CHAPTER 2 –OUTLINE I. Introduction: Neuroscience and Behavior
... IV. A Guided Tour of the Brain Brain functions involve the activation of neural pathways that link different brain structures; however, the best way to think of the brain is as an integrated system. 1. Science Versus Pseudoscience: Phrenology a. In the early 1800s, Franz Gall developed phrenology, w ...
... IV. A Guided Tour of the Brain Brain functions involve the activation of neural pathways that link different brain structures; however, the best way to think of the brain is as an integrated system. 1. Science Versus Pseudoscience: Phrenology a. In the early 1800s, Franz Gall developed phrenology, w ...
جامعة تكريت كلية طب االسنان
... Widespread activation of the sympathetic nervous system can be brought about by fear, rage, or severe pain. The alarm or stress response that results is often called the (fight or flight) reaction. Widespread sympathetic activation causes increases in arterial pressure، muscle blood flow, metabolic ...
... Widespread activation of the sympathetic nervous system can be brought about by fear, rage, or severe pain. The alarm or stress response that results is often called the (fight or flight) reaction. Widespread sympathetic activation causes increases in arterial pressure، muscle blood flow, metabolic ...
Autonomic Nervous System
... •The autonomic nervous system provides internal homeostasis. •Autonomic reflexes control blood pressure, heart rate, respiration, water balance, body temperature and other homeostatic functions. •Divided into two major subdivisions: the sympathetic and parasympathetic divisions. The two divisions ca ...
... •The autonomic nervous system provides internal homeostasis. •Autonomic reflexes control blood pressure, heart rate, respiration, water balance, body temperature and other homeostatic functions. •Divided into two major subdivisions: the sympathetic and parasympathetic divisions. The two divisions ca ...
Regulation of respiration
... Neural generation of rhythmical breathing The discharge of medullary inspiratory neurons provides rhythmic input to the motor neurons innervating the inspiratory muscles. Then the action potential t ti l cease, th the inspiratory muscles relax, and expiration occurs as the elastic lungs recoil. ...
... Neural generation of rhythmical breathing The discharge of medullary inspiratory neurons provides rhythmic input to the motor neurons innervating the inspiratory muscles. Then the action potential t ti l cease, th the inspiratory muscles relax, and expiration occurs as the elastic lungs recoil. ...
the autonomic nervous system
... FIGHT REACTION (SYMPATHETIC POSTGANGLIONIC) • ACETYLCHOLINE (CHOLINERGIC): “COUCH POTATO” RESPONSE (PARASYMPATHETIC POSTGANGLIONIC AND ALL PREGANGLIONIC). ...
... FIGHT REACTION (SYMPATHETIC POSTGANGLIONIC) • ACETYLCHOLINE (CHOLINERGIC): “COUCH POTATO” RESPONSE (PARASYMPATHETIC POSTGANGLIONIC AND ALL PREGANGLIONIC). ...
Nervous System
... in the number and sensitivity of receptors on the post-synaptic neuron (increasing the strength of the synapse) ...
... in the number and sensitivity of receptors on the post-synaptic neuron (increasing the strength of the synapse) ...
CNS: Brain and Spinal Cord
... II. CSF, the cranial meninges, the ventricles, and the blood-brain barrier: how the brain is fed and protected (out of synch with book presentation) A. Meninges 1. Dura mater- the dura mater around the brain has two layers- an outer (endosteal) layer that is tied to the skull, and an inner (meningea ...
... II. CSF, the cranial meninges, the ventricles, and the blood-brain barrier: how the brain is fed and protected (out of synch with book presentation) A. Meninges 1. Dura mater- the dura mater around the brain has two layers- an outer (endosteal) layer that is tied to the skull, and an inner (meningea ...
Nervous System Notes
... How a Nerve Impulse Travels • Nerve impulses can travels as fast as 120 meters per second! THAT’S FAST! • Messages travel from the Cell Body, down the axon, and to the axon tips! ...
... How a Nerve Impulse Travels • Nerve impulses can travels as fast as 120 meters per second! THAT’S FAST! • Messages travel from the Cell Body, down the axon, and to the axon tips! ...
Chapter 6 - Sensory - Austin Community College
... oblongata with input from the limbic system and other regions of the cerebrum. The afferent component of the ANS consists of general visceral sensory neurons. Interoreceptors such as chemoreceptors (CO2 levels) and mechanoreceptors (degree of stretch of organs and vessels). Afferent signals are not ...
... oblongata with input from the limbic system and other regions of the cerebrum. The afferent component of the ANS consists of general visceral sensory neurons. Interoreceptors such as chemoreceptors (CO2 levels) and mechanoreceptors (degree of stretch of organs and vessels). Afferent signals are not ...
Nervous System
... which has changed a variable from its set point • from eyes, skin, blood vessels, ears, digestive tract, joints, muscles, lungs… • Integration – interpretation of sensory information by the CNS • type, location and magnitude of stimulus • Transmit motor information – propagate APs from the CNS to va ...
... which has changed a variable from its set point • from eyes, skin, blood vessels, ears, digestive tract, joints, muscles, lungs… • Integration – interpretation of sensory information by the CNS • type, location and magnitude of stimulus • Transmit motor information – propagate APs from the CNS to va ...
Lecture 6 - School of Computing | University of Leeds
... Forget the complexity. Focus on cartoon models of biological nnets & further simplify them. Build on biology to design simple artificial networks that perform classification tasks. Today, we start with a single artificial neuron and study its computational power. ...
... Forget the complexity. Focus on cartoon models of biological nnets & further simplify them. Build on biology to design simple artificial networks that perform classification tasks. Today, we start with a single artificial neuron and study its computational power. ...
Nervous System
... which has changed a variable from its set point • from eyes, skin, blood vessels, ears, digestive tract, joints, muscles, lungs… • Integration – interpretation of sensory information by the CNS • type, location and magnitude of stimulus • Transmit motor information – propagate APs from the CNS to va ...
... which has changed a variable from its set point • from eyes, skin, blood vessels, ears, digestive tract, joints, muscles, lungs… • Integration – interpretation of sensory information by the CNS • type, location and magnitude of stimulus • Transmit motor information – propagate APs from the CNS to va ...
CHAPTER 2 outline
... 2. Drugs may affect the length of time the neurotransmitter remains in the synaptic gap, either increasing or decreasing the amount available to the postsynaptic receptor. 3. Drugs may prolong the effects of the neurotransmitter by blocking its reuptake by the sending neuron. 4. Drugs can mimic spec ...
... 2. Drugs may affect the length of time the neurotransmitter remains in the synaptic gap, either increasing or decreasing the amount available to the postsynaptic receptor. 3. Drugs may prolong the effects of the neurotransmitter by blocking its reuptake by the sending neuron. 4. Drugs can mimic spec ...
The caudal part of the frontal cortex is strongly involved - LIRA-Lab
... Electrical stimulation studies revealed that area F5 contains extensively overlapping representations of hand and mouth movements (Rizzolatti et al., 1988; Hepp-Reymond, et al., 1994). Single neurons studies have shown that most F5 neurons code specific actions, rather than the single movements that ...
... Electrical stimulation studies revealed that area F5 contains extensively overlapping representations of hand and mouth movements (Rizzolatti et al., 1988; Hepp-Reymond, et al., 1994). Single neurons studies have shown that most F5 neurons code specific actions, rather than the single movements that ...
Hypothalamic arcuate nucleus: neurons in the meeting
... and autonomic regulatory mechanisms of the central nervous system. More than 50 years ago. the parvicellular neurosecretion. as a concept has been introduced on the basis of studies by what the secretory activity of arcute neurons into the pituitary portal vessels had been clearly demonstrated. The ...
... and autonomic regulatory mechanisms of the central nervous system. More than 50 years ago. the parvicellular neurosecretion. as a concept has been introduced on the basis of studies by what the secretory activity of arcute neurons into the pituitary portal vessels had been clearly demonstrated. The ...
COMPUTATIONAL INTELLIGENCE Medical Diagnostic Systems
... impulses originate in the cell body, and are propagated along the axon, which may have one or more branches. This axon, which is folded for diagrammatic purposes, would be a centimeter long at actual size. Some axons are more than a meter long. The axon’s terminal branches form synapses with as many ...
... impulses originate in the cell body, and are propagated along the axon, which may have one or more branches. This axon, which is folded for diagrammatic purposes, would be a centimeter long at actual size. Some axons are more than a meter long. The axon’s terminal branches form synapses with as many ...
Understanding mirror neurons - LIRA-Lab
... in the monkey. Based on these observations we propose a model of this brain system which is responsible for action recognition. The link between object affordances and action understanding is considered. To support our hypothesis we describe two experiments where some aspects of the model have been i ...
... in the monkey. Based on these observations we propose a model of this brain system which is responsible for action recognition. The link between object affordances and action understanding is considered. To support our hypothesis we describe two experiments where some aspects of the model have been i ...
Physiolgy of the nervous system
... (12 pairs) and spinal nerves (31 pairs). Functional classification This classification is concerned only with PNS or peripheral nervous system, which subdivided into: 1) Somatic (voluntary) nervous system, which controls the skeletal muscle 2) Autonomic (involuntary) nervous system, which controls s ...
... (12 pairs) and spinal nerves (31 pairs). Functional classification This classification is concerned only with PNS or peripheral nervous system, which subdivided into: 1) Somatic (voluntary) nervous system, which controls the skeletal muscle 2) Autonomic (involuntary) nervous system, which controls s ...
Slide ()
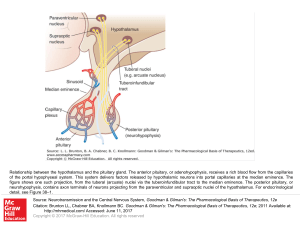
... Relationship between the hypothalamus and the pituitary gland. The anterior pituitary, or adenohypophysis, receives a rich blood flow from the capillaries of the portal hypophyseal system. This system delivers factors released by hypothalamic neurons into portal capillaries at the median eminence. T ...
... Relationship between the hypothalamus and the pituitary gland. The anterior pituitary, or adenohypophysis, receives a rich blood flow from the capillaries of the portal hypophyseal system. This system delivers factors released by hypothalamic neurons into portal capillaries at the median eminence. T ...
Module overview
... – number of different encodings as we transit a line – each time the line crosses a RF the encoding changes – number of encodings = 2 x RF that the line penetrates= proportional to the line density and number of neurons ...
... – number of different encodings as we transit a line – each time the line crosses a RF the encoding changes – number of encodings = 2 x RF that the line penetrates= proportional to the line density and number of neurons ...