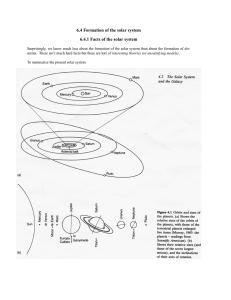
Formation of the solar system
... and collisions - lots of different models here - eventually forming planets. The form of this accretion is important and controversial. At some point in this processes the sun became fully active - early in this processes it went through what is called a T-TAURI stage (by analogy to other stars) in ...
... and collisions - lots of different models here - eventually forming planets. The form of this accretion is important and controversial. At some point in this processes the sun became fully active - early in this processes it went through what is called a T-TAURI stage (by analogy to other stars) in ...
Review_game_and_answers
... 24- Main sequence stars show that they increase in brightness as they increase in temperature on what kind of diagram? ...
... 24- Main sequence stars show that they increase in brightness as they increase in temperature on what kind of diagram? ...
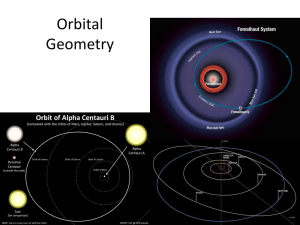
Orbital Geometry Notes
... The Solar System • Looking at the Solar System Data table, most of the planets have fairly circular orbits (low eccentricities) with the exception of Mercury. ...
... The Solar System • Looking at the Solar System Data table, most of the planets have fairly circular orbits (low eccentricities) with the exception of Mercury. ...
Where a limit?
... Solar system — a tiny part of the Milky Way. It consists of the Sun and nine major planets. Each planet moves round the Sun on an elliptic (oval) orbit. Round the Sun thousand asteroids — the blocks of ice covered with a cloud of a dust and gases rotate also. ...
... Solar system — a tiny part of the Milky Way. It consists of the Sun and nine major planets. Each planet moves round the Sun on an elliptic (oval) orbit. Round the Sun thousand asteroids — the blocks of ice covered with a cloud of a dust and gases rotate also. ...
Solar System - Physics Rocks!
... Those objects orbiting the Sun, but that have not cleared their orbital pathway of other objects ...
... Those objects orbiting the Sun, but that have not cleared their orbital pathway of other objects ...
Name__________________________________________ J
... There was a problem though! The planets seemed to stray from their predicted positions….wonder why? SEE KEPLER! Brahe - 1546-1601 (Denmark) Brahe’s observations, especially of Mars, were far more precise than any made previously. The telescope had not yet been invented; he used other instrumen ...
... There was a problem though! The planets seemed to stray from their predicted positions….wonder why? SEE KEPLER! Brahe - 1546-1601 (Denmark) Brahe’s observations, especially of Mars, were far more precise than any made previously. The telescope had not yet been invented; he used other instrumen ...
Early Observers (The Beginnings of Astronomy)
... Planets traveled in smaller circular paths as they traveled around the Earth (epicycles and deferents) Popular model of universe for 1,500 years. ...
... Planets traveled in smaller circular paths as they traveled around the Earth (epicycles and deferents) Popular model of universe for 1,500 years. ...
First detection of a planet that survived the red giant expansion of its
... whereas Mars should survive. The fate of the Earth is less clear because its position is really at the limit: it appears more likely that the Earth will not survive the red giant expansion of the Sun either, but it is not for sure. All this will happen in about five billion years, when the Earth ...
... whereas Mars should survive. The fate of the Earth is less clear because its position is really at the limit: it appears more likely that the Earth will not survive the red giant expansion of the Sun either, but it is not for sure. All this will happen in about five billion years, when the Earth ...
PowerPoint - Chandra X
... The young Sun-like stars in Orion produce violent X-ray outbursts, or flares, that are much more frequent and energetic than anything seen today from our Sun. The range of flare energies is large, with some of the stars producing flares that are a hundred times larger than others. The different flar ...
... The young Sun-like stars in Orion produce violent X-ray outbursts, or flares, that are much more frequent and energetic than anything seen today from our Sun. The range of flare energies is large, with some of the stars producing flares that are a hundred times larger than others. The different flar ...
BABYLON and SUMERIA 3000BC
... recorded their observations about the daily, monthly and yearly position of the stars and planets. They advised the king about how their observations affected the calendar. And they advised the king about how omens seen on earth or in the skies might effect future events. ...
... recorded their observations about the daily, monthly and yearly position of the stars and planets. They advised the king about how their observations affected the calendar. And they advised the king about how omens seen on earth or in the skies might effect future events. ...
Planets orbit the Sun at different distances.
... You may have seen some planets in the sky without realizing it. They are so far from Earth that they appear as tiny dots of light in the darkened sky. If you have seen something that looks like a very bright star in the western sky in the early evening, you have probably seen the planet Venus. Even ...
... You may have seen some planets in the sky without realizing it. They are so far from Earth that they appear as tiny dots of light in the darkened sky. If you have seen something that looks like a very bright star in the western sky in the early evening, you have probably seen the planet Venus. Even ...
Name: Date: Period: ______ Unit 9
... 3. How did the land and atmosphere of Earth form? 4. How do the theories of Aristotle and Copernicus differ? 5. What did Ptolemy propose about the solar system? 6. What is a protoplanet? 7. What is differentiation? What part(s) of Earth did this create? 8. What is Kepler’s first law? 9. What is outg ...
... 3. How did the land and atmosphere of Earth form? 4. How do the theories of Aristotle and Copernicus differ? 5. What did Ptolemy propose about the solar system? 6. What is a protoplanet? 7. What is differentiation? What part(s) of Earth did this create? 8. What is Kepler’s first law? 9. What is outg ...
Astronomy HOMEWORK Chapter 5 - 9th Edition 2. Pluto is most
... snow line, these could remain frozen solid, allowing them to survive. This marks the difference between rock-and-metal objects (terrestrial planets and asteroids) and objects which have in addition volatile substances (giant planets and comet nuclei). 17. What if Earth had a highly elliptical orbit ...
... snow line, these could remain frozen solid, allowing them to survive. This marks the difference between rock-and-metal objects (terrestrial planets and asteroids) and objects which have in addition volatile substances (giant planets and comet nuclei). 17. What if Earth had a highly elliptical orbit ...
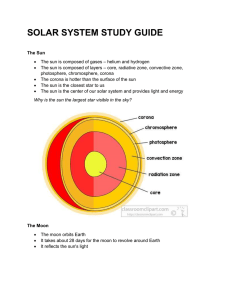
solar system study guide
... The sun is composed of layers – core, radiative zone, convective zone, photosphere, chromosphere, corona The corona is hotter than the surface of the sun The sun is the closest star to us The sun is the center of our solar system and provides light and energy ...
... The sun is composed of layers – core, radiative zone, convective zone, photosphere, chromosphere, corona The corona is hotter than the surface of the sun The sun is the closest star to us The sun is the center of our solar system and provides light and energy ...
Space Science Chapter 1 Study Guide
... 1. What is a constellation? A constellation is group of stars that form a pattern in the sky. 2. Our solar system is made up of what? The Sun and its family of orbiting planets, moons, and other objects. 3. Radio telescopes gather radiation with what type of dish? Metal dish 4. What type of mission ...
... 1. What is a constellation? A constellation is group of stars that form a pattern in the sky. 2. Our solar system is made up of what? The Sun and its family of orbiting planets, moons, and other objects. 3. Radio telescopes gather radiation with what type of dish? Metal dish 4. What type of mission ...
The Solar System. The Inner Planets.
... Venus has very similar parameters to those of the Earth. However, it spins backwards (clockwise if looking from its north pole). Its atmosphere has 96% CO2, surface temperature 400740 K, surface pressure is 90 times the Earth’s one. It has volcanic activity, but probably no tectonic activity. The S ...
... Venus has very similar parameters to those of the Earth. However, it spins backwards (clockwise if looking from its north pole). Its atmosphere has 96% CO2, surface temperature 400740 K, surface pressure is 90 times the Earth’s one. It has volcanic activity, but probably no tectonic activity. The S ...
A B C`s of Space Aleks Slocum Second Grade SCI.2.2 2010
... A galaxy is a system of millions of stars and planets. Earth is in a galaxy called The Milky Way. ...
... A galaxy is a system of millions of stars and planets. Earth is in a galaxy called The Milky Way. ...
Solar Nebula Theory
... Solar Nebula Theory Basic properties of the Solar System that need to be explained: 1. All planets orbit the Sun in the same direction as the Sun’s rotation 2. All planetary orbits are confined to the same general plane 3. Terrestrial planets form near the Sun, Jovian planets further out ...
... Solar Nebula Theory Basic properties of the Solar System that need to be explained: 1. All planets orbit the Sun in the same direction as the Sun’s rotation 2. All planetary orbits are confined to the same general plane 3. Terrestrial planets form near the Sun, Jovian planets further out ...
The Solar System - MHS-Integrated
... What are Nebulae? Nebula are cosmic clouds of gas and dust floating in space. Nebulae are the basic building blocks of the universe. They contain the elements from which stars and solar systems are ...
... What are Nebulae? Nebula are cosmic clouds of gas and dust floating in space. Nebulae are the basic building blocks of the universe. They contain the elements from which stars and solar systems are ...
PHYSICS DEPARTMENT Syllabus: Phys 200 (3 cr
... Stellar Evolution and the Death of Stars Birth of stars. Evolution from the main-sequence to Red Giants. Testing stellar evolution using observed star clusters. Evolution to white Dwarfs, Neutron Stars or Black Holes. ...
... Stellar Evolution and the Death of Stars Birth of stars. Evolution from the main-sequence to Red Giants. Testing stellar evolution using observed star clusters. Evolution to white Dwarfs, Neutron Stars or Black Holes. ...
Slide 1
... became hot and dense enough for the first star to form. A Galaxy is billions of stars with gas and dust. They are held together by a gravitational attraction. Wow! ...
... became hot and dense enough for the first star to form. A Galaxy is billions of stars with gas and dust. They are held together by a gravitational attraction. Wow! ...
Document
... planets. Also our solar system has a dwarf planet. All of our planets revolve around our central star, or in other words, a sun. ...
... planets. Also our solar system has a dwarf planet. All of our planets revolve around our central star, or in other words, a sun. ...
knowledge quiz - Discovery Education
... in the middle where it has many stars. Where is the Milky Way brightest? A. in its middle B. on its edges C. It has the same brightness throughout. D. It’s not bright at all. 10. Galaxies are made up of billions of stars, all giving off light, but many galaxies can only be seen with powerful telesco ...
... in the middle where it has many stars. Where is the Milky Way brightest? A. in its middle B. on its edges C. It has the same brightness throughout. D. It’s not bright at all. 10. Galaxies are made up of billions of stars, all giving off light, but many galaxies can only be seen with powerful telesco ...
Planetary system

A planetary system is a set of gravitationally bound non-stellar objects in orbit around a star or star system. Generally speaking, systems with one or more planets constitute a planetary system, although such systems may also consist of bodies such as dwarf planets, asteroids, natural satellites, meteoroids, comets, planetesimals and circumstellar disks. The Sun together with its planetary system, which includes Earth, is known as the Solar System. The term exoplanetary system is sometimes used in reference to other planetary systems.A total of 1968 exoplanets (in 1248 planetary systems, including 490 multiple planetary systems) have been identified as of 1 October 2015.Of particular interest to astrobiology is the habitable zone of planetary systems where planets could have surface liquid water.