Chapter 34 The Biosphere 34.1 The biosphere is the global
... F. Severe Disturbances – fire, hurricane, drought, floods, volcanoes, etc. allow some organisms to adapt Ex: brush growing after a fire ...
... F. Severe Disturbances – fire, hurricane, drought, floods, volcanoes, etc. allow some organisms to adapt Ex: brush growing after a fire ...
Sea-Floor Spreading - Madison County Schools
... • Sea-floor spreading makes the ocean floors get wider. New rock keeps forming at mid-ocean ridges. Old rock keeps getting pushed farther away from both sides of the ridges. ...
... • Sea-floor spreading makes the ocean floors get wider. New rock keeps forming at mid-ocean ridges. Old rock keeps getting pushed farther away from both sides of the ridges. ...
- Catalyst
... Ocean-Continental Convergence and formation of a continental volcanic arc. What is the source of magma produced along a continental arc? Is this consistent with the similar composition of volcanic rocks collected from Japan and the Cascades? ...
... Ocean-Continental Convergence and formation of a continental volcanic arc. What is the source of magma produced along a continental arc? Is this consistent with the similar composition of volcanic rocks collected from Japan and the Cascades? ...
Notes - Seawater Chemistry
... • water’s ability to dissolve crustal material as it cycles from ocean to atmosphere have added solids and gases to the ocean • ~97.2% of 1,370 million cubic kilometers (329 million cubic miles) is salt ...
... • water’s ability to dissolve crustal material as it cycles from ocean to atmosphere have added solids and gases to the ocean • ~97.2% of 1,370 million cubic kilometers (329 million cubic miles) is salt ...
Slide 1
... • water’s ability to dissolve crustal material as it cycles from ocean to atmosphere have added solids and gases to the ocean • ~97.2% of 1,370 million cubic kilometers (329 million cubic miles) is salt ...
... • water’s ability to dissolve crustal material as it cycles from ocean to atmosphere have added solids and gases to the ocean • ~97.2% of 1,370 million cubic kilometers (329 million cubic miles) is salt ...
The Australian Integrated Marine Observing System
... services that collectively will contribute to meeting the needs of marine research in both open oceans and coastal oceans around Australia. In particular, if sustained in the long term, it will permit identification and management of climate change in the marine environment, an area of research that ...
... services that collectively will contribute to meeting the needs of marine research in both open oceans and coastal oceans around Australia. In particular, if sustained in the long term, it will permit identification and management of climate change in the marine environment, an area of research that ...
Chapter 34 The Biosphere 34.1 The biosphere is the global
... F. Severe Disturbances – fire, hurricane, drought, floods, volcanoes, etc. allow some organisms to adapt Ex: brush growing after a fire ...
... F. Severe Disturbances – fire, hurricane, drought, floods, volcanoes, etc. allow some organisms to adapt Ex: brush growing after a fire ...
EE I Chapter 2 The Dynamic Earth
... when toxins from a factory run off into a water system and poison fish in a body of water Hydrosphere interacts with the Atmosphere when water evaporates and forms clouds Atmosphere interacts with the Lithosphere when acid rain falls and dissolves limestone ...
... when toxins from a factory run off into a water system and poison fish in a body of water Hydrosphere interacts with the Atmosphere when water evaporates and forms clouds Atmosphere interacts with the Lithosphere when acid rain falls and dissolves limestone ...
Earthquake Notes
... Mantle - A layer of earth that lies beneath the crust Lithosphere - Outer portion of the earth comprised of the crust and mantle Astenosphere – The layer of the mantle that lies directly below the lithosphere and flows, like taffy. Tectonic Plates - Large pieces of the lithosphere that are always mo ...
... Mantle - A layer of earth that lies beneath the crust Lithosphere - Outer portion of the earth comprised of the crust and mantle Astenosphere – The layer of the mantle that lies directly below the lithosphere and flows, like taffy. Tectonic Plates - Large pieces of the lithosphere that are always mo ...
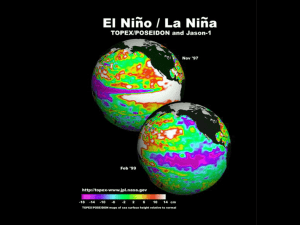
El Nino - Cloudfront.net
... El Nino Years: The first signs of an El Niño are: • Warm water spreads back from the west Pacific to the east Pacific • Warm air rises near Peru (low pressure), causing rain in the Americas • Decrease in air pressure over central and eastern Pacific Ocean • Winds in the Pacific ocean weaken or stop ...
... El Nino Years: The first signs of an El Niño are: • Warm water spreads back from the west Pacific to the east Pacific • Warm air rises near Peru (low pressure), causing rain in the Americas • Decrease in air pressure over central and eastern Pacific Ocean • Winds in the Pacific ocean weaken or stop ...
Strand: Interrelationships in Earth/Space Systems
... 2. The shoreline, where the land meets the ocean, is part of the: a. continental slope b. continental shelf c. abyssal plain 3. The continental shelf is: a. the deepest part of the ocean b. fairly deep c. relatively shallow 4. True or False: The shallow water of the continental shelf is teeming with ...
... 2. The shoreline, where the land meets the ocean, is part of the: a. continental slope b. continental shelf c. abyssal plain 3. The continental shelf is: a. the deepest part of the ocean b. fairly deep c. relatively shallow 4. True or False: The shallow water of the continental shelf is teeming with ...
Midterm Exam 1 Study Guide
... What is the principle of constant proportions? Why does it save oceanographers time? What are the various ways salinity can be measured? How should it not be measured? What is the easiest and most popular method today? When a region of ocean has high salinity, what does that suggest? What is suggest ...
... What is the principle of constant proportions? Why does it save oceanographers time? What are the various ways salinity can be measured? How should it not be measured? What is the easiest and most popular method today? When a region of ocean has high salinity, what does that suggest? What is suggest ...
Sea-Floor Spreading - Madison County Schools
... • Sea-floor spreading makes the ocean floors get wider. New rock keeps forming at mid-ocean ridges. Old rock keeps getting pushed farther away from both sides of the ridges. ...
... • Sea-floor spreading makes the ocean floors get wider. New rock keeps forming at mid-ocean ridges. Old rock keeps getting pushed farther away from both sides of the ridges. ...
Chapter 6
... low & high pressure: - low pressure near 0º latitude (tropics), leads to high rainfall as warm, moisture–laden air rises; - high pressure at 30º N & S latitudes, results in deserts as dry air descends; ...
... low & high pressure: - low pressure near 0º latitude (tropics), leads to high rainfall as warm, moisture–laden air rises; - high pressure at 30º N & S latitudes, results in deserts as dry air descends; ...
File
... Waves affect shore by: longshore drift, rip currents, beach erosion, barrier beaches (like Tybee) As you go deeper in the ocean, temperature & light decrease and pressure and density increase. ...
... Waves affect shore by: longshore drift, rip currents, beach erosion, barrier beaches (like Tybee) As you go deeper in the ocean, temperature & light decrease and pressure and density increase. ...
20081 Study Guide_77-120
... decreases, the straw will sink deeper below the water’s surface. 2. Answers will vary. A typical answer would be to warm the water. 3. It would decrease the water’s density. 4. Answers will vary. A typical answer would be that the water will be least dense in areas where the water has a low salinity ...
... decreases, the straw will sink deeper below the water’s surface. 2. Answers will vary. A typical answer would be to warm the water. 3. It would decrease the water’s density. 4. Answers will vary. A typical answer would be that the water will be least dense in areas where the water has a low salinity ...
The Oceans - BradyGreatPath
... bacteria, and atmospheric diffusion © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
... bacteria, and atmospheric diffusion © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
OUR LIVING, MOVING SEA
... Geoscientists have discovered ______ lakes of extremely salty brine lying in pockets on the floor of the _______________ Sea, south west of the island of Crete. Such Lakes could help explain why the __________________ is saltier than typical ocean water. The three brine lakes situated more than 3300 ...
... Geoscientists have discovered ______ lakes of extremely salty brine lying in pockets on the floor of the _______________ Sea, south west of the island of Crete. Such Lakes could help explain why the __________________ is saltier than typical ocean water. The three brine lakes situated more than 3300 ...
Oceanographer publishes atlas of seafloor volcanoes
... A University of Washington oceanographer has helped create the first full-color photographic atlas of the ocean floor. "Discovering the Deep: A Photographic Atlas of the Seafloor and Ocean Crust" (Cambridge University Press, 2015) was almost a decade in the making and contains more than 500 original ...
... A University of Washington oceanographer has helped create the first full-color photographic atlas of the ocean floor. "Discovering the Deep: A Photographic Atlas of the Seafloor and Ocean Crust" (Cambridge University Press, 2015) was almost a decade in the making and contains more than 500 original ...
Earth Science Unit Review
... 44. Students’ answers will vary but should include examples such as changes in water supply, change in biomes, increase in average temperatures, etc. 45. (a) Location A is continental crust, which is thicker than B, oceanic crust. (b) C (c) Crust at A and D would be the same age. They were previousl ...
... 44. Students’ answers will vary but should include examples such as changes in water supply, change in biomes, increase in average temperatures, etc. 45. (a) Location A is continental crust, which is thicker than B, oceanic crust. (b) C (c) Crust at A and D would be the same age. They were previousl ...
The Chemistry of Seawater Chapter 5-6
... iv. Most recently, we switched to the Presumed Salinity Scale (pss) because there aren’t actually any units associated with conductivity Besides the 6 major elements, there are many minor ones. The next group, found at 1-100 parts per million (ppm), include Bromine, Carbon, Strontium, Boron, Silicon ...
... iv. Most recently, we switched to the Presumed Salinity Scale (pss) because there aren’t actually any units associated with conductivity Besides the 6 major elements, there are many minor ones. The next group, found at 1-100 parts per million (ppm), include Bromine, Carbon, Strontium, Boron, Silicon ...
Chapter 9 Plate Tectonics
... Convection currents within Earth drive plate motion Hot material deep in the mantle moves upward by convection At the same time, cooler, denser slabs of oceanic lithosphere sink into the mantle ...
... Convection currents within Earth drive plate motion Hot material deep in the mantle moves upward by convection At the same time, cooler, denser slabs of oceanic lithosphere sink into the mantle ...
Water Cycle Vocabulary
... is responsible for the formation of clouds. Transpiration: process by which moisture is carried through plants from roots to small pores on the underside of leaves, where it changes to vapor and is released to the atmosphere; essentially evaporation of water from plant leaves. Gravity: one of the dr ...
... is responsible for the formation of clouds. Transpiration: process by which moisture is carried through plants from roots to small pores on the underside of leaves, where it changes to vapor and is released to the atmosphere; essentially evaporation of water from plant leaves. Gravity: one of the dr ...
mitrie_sediment_marine
... Why Study Ocean Water Temperature? The oceans cover over 70% of the Earth’s surface and influence climate on a global scale. Heat exchange between the ocean’s surface and the atmosphere is crucial to both oceanic and atmospheric circulation patterns. All ocean basins are connected, and ocean waters ...
... Why Study Ocean Water Temperature? The oceans cover over 70% of the Earth’s surface and influence climate on a global scale. Heat exchange between the ocean’s surface and the atmosphere is crucial to both oceanic and atmospheric circulation patterns. All ocean basins are connected, and ocean waters ...
Physical oceanography

Physical oceanography is the study of physical conditions and physical processes within the ocean, especially the motions and physical properties of ocean waters.Physical oceanography is one of several sub-domains into which oceanography is divided. Others include biological, chemical and geological oceanographies.