Nuclear and Radiation Section - University of Toronto Physics
... of Quantum Mechanics and the discovery of electron ‘spin’ (discussed in SNVI). The electrons in multi-electron atoms lie in shells, each shell containing a few levels of closely similar energies that depend in a complicated way on the electron spins. Each shell corresponds to the “principal quantum ...
... of Quantum Mechanics and the discovery of electron ‘spin’ (discussed in SNVI). The electrons in multi-electron atoms lie in shells, each shell containing a few levels of closely similar energies that depend in a complicated way on the electron spins. Each shell corresponds to the “principal quantum ...
Review & Closure - Little Shop of Physics
... get a sense for the scale of the energy, if we were to use this energy to create electron-positron pairs, approximately how many pairs could we create? A. 50 B. 100 C. 200 D. 400 13. The two fragments of a fission reaction are isotopes that are neutron-rich; each has more neutrons than the stable is ...
... get a sense for the scale of the energy, if we were to use this energy to create electron-positron pairs, approximately how many pairs could we create? A. 50 B. 100 C. 200 D. 400 13. The two fragments of a fission reaction are isotopes that are neutron-rich; each has more neutrons than the stable is ...
Chapter 22-23 Review
... The primary source of electrons in an ordinary electrical circuit is a. b. c. d. ...
... The primary source of electrons in an ordinary electrical circuit is a. b. c. d. ...
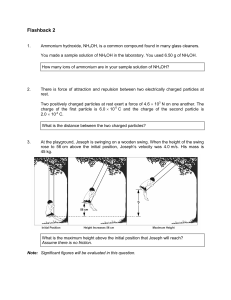
Flashback 2
... 4. An engineering student is designing a circuit with a solenoid. The design is such that the circuit uses an acidic solution as shown below. ...
... 4. An engineering student is designing a circuit with a solenoid. The design is such that the circuit uses an acidic solution as shown below. ...
Sample pages 1 PDF
... an equivalent number of positively charged particles are uniformly distributed throughout the atom. The resulting atom is electrically neutral. Rutherford, Geiger and Marsden succeeded in disproving this picture. In their famous experiments, where they scattered ˛-particles off heavy atoms, they wer ...
... an equivalent number of positively charged particles are uniformly distributed throughout the atom. The resulting atom is electrically neutral. Rutherford, Geiger and Marsden succeeded in disproving this picture. In their famous experiments, where they scattered ˛-particles off heavy atoms, they wer ...
states of Matter
... Plasma discharges and nuclear fusion have been around since shortly after the big bang, some 13 billion years ago. The development of the universe as we understand it today has been shaped, both in terms of time and of space, by the interactions of plasmas with their surroundings and by the hard-to- ...
... Plasma discharges and nuclear fusion have been around since shortly after the big bang, some 13 billion years ago. The development of the universe as we understand it today has been shaped, both in terms of time and of space, by the interactions of plasmas with their surroundings and by the hard-to- ...
Atomic Structure Development
... 1934 began experimental work on neutron bombardment of matter; light elements transmuted to lighter elements by ejecting either a proton or an alpha. Heavy elements lost energy by emission of a gamma ray and formation of a heavier isotope; Uranium – emitted a beta ray (electron) – several diferent ...
... 1934 began experimental work on neutron bombardment of matter; light elements transmuted to lighter elements by ejecting either a proton or an alpha. Heavy elements lost energy by emission of a gamma ray and formation of a heavier isotope; Uranium – emitted a beta ray (electron) – several diferent ...
2.1 Historical Development
... them at very low pressures convinced the scientists that atom is not indivisible but consists of much smaller fundamental particles. Thus, if electric discharge from a high potential source is passed through a discharge tube evacuated to pressures around 0.01mm or less, rays are emitted from the cat ...
... them at very low pressures convinced the scientists that atom is not indivisible but consists of much smaller fundamental particles. Thus, if electric discharge from a high potential source is passed through a discharge tube evacuated to pressures around 0.01mm or less, rays are emitted from the cat ...
Electromagnetic Radiation and Atomic Physics
... Since mp = 1836 me and mn = 1839 me, most of the mass of an atom is concentrated in its nucleus. An ion is an atom that has either a deficit or a surplus of electrons. The process of removing an electron from an atom is called “ionization”. The number of protons in the nucleus determines the chemica ...
... Since mp = 1836 me and mn = 1839 me, most of the mass of an atom is concentrated in its nucleus. An ion is an atom that has either a deficit or a surplus of electrons. The process of removing an electron from an atom is called “ionization”. The number of protons in the nucleus determines the chemica ...
THE ATOM Elements Isotopes Ions
... The electrons of an atom are not arranged randomly, but exist in shells. They are negatively charged but they do tend to pair up (much like girls going to the toilet!!! ☺). They can pair up because they spin on their axis and thus generate a magnetic field. Two electrons spinning on their axis in th ...
... The electrons of an atom are not arranged randomly, but exist in shells. They are negatively charged but they do tend to pair up (much like girls going to the toilet!!! ☺). They can pair up because they spin on their axis and thus generate a magnetic field. Two electrons spinning on their axis in th ...
Helical Particle Waves
... Gravitons and Inertial Mass The more energy a relativistic particle absorbs, the higher its spin moment becomes and thus gains higher resistance to directional change. That is, a stream of relativistic particles (a helical particle wave) starts to lose amplitude as the velocity at which it propagate ...
... Gravitons and Inertial Mass The more energy a relativistic particle absorbs, the higher its spin moment becomes and thus gains higher resistance to directional change. That is, a stream of relativistic particles (a helical particle wave) starts to lose amplitude as the velocity at which it propagate ...
AP C Gauss` Law 26
... asymptotes, maxima or minima with numerical values or algebraic expressions as appropriate. i. The nuclear charge only q ...
... asymptotes, maxima or minima with numerical values or algebraic expressions as appropriate. i. The nuclear charge only q ...
Radioactivity and Nuclear Physics
... Some of the matter on Earth is unstable and undergoing nuclear decay. Alpha decay is the emission of a helium nucleus, causing the product to have an atomic number 2 less than the original and an atomic mass number 4 less than the original. Beta minus decay is the emission of an electron, causing th ...
... Some of the matter on Earth is unstable and undergoing nuclear decay. Alpha decay is the emission of a helium nucleus, causing the product to have an atomic number 2 less than the original and an atomic mass number 4 less than the original. Beta minus decay is the emission of an electron, causing th ...
Goal 4.01
... Experimental Setup A thin piece of gold foil, full of tiny gold atoms, was bombarded with fast moving alpha particles. Alpha particles are a positive type of radiation with four times the mass of a hydrogen. It was thought that all alpha particles would pass through the gold foil because nothing wou ...
... Experimental Setup A thin piece of gold foil, full of tiny gold atoms, was bombarded with fast moving alpha particles. Alpha particles are a positive type of radiation with four times the mass of a hydrogen. It was thought that all alpha particles would pass through the gold foil because nothing wou ...
Dalton`s Atomic Theory Discovery of Electron Properties of Cathode
... Following conclusions were drawn from the Rutherford’s Alpha Particles scattering experiment. 1. The fact that majority of the particles went through the foil undeflected shows that most of the space occupied by an atom is empty. 2. The deflection of a few particles over a wide angle of 150 degrees ...
... Following conclusions were drawn from the Rutherford’s Alpha Particles scattering experiment. 1. The fact that majority of the particles went through the foil undeflected shows that most of the space occupied by an atom is empty. 2. The deflection of a few particles over a wide angle of 150 degrees ...
Chap 3 Atomic Structure
... Following conclusions were drawn from the Rutherford’s Alpha Particles scattering experiment. 1. The fact that majority of the particles went through the foil undeflected shows that most of the space occupied by an atom is empty. 2. The deflection of a few particles over a wide angle of 150 degrees ...
... Following conclusions were drawn from the Rutherford’s Alpha Particles scattering experiment. 1. The fact that majority of the particles went through the foil undeflected shows that most of the space occupied by an atom is empty. 2. The deflection of a few particles over a wide angle of 150 degrees ...
CHAPTER 4: ABUNDANCE AND RADIOACTIVITY OF UNSTABLE
... This results in a daughter nucleus with equal A and a change in atomic number Z to Z+1, and the emission of an electron and an anti-neutrino. A (anti)neutrino is a particle with mainly a relativistic mass, i.e. mass because of its motion. (Neutrino's and negatrons have their spin anti-parallel to th ...
... This results in a daughter nucleus with equal A and a change in atomic number Z to Z+1, and the emission of an electron and an anti-neutrino. A (anti)neutrino is a particle with mainly a relativistic mass, i.e. mass because of its motion. (Neutrino's and negatrons have their spin anti-parallel to th ...
Vocabulary Cards
... Non-charged particle in the nucleus of an atom. To find the number of neutrons: subtract the atomic number from the atomic mass number. ...
... Non-charged particle in the nucleus of an atom. To find the number of neutrons: subtract the atomic number from the atomic mass number. ...
Ask a scientist answers
... (and the accelerators used to produce the primary beams these detectors need) under extreme conditions (very high, or very low pressures, extreme temperatures, very high voltages, high magnetic fields, radiation, etc.). This puts significant constraints on the design and materials that need to be us ...
... (and the accelerators used to produce the primary beams these detectors need) under extreme conditions (very high, or very low pressures, extreme temperatures, very high voltages, high magnetic fields, radiation, etc.). This puts significant constraints on the design and materials that need to be us ...