margarita2007
... accreted earlier than surviving one • Surviving satellites are predominantly low-mass systems and have been accreted recently • The building blocks of the stellar halo were on average more massive and were accreted (and disrupted) earlier than de population of satellites that survive until the prese ...
... accreted earlier than surviving one • Surviving satellites are predominantly low-mass systems and have been accreted recently • The building blocks of the stellar halo were on average more massive and were accreted (and disrupted) earlier than de population of satellites that survive until the prese ...
Chapter 18 The Bizarre Stellar Graveyard What is a white dwarf
... • What would it be like to visit a black hole? – You can orbit a black hole like any other object of the same mass—black holes don’t ...
... • What would it be like to visit a black hole? – You can orbit a black hole like any other object of the same mass—black holes don’t ...
Measuring the Milky Way
... These objects are very close to the Galactic center. The orbit on the right is the best fit; it assumes a central black hole of 3.7 million solar masses. ...
... These objects are very close to the Galactic center. The orbit on the right is the best fit; it assumes a central black hole of 3.7 million solar masses. ...
Comprehensive Census and Complete Characterization of Nearby
... stars (Høg et al. 2000) as a compatible match given the reliable optical photometry and proper motions. Lacking accurate Hipparcos parallax measurements, we used the total proper motion (μtot ) as a proxy for distance and selected sources with μtot > 25 mas yr−1 corresponding to within 200 pc. These ...
... stars (Høg et al. 2000) as a compatible match given the reliable optical photometry and proper motions. Lacking accurate Hipparcos parallax measurements, we used the total proper motion (μtot ) as a proxy for distance and selected sources with μtot > 25 mas yr−1 corresponding to within 200 pc. These ...
Lecture 15 Star Formation and Evolution 3/7
... • test out model of stellar evolution using Star Clusters • HR diagram of a cluster gives “snapshot” of stars with the same age but different masses • Birth Main Sequence Red Giant “live+die” faster if higher mass • tell age of cluster by most massive star still on Main Sequence ...
... • test out model of stellar evolution using Star Clusters • HR diagram of a cluster gives “snapshot” of stars with the same age but different masses • Birth Main Sequence Red Giant “live+die” faster if higher mass • tell age of cluster by most massive star still on Main Sequence ...
AST4930 Star and Planet Formation
... the actual fraction of stars in multiple systems, its variation with stellar mass (e.g., massive stars more likely to be in multiple systems than low-mass stars), and the companion mass distribution. “stellar IMF” – corrected for multiplicity “system IMF” – uncorrected ...
... the actual fraction of stars in multiple systems, its variation with stellar mass (e.g., massive stars more likely to be in multiple systems than low-mass stars), and the companion mass distribution. “stellar IMF” – corrected for multiplicity “system IMF” – uncorrected ...
Modeling the Photophoretic Force and Brownian Motion of a Single
... process, where solid material in a protoplanetary disk grows from micrometer sized dust grains to kilometer sized objects. One force which could be important is the photophoretic force. Dust grains illuminated by the central star will be unevenly heated. As gas molecules come into contact with the w ...
... process, where solid material in a protoplanetary disk grows from micrometer sized dust grains to kilometer sized objects. One force which could be important is the photophoretic force. Dust grains illuminated by the central star will be unevenly heated. As gas molecules come into contact with the w ...
The Milky Way Galaxy (ch. 23)
... nearly spherical shape, rest of gas collapsed to disk which has formed stars continuously since that time. (Think about how above properties suggest this.) More recently it was discovered that our Galaxy has a weak but detectable bar structure in the bulge. This rotating bar is important, because it ...
... nearly spherical shape, rest of gas collapsed to disk which has formed stars continuously since that time. (Think about how above properties suggest this.) More recently it was discovered that our Galaxy has a weak but detectable bar structure in the bulge. This rotating bar is important, because it ...
Chapter 4 Galactic Chemical Evolution
... The material we find around us in the Universe today contains significant quantities of heavy elements, although these are still only minor contributors to the total mass of baryonic matter (most is hydrogen). These heavy elements have been synthesised in nuclear reactions in stars, a process known ...
... The material we find around us in the Universe today contains significant quantities of heavy elements, although these are still only minor contributors to the total mass of baryonic matter (most is hydrogen). These heavy elements have been synthesised in nuclear reactions in stars, a process known ...
PH607lec10-4gal2
... Best interpretation of many of these is a trend in star formation history Early type spirals formed most of their stars early on (used up their gas, have older/redder stars) Late type spirals have substantial on-going star-formation, didn’t form as many stars early-on (and thus lots of gas left) ...
... Best interpretation of many of these is a trend in star formation history Early type spirals formed most of their stars early on (used up their gas, have older/redder stars) Late type spirals have substantial on-going star-formation, didn’t form as many stars early-on (and thus lots of gas left) ...
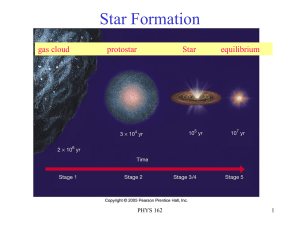
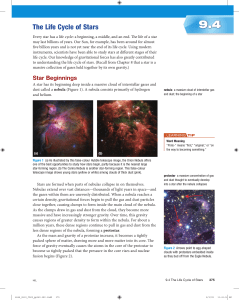
The Life Cycle of Stars
... helium into carbon (like our Sun). The core of a massive star becomes so hot that when helium is no longer available for fusion, carbon undergoes fusion. This produces heavier elements, beginning with oxygen and up to iron. Once iron is produced in the core, fusion can no longer occur. (This is beca ...
... helium into carbon (like our Sun). The core of a massive star becomes so hot that when helium is no longer available for fusion, carbon undergoes fusion. This produces heavier elements, beginning with oxygen and up to iron. Once iron is produced in the core, fusion can no longer occur. (This is beca ...
Age aspects of habitability - Cambridge University Press
... collisions between asteroids, planetesimals or even possible planets (Song et al. 2005). Out of these seven stars, five are young systems within their first Gyr of life. It is also well-known that solar-type stars remain very active in the first billion years of their life, sustaining conditions tha ...
... collisions between asteroids, planetesimals or even possible planets (Song et al. 2005). Out of these seven stars, five are young systems within their first Gyr of life. It is also well-known that solar-type stars remain very active in the first billion years of their life, sustaining conditions tha ...
Word doc - GDN - University of Gloucestershire
... One of the predictions of the Big Bang model for the origin of the Universe is that the initial explosion was extremely hot and that the remnants of the initial fireball might still be detected at the edges of the Universe. Support for this hypothesis came from the discovery in the 1960s by Arno Pen ...
... One of the predictions of the Big Bang model for the origin of the Universe is that the initial explosion was extremely hot and that the remnants of the initial fireball might still be detected at the edges of the Universe. Support for this hypothesis came from the discovery in the 1960s by Arno Pen ...
Main Sequence Lifetime
... • Stars in this phase have a narrow range of luminosities, about one hundredth of their luminosity at the time of the helium flash, but still much more luminous than their main sequence ...
... • Stars in this phase have a narrow range of luminosities, about one hundredth of their luminosity at the time of the helium flash, but still much more luminous than their main sequence ...