1 Lecture 14 - Marine Sediments – Formation and Distribution
... terrigenous and hydrogenous minerals are the dominant components of red clays. This does not mean that the input of this material is larger there but rather that there is nothing else to dilute it with. Terrigenous sediments enclose information about river fluxes, sources of the weathered material ( ...
... terrigenous and hydrogenous minerals are the dominant components of red clays. This does not mean that the input of this material is larger there but rather that there is nothing else to dilute it with. Terrigenous sediments enclose information about river fluxes, sources of the weathered material ( ...
Chapter 13 Exploring the Oceans
... If there were no oceans on Earth, the air temperature could vary from above 100°C to below ⫺100°C in a single day! Such large temperature changes could cause a lot of severe weather. Life as we know it could not exist in these conditions. The ocean can also affect the climate of different areas. Rem ...
... If there were no oceans on Earth, the air temperature could vary from above 100°C to below ⫺100°C in a single day! Such large temperature changes could cause a lot of severe weather. Life as we know it could not exist in these conditions. The ocean can also affect the climate of different areas. Rem ...
Plate Tectonics Earth`s outer shell, the lithosphere, long thought to
... year - a typical speed - adds up to 30 miles in one million years. It took only 150 million years for a slight fracture in an ancient continent to turn into today’s Atlantic Ocean. While the Atlantic Ocean opened, the Pacific began to shrink. The Americas slid west while the huge Eurasian plate and ...
... year - a typical speed - adds up to 30 miles in one million years. It took only 150 million years for a slight fracture in an ancient continent to turn into today’s Atlantic Ocean. While the Atlantic Ocean opened, the Pacific began to shrink. The Americas slid west while the huge Eurasian plate and ...
Plate Tectonics Earth`s outer shell, the lithosphere, long
... year - a typical speed - adds up to 30 miles in one million years. It took only 150 million years for a slight fracture in an ancient continent to turn into today’s Atlantic Ocean. While the Atlantic Ocean opened, the Pacific began to shrink. The Americas slid west while the huge Eurasian plate and ...
... year - a typical speed - adds up to 30 miles in one million years. It took only 150 million years for a slight fracture in an ancient continent to turn into today’s Atlantic Ocean. While the Atlantic Ocean opened, the Pacific began to shrink. The Americas slid west while the huge Eurasian plate and ...
19.3 Regional Wind Systems
... Look at Figure 16. The cold Peruvian current flows toward the equator along the coasts of Ecuador and Peru. This flow encourages upwelling of cold nutrient-filled waters that are the primary food source for millions of fish, particularly anchovies. Near the end of the year, however, a warm current tha ...
... Look at Figure 16. The cold Peruvian current flows toward the equator along the coasts of Ecuador and Peru. This flow encourages upwelling of cold nutrient-filled waters that are the primary food source for millions of fish, particularly anchovies. Near the end of the year, however, a warm current tha ...
plate tectonics
... can cause ocean floors to spread and continents to move. • This theory describes the lithosphere as being made of huge plates of solid rock. • The Earth’s continents rest on these plates. • The almost-melted rock of the asthenospere acts as a slippery surface on which the plates can move. • In the m ...
... can cause ocean floors to spread and continents to move. • This theory describes the lithosphere as being made of huge plates of solid rock. • The Earth’s continents rest on these plates. • The almost-melted rock of the asthenospere acts as a slippery surface on which the plates can move. • In the m ...
2-Unit4Part2 EarthsInteriors
... – Measures the amount of energy (magnitude) released by an earthquake – Allows for easier comparison of earthquake magnitudes regardless of location – Logarithmic • Measurements range from 1 to over 9 • Meaning a 6 is 10 times more powerful than a 5 ...
... – Measures the amount of energy (magnitude) released by an earthquake – Allows for easier comparison of earthquake magnitudes regardless of location – Logarithmic • Measurements range from 1 to over 9 • Meaning a 6 is 10 times more powerful than a 5 ...
Exam in BI3061 Biological Oceanography
... C. Rogue waves are especially common along the east coast of southern Africa D. Undertows are caused by internal waves E. A soliton is a half wave in which both energy and water move forwards 22. Waves. What statement is true? A. Shallow-water waves reach down to the bottom B. Shallow-water waves ex ...
... C. Rogue waves are especially common along the east coast of southern Africa D. Undertows are caused by internal waves E. A soliton is a half wave in which both energy and water move forwards 22. Waves. What statement is true? A. Shallow-water waves reach down to the bottom B. Shallow-water waves ex ...
evidence that our plates move - HULK SCIENCE
... The Earth’s lithosphere is cracked and broken into massive giant sections called tectonic plates. Like an egg with a completely cracked shell. Tectonic plates are made of continental crust and ocean crust Continental Drift The theory that our tectonic plates move. Pangaea The name given to the ...
... The Earth’s lithosphere is cracked and broken into massive giant sections called tectonic plates. Like an egg with a completely cracked shell. Tectonic plates are made of continental crust and ocean crust Continental Drift The theory that our tectonic plates move. Pangaea The name given to the ...
File
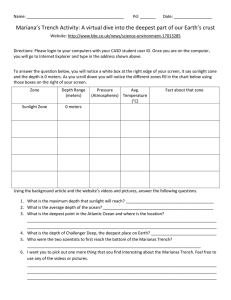
... Challenger II returned to the spot with an echo-sounder and measured a depth of nearly 7 miles (11 kilometers). HISTORIC DIVE Because of its extreme depth, the Mariana Trench is cloaked in perpetual darkness and the temperature is just a few degrees above freezing. The water pressure at the bottom o ...
... Challenger II returned to the spot with an echo-sounder and measured a depth of nearly 7 miles (11 kilometers). HISTORIC DIVE Because of its extreme depth, the Mariana Trench is cloaked in perpetual darkness and the temperature is just a few degrees above freezing. The water pressure at the bottom o ...
Plate Tectonics Notes
... This layer is known as the _____________ A _________ is one of numerous rigid sections of the _____________ that move as a unit over the material of the _ _ _ __ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ Types of Plate Boundaries __________________ (also called spreading centers) are the place where two plates move apar ...
... This layer is known as the _____________ A _________ is one of numerous rigid sections of the _____________ that move as a unit over the material of the _ _ _ __ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ Types of Plate Boundaries __________________ (also called spreading centers) are the place where two plates move apar ...
Lecture Chapter 7 Part 1
... the mantle. • Denser oceanic crust floats lower, forming ocean basins. • Less dense continental crust floats higher, forming continents. • As erosion removes part of the crust, it rises isostatically to a new level. ...
... the mantle. • Denser oceanic crust floats lower, forming ocean basins. • Less dense continental crust floats higher, forming continents. • As erosion removes part of the crust, it rises isostatically to a new level. ...
2 Precambrian Geology
... Younger lavas richer in silica Increasingly Silica-rich extrusives, some rhyolites with granites below them. ...
... Younger lavas richer in silica Increasingly Silica-rich extrusives, some rhyolites with granites below them. ...
Review for Exam 32 & 33
... The plates move in conveyor-belt fashion as new crust is generated at the continental margins and destroyed at the mid-ocean ridge The lithosphere is broken up into large palates that move as the result of convection within the asthenosphere Earthquakes & volcanic activity results from convection mo ...
... The plates move in conveyor-belt fashion as new crust is generated at the continental margins and destroyed at the mid-ocean ridge The lithosphere is broken up into large palates that move as the result of convection within the asthenosphere Earthquakes & volcanic activity results from convection mo ...
SIXTH GRADE EARTHQUAKES
... point of a wave. The trough is the low point. The wavelength is the distance between adjacent crests (or troughs). The wave height is the vertical distance from the undisturbed surface to the wave crest. In general, the bigger the waves, the more energy they carry. Larger waves will be steeper than ...
... point of a wave. The trough is the low point. The wavelength is the distance between adjacent crests (or troughs). The wave height is the vertical distance from the undisturbed surface to the wave crest. In general, the bigger the waves, the more energy they carry. Larger waves will be steeper than ...
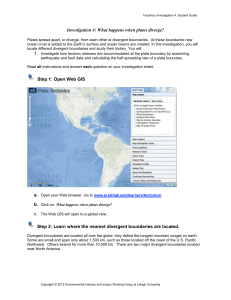
What happens when plates diverge - KMS 8th Grade Science
... the North American plate at the divergent boundary in the Atlantic Ocean, you will divide the distance the plate has traveled by the time it took to travel that distance. ...
... the North American plate at the divergent boundary in the Atlantic Ocean, you will divide the distance the plate has traveled by the time it took to travel that distance. ...
earth science 140 - College of DuPage
... Describe the distribution and generalized rates of deposition of terrigenous, biogenous and hydrogenous sediments. Identify the sediments most likely present at the continental shelf, continental slope and rise, abyssal plain, ridges and near islands. ...
... Describe the distribution and generalized rates of deposition of terrigenous, biogenous and hydrogenous sediments. Identify the sediments most likely present at the continental shelf, continental slope and rise, abyssal plain, ridges and near islands. ...
Document
... There are four types of plate boundaries: 1. Divergent boundaries -- where new crust is generated as the plates pull away from each other. 2. Convergent boundaries -- where crust is destroyed as one plate dives under another. 3. Transform boundaries -- where crust is neither produced nor destroyed ...
... There are four types of plate boundaries: 1. Divergent boundaries -- where new crust is generated as the plates pull away from each other. 2. Convergent boundaries -- where crust is destroyed as one plate dives under another. 3. Transform boundaries -- where crust is neither produced nor destroyed ...
Chapter 11 Notes: Plate Tectonics
... mantle o Plates – pieces of Earth’s lithosphere (all the crust and the upper part of the mantle) o Plate motion – occurs because the plates are the top part of a large convection current in Earth’s mantle During subduction, denser material (at the edge of a plate) is pulled down into the mantle by ...
... mantle o Plates – pieces of Earth’s lithosphere (all the crust and the upper part of the mantle) o Plate motion – occurs because the plates are the top part of a large convection current in Earth’s mantle During subduction, denser material (at the edge of a plate) is pulled down into the mantle by ...
Chapter 9 Plate Tectonics
... Rock evidence for continental exists in the form of several _______________ belts that end at one coastline, only to reappear on a landmass _______________ the ocean. Ancient _______________ _______________ deposits were found in large areas of the Southern Hemisphere large tropical ________ ...
... Rock evidence for continental exists in the form of several _______________ belts that end at one coastline, only to reappear on a landmass _______________ the ocean. Ancient _______________ _______________ deposits were found in large areas of the Southern Hemisphere large tropical ________ ...
the project description here
... distribution of species and oceanographic processes. Nevertheless, preliminary evidence does point towards a western Indian Ocean region of high diversity, delimited by northwest Madagascar, central Tanzania at Mafia Island and northern Mozambique from about Mozambique Island or Angoche northwards. ...
... distribution of species and oceanographic processes. Nevertheless, preliminary evidence does point towards a western Indian Ocean region of high diversity, delimited by northwest Madagascar, central Tanzania at Mafia Island and northern Mozambique from about Mozambique Island or Angoche northwards. ...
Geodynamics: Surface impact of mantle processes
... Triggers of this climatic event are unclear, but could be linked to the release of large quantities of methane stored in sediments on the sea bed. Uplift of the sea bed would have caused the methane stored in the ocean floor to become unstable, triggering its release into the atmosphere7. Pulses of ...
... Triggers of this climatic event are unclear, but could be linked to the release of large quantities of methane stored in sediments on the sea bed. Uplift of the sea bed would have caused the methane stored in the ocean floor to become unstable, triggering its release into the atmosphere7. Pulses of ...
Earth Science Chapter 5: Earthquakes Lecture Notes
... 5-2 Earthquakes and Seismic Waves An earthquake is the shaking that results from the movement of rock beneath Earth's surface. The area beneath Earth's surface where rock under stress breaks to cause an earthquake is called the focus. The point on the surface directly above the focus is called the e ...
... 5-2 Earthquakes and Seismic Waves An earthquake is the shaking that results from the movement of rock beneath Earth's surface. The area beneath Earth's surface where rock under stress breaks to cause an earthquake is called the focus. The point on the surface directly above the focus is called the e ...
Physical oceanography

Physical oceanography is the study of physical conditions and physical processes within the ocean, especially the motions and physical properties of ocean waters.Physical oceanography is one of several sub-domains into which oceanography is divided. Others include biological, chemical and geological oceanographies.