 yrs very early in formation. • 3. CAI’s are enriched in Mg-26 relativ ...
Stars and Temperature and Color
... surface of the star. • The same is true for the filament in a light bulb or any other hot object. In general, we call radiation from a hot body `black body’ radiation (do demonstration 6B40.10). ...
... surface of the star. • The same is true for the filament in a light bulb or any other hot object. In general, we call radiation from a hot body `black body’ radiation (do demonstration 6B40.10). ...
Telescopes: From Galileo to Hi
... We don’t know Identifying what dark energy is requires bigger telescopes and new techniques ...
... We don’t know Identifying what dark energy is requires bigger telescopes and new techniques ...
science - Amazon Web Services
... motions, positions, dimensions, and destinies of the planets, stars, and other heavenly bodies in our universe. Man has known or conjectured about our solar system for many years through mathematical computations, telescopic observation, and just plain imagination. Scientists have made startling new ...
... motions, positions, dimensions, and destinies of the planets, stars, and other heavenly bodies in our universe. Man has known or conjectured about our solar system for many years through mathematical computations, telescopic observation, and just plain imagination. Scientists have made startling new ...
Star Light, Star Bright, Let`s Find Some Stars Tonight!
... Star. It just happens to be above the North Pole, and when you look to the north, you can find the Big Dipper. Now spin around as you circle the table. The room looks like it’s spinning but it’s really you. Just like the room, the Big Dipper and other northern constellations appear to circle slowly ...
... Star. It just happens to be above the North Pole, and when you look to the north, you can find the Big Dipper. Now spin around as you circle the table. The room looks like it’s spinning but it’s really you. Just like the room, the Big Dipper and other northern constellations appear to circle slowly ...
Stars
... amount of energy, but there are billions of reactions per second. Each second, the Sun produces 4 × 1026 joules of energy. It would take 2,000 million nuclear power plants a whole year to produce the same amount of energy on Earth. In the Sun, and in most stars, hydrogen atoms fuse together to form ...
... amount of energy, but there are billions of reactions per second. Each second, the Sun produces 4 × 1026 joules of energy. It would take 2,000 million nuclear power plants a whole year to produce the same amount of energy on Earth. In the Sun, and in most stars, hydrogen atoms fuse together to form ...
3 Nightly Motions
... If a star is far enough to the north: It will not rise or set at all! Its path will simply carry it around the North Star in approximately 24 hours, always staying above the horizon. ...
... If a star is far enough to the north: It will not rise or set at all! Its path will simply carry it around the North Star in approximately 24 hours, always staying above the horizon. ...
Telescope Lending Program brochure - Hamilton
... It might be best to hold your observation session in a dark area such as a park or atop a hill where a large portion of the night sky is visible. If observing from your back yard, turn off or dim lights to maximize darkness. Use skymaps.com to print an easy-to-use map to help identify planets, stars ...
... It might be best to hold your observation session in a dark area such as a park or atop a hill where a large portion of the night sky is visible. If observing from your back yard, turn off or dim lights to maximize darkness. Use skymaps.com to print an easy-to-use map to help identify planets, stars ...
Working with the Illinois Learning Standards: A Constructivist
... Novas and supernovas are new stars. Stars evolve much as animals evolve. The source of energy of the stars is unknown. As stars shrink due to gravity, they change from red to blue. Red stars are hot; blue stars are cool. Stars are all roughly the same size. Stars change little over their life spans. ...
... Novas and supernovas are new stars. Stars evolve much as animals evolve. The source of energy of the stars is unknown. As stars shrink due to gravity, they change from red to blue. Red stars are hot; blue stars are cool. Stars are all roughly the same size. Stars change little over their life spans. ...
17 The Deaths of Stars
... leaving stars of reduced mass called white dwarfs and remnants of expanding gases called planetary nebulae. High-mass stars die explosively as type II supernovae leaving cores of reduced mass, neutron stars or stellar black holes, and remnants of expanding gas and dust called a supernova remnants. ...
... leaving stars of reduced mass called white dwarfs and remnants of expanding gases called planetary nebulae. High-mass stars die explosively as type II supernovae leaving cores of reduced mass, neutron stars or stellar black holes, and remnants of expanding gas and dust called a supernova remnants. ...