printer-friendly version of benchmark
... Gravitational attraction still dominates in a protostar, allowing it to accrete more mass and its internal temperature to rise. Particles (mostly protons) in the protostar gain more and more kinetic energy as matter is compressed and electromagnetic forces repel these like-charged particles in every ...
... Gravitational attraction still dominates in a protostar, allowing it to accrete more mass and its internal temperature to rise. Particles (mostly protons) in the protostar gain more and more kinetic energy as matter is compressed and electromagnetic forces repel these like-charged particles in every ...
Galileo & the Telescope— Sept 20
... stars, but especially about the four planets flying around the star of Jupiter at unequal intervals and periods with wonderful swiftness; which unknown by anyone until this day, the first author detected recently and decided to name Midicean Stars. Venice ...
... stars, but especially about the four planets flying around the star of Jupiter at unequal intervals and periods with wonderful swiftness; which unknown by anyone until this day, the first author detected recently and decided to name Midicean Stars. Venice ...
Multi-physics simulations using a hierarchical interchangeable
... combined to conduct numerical experiments. The community codes are generally written independently, so AMUSE encompasses a wide variety of computer languages and programming styles. The fundamental design feature of the framework is the abstraction of the functionality of individual community codes ...
... combined to conduct numerical experiments. The community codes are generally written independently, so AMUSE encompasses a wide variety of computer languages and programming styles. The fundamental design feature of the framework is the abstraction of the functionality of individual community codes ...
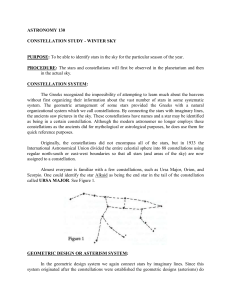
ASTRONOMY 130
... International Astronomical Union divided the entire celestial sphere into 88 constellations using regular north-south or east-west boundaries so that all stars (and areas of the sky) are now assigned to a constellation. Almost everyone is familiar with a few constellations, such as Ursa Major, Orion ...
... International Astronomical Union divided the entire celestial sphere into 88 constellations using regular north-south or east-west boundaries so that all stars (and areas of the sky) are now assigned to a constellation. Almost everyone is familiar with a few constellations, such as Ursa Major, Orion ...
E N 1”=140 AU
... ・Accretion from the circumstellar disk around the primary is very active(White & Ghez 2001). ・The primary is an EXor, which periodically undergo outbursts (Coffey et al. 2004). ...
... ・Accretion from the circumstellar disk around the primary is very active(White & Ghez 2001). ・The primary is an EXor, which periodically undergo outbursts (Coffey et al. 2004). ...
printer-friendly version of benchmark
... directly observable (such as temperature and some motions), while others (such as mass) require inference from other data. Of these characteristics, the most important are color, temperature, mass, and luminosity. Although most appear white to our eyes, most stars have a predominant color that is de ...
... directly observable (such as temperature and some motions), while others (such as mass) require inference from other data. Of these characteristics, the most important are color, temperature, mass, and luminosity. Although most appear white to our eyes, most stars have a predominant color that is de ...
Day 3
... feature molecular bands in emission rather than absorption. From simple physical arguments, we show that they will have large day/night temperature contrasts and negligible phase shifts between orbital phase and thermal emission light curves, because radiative timescales are much shorter than possib ...
... feature molecular bands in emission rather than absorption. From simple physical arguments, we show that they will have large day/night temperature contrasts and negligible phase shifts between orbital phase and thermal emission light curves, because radiative timescales are much shorter than possib ...
Paper - Astrophysics - University of Oxford
... study include the following (discussed in more detail below). ...
... study include the following (discussed in more detail below). ...
Name:
... evening’s sky. Can you find the open cluster located below Gemini? How many “deep space” objects like galaxies, clusters, and nebulae can you find on this sky map? Nearly all are suitable objects for viewing with small telescopes or binoculars. Turn your star map to the SW and face that direction. W ...
... evening’s sky. Can you find the open cluster located below Gemini? How many “deep space” objects like galaxies, clusters, and nebulae can you find on this sky map? Nearly all are suitable objects for viewing with small telescopes or binoculars. Turn your star map to the SW and face that direction. W ...
Document
... Betelgeuse has a very high luminosity (40,000 times as bright as our Sun), but its surface is cool (below 4000 K). Which of the following explains this? a. ...
... Betelgeuse has a very high luminosity (40,000 times as bright as our Sun), but its surface is cool (below 4000 K). Which of the following explains this? a. ...
The Life Cycle of a Star
... to gravity, the protostar has reached equilibrium and is therefore reached a reasonably stable size. ...
... to gravity, the protostar has reached equilibrium and is therefore reached a reasonably stable size. ...
PDF of story and photos
... MAGINE visiting a hospital to see thousands of babies being born at the same time. The weight of these newborns ranges from a few pounds to a ton (2,000 pounds). Does this story seem possible? The story may not be possible for babies, but it is an ordinary event for stars. In fact, the Hubble Space ...
... MAGINE visiting a hospital to see thousands of babies being born at the same time. The weight of these newborns ranges from a few pounds to a ton (2,000 pounds). Does this story seem possible? The story may not be possible for babies, but it is an ordinary event for stars. In fact, the Hubble Space ...
Night Sky Course Stars and Star Clusters within the
... We find the age of the cluster by noting which stars have had the time to evolve into red giants. Such calculations, according to the model for stellar evolution are at least as old as the galaxy itself. Stars in this collection belong to a population of stars whose chemical composition consists mos ...
... We find the age of the cluster by noting which stars have had the time to evolve into red giants. Such calculations, according to the model for stellar evolution are at least as old as the galaxy itself. Stars in this collection belong to a population of stars whose chemical composition consists mos ...
Why does Sirius twinkle?
... our atmosphere, and even sometimes when looking at planets that are low in the thicker parts of the atmosphere, they will twinkle. Phil Plait, the Bad Astronomer explains it very well on his website.) This optical illusion is a big pain for astronomers and some very large telescopes such as those in ...
... our atmosphere, and even sometimes when looking at planets that are low in the thicker parts of the atmosphere, they will twinkle. Phil Plait, the Bad Astronomer explains it very well on his website.) This optical illusion is a big pain for astronomers and some very large telescopes such as those in ...
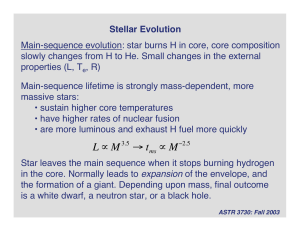
Lecture 30
... • Core contracts, heats up • Helium burning stars • If star is massive enough, sequence repeats for carbon burning, then oxygen, silicon etc… Dominant observational signature of post-main-sequence evolution is rapid expansion of the envelope to form a red giant star. ...
... • Core contracts, heats up • Helium burning stars • If star is massive enough, sequence repeats for carbon burning, then oxygen, silicon etc… Dominant observational signature of post-main-sequence evolution is rapid expansion of the envelope to form a red giant star. ...
Crux The Southern Cross
... There are many stars in the sky that when viewed through a telescope appear as two dots. It is common for two stars to be locked together gravitationally to form a binary star system. Sometimes double stars may only appear close together from our vantage point on earth. If in reality they do not int ...
... There are many stars in the sky that when viewed through a telescope appear as two dots. It is common for two stars to be locked together gravitationally to form a binary star system. Sometimes double stars may only appear close together from our vantage point on earth. If in reality they do not int ...
Herschel
... the Solar System placed beyond the orbit of Neptune (30 UA) up to ~55 UA. It is similar to the asteroid belt but 20 times wider and 20-200 times more massive. ...
... the Solar System placed beyond the orbit of Neptune (30 UA) up to ~55 UA. It is similar to the asteroid belt but 20 times wider and 20-200 times more massive. ...
HR Diagram
... It has been shown through observational data of many stars that the more massive a star, the more luminous it is. If you observe the H-R diagram on the cover of the lab, it is clear that there are fewer luminous stars as compared to the less luminous ones. In terms of the diagram, there are more sta ...
... It has been shown through observational data of many stars that the more massive a star, the more luminous it is. If you observe the H-R diagram on the cover of the lab, it is clear that there are fewer luminous stars as compared to the less luminous ones. In terms of the diagram, there are more sta ...
The Magnitude Scale
... filtered band intended to be close to visual) is around 550 nm; CCDs tend to peak around 700 nm. The examples are given for integer values are not "exact", in that celestial objects are often measured to a precision or 0.1 or 0.01 magnitude; for example, Sirius shines at V = -1.47 (Yale Bright Star ...
... filtered band intended to be close to visual) is around 550 nm; CCDs tend to peak around 700 nm. The examples are given for integer values are not "exact", in that celestial objects are often measured to a precision or 0.1 or 0.01 magnitude; for example, Sirius shines at V = -1.47 (Yale Bright Star ...
The Sun - MsLeeClass
... 8. Why do stars in the night sky look like points of light? (1) They are very small (3) They are very far away (2) They do not have planets (4) They do not give off much light 9. Energy from the Sun takes the longest to reach which planet? (1) B (2) C (3) D (4) E ...
... 8. Why do stars in the night sky look like points of light? (1) They are very small (3) They are very far away (2) They do not have planets (4) They do not give off much light 9. Energy from the Sun takes the longest to reach which planet? (1) B (2) C (3) D (4) E ...