Word - Bryanston School
... The pair of coils labelled H produce a horizontal magnetic field through the rotor. The pair of coils labelled V produce a vertical magnetic field through the rotor. There is an alternating current in each pair of coils, but there is a phase difference between these currents. This results in horizon ...
... The pair of coils labelled H produce a horizontal magnetic field through the rotor. The pair of coils labelled V produce a vertical magnetic field through the rotor. There is an alternating current in each pair of coils, but there is a phase difference between these currents. This results in horizon ...
Conceptual Questions 1. Compare the kinetic energy gained by a
... the edges), so the electric field strength at both locations A and B will be equal. b) Which point will have the higher electric potential? Explain. The electric potential of a charged particle in a parallel plate apparatus has a linear dependence (V α d) on its distance from the oppositely charged ...
... the edges), so the electric field strength at both locations A and B will be equal. b) Which point will have the higher electric potential? Explain. The electric potential of a charged particle in a parallel plate apparatus has a linear dependence (V α d) on its distance from the oppositely charged ...
physics - Regents
... 15 A wound spring provides the energy to propel a toy car across a level floor. At time ti ,the car is moving at speed vi across the floor and the spring is unwinding, as shown below. At time tf , the spring has fully unwound and the car has coasted to a stop. ...
... 15 A wound spring provides the energy to propel a toy car across a level floor. At time ti ,the car is moving at speed vi across the floor and the spring is unwinding, as shown below. At time tf , the spring has fully unwound and the car has coasted to a stop. ...
Modern Physics 342
... Pauli Exclusion Principle It was believed that different atoms in the ground states have all their electrons dropped down in the 1s state. This means they all must have the same physical properties. This is not the case, in fact. A conclusion was drawn by Pauli that states that: No two electrons in ...
... Pauli Exclusion Principle It was believed that different atoms in the ground states have all their electrons dropped down in the 1s state. This means they all must have the same physical properties. This is not the case, in fact. A conclusion was drawn by Pauli that states that: No two electrons in ...
Lecture 35
... now a function of position because they are energies that need to take into account the electric potential. [[DIAGRAM, electron energy levels as a function of position]] ...
... now a function of position because they are energies that need to take into account the electric potential. [[DIAGRAM, electron energy levels as a function of position]] ...
question bank physics class 10
... 1. In a household electric circuit different appliances are connected in parallel to one another. Give two reasons. An electrician puts a fuse of rating 15A in that part of domestic electrical circuit in which an electrical heater of rating 1.5kW, 220V is operating. What is likely to happen in this ...
... 1. In a household electric circuit different appliances are connected in parallel to one another. Give two reasons. An electrician puts a fuse of rating 15A in that part of domestic electrical circuit in which an electrical heater of rating 1.5kW, 220V is operating. What is likely to happen in this ...
Mass Spectrometer
... The Relative Molecular Mass (Mr) of an element or compound • Relative atomic mass values (Ar) can be used to calculate the Relative molecular mass (Mr) of an element or compound • The relative molecular mass (Mr) of an element or compound is the sum of the relative atomic masses of all the atoms in ...
... The Relative Molecular Mass (Mr) of an element or compound • Relative atomic mass values (Ar) can be used to calculate the Relative molecular mass (Mr) of an element or compound • The relative molecular mass (Mr) of an element or compound is the sum of the relative atomic masses of all the atoms in ...
Quantum Numbers
... • The p sublevel has three orbitals, each of which can hold 2 electrons. That is why there are six columns in the “p” block. • The d sublevel has five orbitals, each of which can hold 2 electrons. That is why there are ten columns in the ...
... • The p sublevel has three orbitals, each of which can hold 2 electrons. That is why there are six columns in the “p” block. • The d sublevel has five orbitals, each of which can hold 2 electrons. That is why there are ten columns in the ...
Lecture 3
... a region of negative charge to an area of positive charge. As a potential difference is impressed across the conductor, the positive terminal of the battery attracts electrons beyond point A. Point A becomes positive because it now has an electron deficiency. As a result, electrons are attracted f ...
... a region of negative charge to an area of positive charge. As a potential difference is impressed across the conductor, the positive terminal of the battery attracts electrons beyond point A. Point A becomes positive because it now has an electron deficiency. As a result, electrons are attracted f ...
Part II
... suited for MRI. • It has the largest magnetic moment among all naturally occurring nuclei and ...
... suited for MRI. • It has the largest magnetic moment among all naturally occurring nuclei and ...
AP Revision Guide Examination Questions Ch
... (ii) The magnitude and direction of the horizontal and vertical magnetic fields through the rotor, at any instant, can be represented by vectors. These two vectors at times of 5 ms, 6 ms, 9 ms and 10 ms are shown below. ...
... (ii) The magnitude and direction of the horizontal and vertical magnetic fields through the rotor, at any instant, can be represented by vectors. These two vectors at times of 5 ms, 6 ms, 9 ms and 10 ms are shown below. ...
Word - Bryanston School
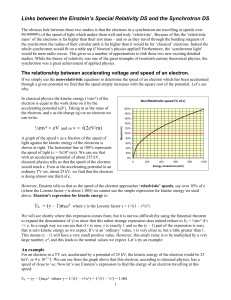
... (iii) The student considers the risk that he has taken. He assumes that the dose of 6 µJ is shared evenly over his mass of 60 kg. This gives a dose equivalent of 0.1 µSv. The whole-body dose equivalent from background radiation is about 2 mSv per year, equivalent to 4 nSv per hour. The student concl ...
... (iii) The student considers the risk that he has taken. He assumes that the dose of 6 µJ is shared evenly over his mass of 60 kg. This gives a dose equivalent of 0.1 µSv. The whole-body dose equivalent from background radiation is about 2 mSv per year, equivalent to 4 nSv per hour. The student concl ...
2a 4ac bbx 2
... • Wave motion: The process in which the disturbance in a point in the medium is transmitted to other parts of the medium without the bodily movement of the particles. • Longitudional Waves: The particles in the medium move parallel to the direction of the wave. Eg. Sound waves • Transverse waves: In ...
... • Wave motion: The process in which the disturbance in a point in the medium is transmitted to other parts of the medium without the bodily movement of the particles. • Longitudional Waves: The particles in the medium move parallel to the direction of the wave. Eg. Sound waves • Transverse waves: In ...
Tips and Strategies
... What is the energy equation if you see a particle accelerated perpendicular to two charged plates, or the problem states that the particle is accelerated through a potential difference? What is Kinetic Energy lost and how is it calculated? What is the energy equation for the change in temperature if ...
... What is the energy equation if you see a particle accelerated perpendicular to two charged plates, or the problem states that the particle is accelerated through a potential difference? What is Kinetic Energy lost and how is it calculated? What is the energy equation for the change in temperature if ...
When you get stuck: Think
... What is the energy equation if you see a particle accelerated perpendicular to two charged plates, or the problem states that the particle is accelerated through a potential difference? What is Kinetic Energy lost and how is it calculated? What is the energy equation for the change in temperature if ...
... What is the energy equation if you see a particle accelerated perpendicular to two charged plates, or the problem states that the particle is accelerated through a potential difference? What is Kinetic Energy lost and how is it calculated? What is the energy equation for the change in temperature if ...
Tips and Strategies
... What is the energy equation if you see a particle accelerated perpendicular to two charged plates, or the problem states that the particle is accelerated through a potential difference? What is Kinetic Energy lost and how is it calculated? What is the energy equation for the change in temperature if ...
... What is the energy equation if you see a particle accelerated perpendicular to two charged plates, or the problem states that the particle is accelerated through a potential difference? What is Kinetic Energy lost and how is it calculated? What is the energy equation for the change in temperature if ...
Fundamental of Atomic Theory, Periodic Law, and the Periodic Table
... positively (+2) charged particles emitted from the nucleus of an atom in the process of decay. These particles are also very dense which, with their strong positive charge, precludes them from penetrating more than an inch of air or a sheet of paper. Ther mass was determine to correspond to the mass ...
... positively (+2) charged particles emitted from the nucleus of an atom in the process of decay. These particles are also very dense which, with their strong positive charge, precludes them from penetrating more than an inch of air or a sheet of paper. Ther mass was determine to correspond to the mass ...
Fundamentals of NMR
... 15N, 19F, and 31P; i.e., all those which have nuclear spin quantum number I = l/2. It is a quantum mechanical requirement that any individual nuclear spins of a nucleus with I = l/2 be in one of the two states (and nothing in between) whenever the nuclei are in a magnetic field. It is important to n ...
... 15N, 19F, and 31P; i.e., all those which have nuclear spin quantum number I = l/2. It is a quantum mechanical requirement that any individual nuclear spins of a nucleus with I = l/2 be in one of the two states (and nothing in between) whenever the nuclei are in a magnetic field. It is important to n ...
The principle effect of gravitational potential
... The analysis we have used here applies only to objects at rest in a gravitational field because gravitational mass is equal to relativistic mass. A free falling mass does not loose energy and its mass remains constant. The energy released from its electric field changes into kinetic energy contained ...
... The analysis we have used here applies only to objects at rest in a gravitational field because gravitational mass is equal to relativistic mass. A free falling mass does not loose energy and its mass remains constant. The energy released from its electric field changes into kinetic energy contained ...